
What will happen when a 40 watt, 220 volt and 100 watt 220 volt lamp are connected in series across 40 volt supply
(A) 100 W lamp will fuse
(B) 40 W lamp will fuse
(C) Both lamp will fuse
(D) Neither lamp will fuse
Answer
478.5k+ views
Hint: Electric power is the rate at which electrical energy is transmitted by an electric circuit per unit of time. The watt, or one joule per second, is the SI unit of power. Electric generators are the most common source of electricity, however other sources such as electric batteries can also be used. The electric power sector often provides it to companies and residences (as residential mains electricity) via an electric power grid.
P = V I
Power = Potential difference $ \times $ Current.
Complete answer:
Electric power, like mechanical power, is the rate at which work is completed, measured in watts and symbolised by the letter P. Wattage is a slang word that means "electric power in watts." An electric current I carrying a charge of Q coulombs per t seconds flowing through an electric potential (voltage) differential of V produces an electric power in watts. $ P = {\text{work done per unit time}} = \dfrac{W}{t} = \dfrac{W}{Q}\dfrac{Q}{t} = VI{\mkern 1mu} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R} $
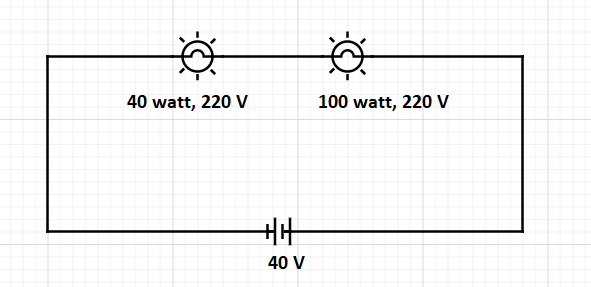
Let us consider the following details
Bulb (I) is Rated current.
$ {{\text{I}}_1} = \dfrac{{\mathbf{P}}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{40}}{{220}} = \dfrac{2}{{11}}amp $
Upon finding the resistance we get
$ {{\mathbf{R}}_1} = \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}^2}}}{{\text{P}}} = \dfrac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{40}} = 1210\Omega $
Now for second bulb
$ {{\text{I}}_2} = \dfrac{{100}}{{220}} = \dfrac{5}{{11}}{\text{amp}} $
$ {{\text{R}}_2} = \dfrac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{100}} = 484\Omega $
When both of these devices are linked in series over a 40 V supply, Total current delivered through the supply
$ I = {I_1} + {I_2} = \dfrac{2}{{11}} + \dfrac{5}{{11}} = \dfrac{7}{{11}}A = 0.63A $
$ I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}} = \dfrac{{40}}{{1210 + 484}} = \dfrac{{40}}{{1254}} = 0.03A $
This current is less than the rated current of each bulb. So neither bulb will fuse.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
Take proper care of conversions of power formulas. P = VI is converted to $ P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R} $ where $ I = \dfrac{V}{R} $ .
Through a grid link, the electric power sector produces and distributes power in adequate amounts to regions that require it. The grid is responsible for distributing electricity to consumers. Electricity is generated in two ways: central power plants and distributed production. The electric power business has been steadily deregulating, with new firms providing consumers with alternatives to the old public utility providers.
P = V I
Power = Potential difference $ \times $ Current.
Complete answer:
Electric power, like mechanical power, is the rate at which work is completed, measured in watts and symbolised by the letter P. Wattage is a slang word that means "electric power in watts." An electric current I carrying a charge of Q coulombs per t seconds flowing through an electric potential (voltage) differential of V produces an electric power in watts. $ P = {\text{work done per unit time}} = \dfrac{W}{t} = \dfrac{W}{Q}\dfrac{Q}{t} = VI{\mkern 1mu} = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R} $

Let us consider the following details
Bulb (I) is Rated current.
$ {{\text{I}}_1} = \dfrac{{\mathbf{P}}}{{\text{V}}} = \dfrac{{40}}{{220}} = \dfrac{2}{{11}}amp $
Upon finding the resistance we get
$ {{\mathbf{R}}_1} = \dfrac{{{{\text{V}}^2}}}{{\text{P}}} = \dfrac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{40}} = 1210\Omega $
Now for second bulb
$ {{\text{I}}_2} = \dfrac{{100}}{{220}} = \dfrac{5}{{11}}{\text{amp}} $
$ {{\text{R}}_2} = \dfrac{{{{(220)}^2}}}{{100}} = 484\Omega $
When both of these devices are linked in series over a 40 V supply, Total current delivered through the supply
$ I = {I_1} + {I_2} = \dfrac{2}{{11}} + \dfrac{5}{{11}} = \dfrac{7}{{11}}A = 0.63A $
$ I = \dfrac{V}{{{R_1} + {R_2}}} = \dfrac{{40}}{{1210 + 484}} = \dfrac{{40}}{{1254}} = 0.03A $
This current is less than the rated current of each bulb. So neither bulb will fuse.
Hence option D is correct.
Note:
Take proper care of conversions of power formulas. P = VI is converted to $ P = \dfrac{{{V^2}}}{R} $ where $ I = \dfrac{V}{R} $ .
Through a grid link, the electric power sector produces and distributes power in adequate amounts to regions that require it. The grid is responsible for distributing electricity to consumers. Electricity is generated in two ways: central power plants and distributed production. The electric power business has been steadily deregulating, with new firms providing consumers with alternatives to the old public utility providers.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




