
Explain with an activity scattering of light/ Tyndall effect.
Answer
554.1k+ views
Hint: Tyndall effect occurs when light scattering particles are suspended inside a light transmitting medium. In that case, light scatters by the particles and then reaches the observer’s eyes. If we project a concentrated beam of light through a solution, we cannot see the beam of light passing through it. However, the light beam will be apparent when it passes through a colloid.
Complete answer:
Activity: Take a mixture of milk and water which is a colloidal solution. Then, take a mixture of sugar and water which is a true solution. Now, pass light through both the mixtures. You will see that light passes through the mixture of milk and water but does not pass through the mixture of sugar and water. Thus, light passes through a colloidal solution and not through true solution.
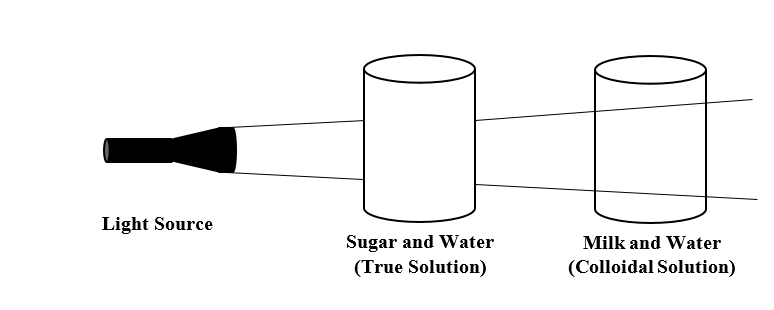
From the above-mentioned activity, we can say that the light scattering through a colloidal solution is known as Tyndall scattering and the effect is known as Tyndall effect. Thus, Tyndall effect is a phenomenon responsible for scattering of light in a colloid or very fine suspension. Under the Tyndall effect, the longer wavelengths are more transmitted while the shorter wavelengths are more reflected via scattering.
The intensity of the scattered light depends on the following factors:
1. Density of the colloidal particles
2. Frequency of the incident light
Note:
Tyndall effect is applicable to colloidal mixtures and fine suspensions. Students must not get confused between Rayleigh scattering and Tyndall effect. Example for this can be taken as, when the daytime sky is cloudless, the sky’s colour is blue due to Rayleigh scattering instead of Tyndall scattering because the scattering particles are air molecules which are much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light.
Complete answer:
Activity: Take a mixture of milk and water which is a colloidal solution. Then, take a mixture of sugar and water which is a true solution. Now, pass light through both the mixtures. You will see that light passes through the mixture of milk and water but does not pass through the mixture of sugar and water. Thus, light passes through a colloidal solution and not through true solution.

From the above-mentioned activity, we can say that the light scattering through a colloidal solution is known as Tyndall scattering and the effect is known as Tyndall effect. Thus, Tyndall effect is a phenomenon responsible for scattering of light in a colloid or very fine suspension. Under the Tyndall effect, the longer wavelengths are more transmitted while the shorter wavelengths are more reflected via scattering.
The intensity of the scattered light depends on the following factors:
1. Density of the colloidal particles
2. Frequency of the incident light
Note:
Tyndall effect is applicable to colloidal mixtures and fine suspensions. Students must not get confused between Rayleigh scattering and Tyndall effect. Example for this can be taken as, when the daytime sky is cloudless, the sky’s colour is blue due to Rayleigh scattering instead of Tyndall scattering because the scattering particles are air molecules which are much smaller than the wavelengths of visible light.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




