
Explain the electromagnetic spectrum with a diagram.
Answer
573.9k+ views
Hint: The electromagnetic spectrum consists of every type of electromagnetic radiation, from longest wavelength to the shortest wavelength or lower frequency to highest frequency.
Complete step by step solution:
The orderly distribution of the electromagnetic waves in the accordance of their wavelength or frequency is divided into different groups, which have different properties and are known as electromagnetic spectrum.
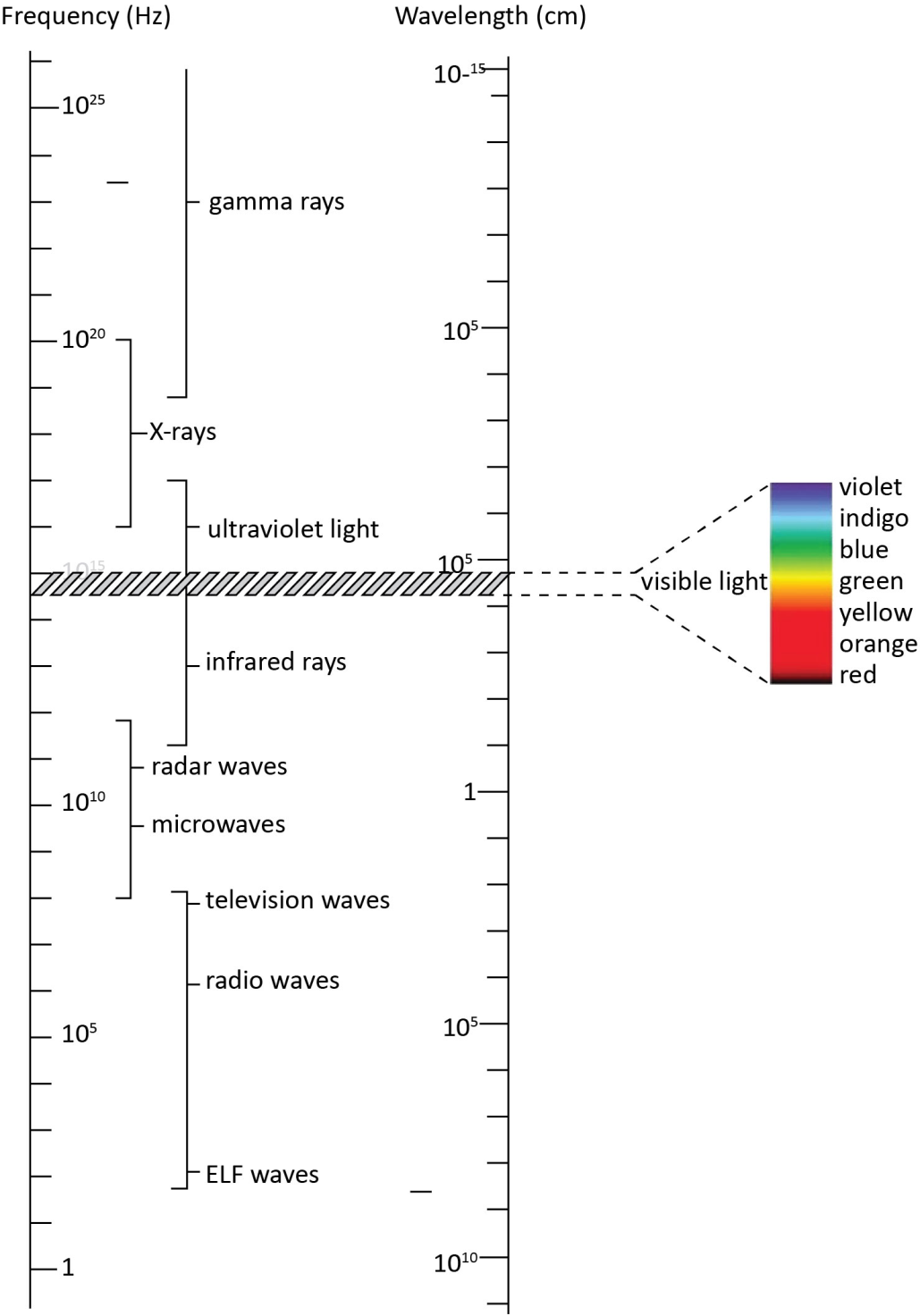
The main parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are $\gamma $rays, X rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwaves and radio waves in the order of decreasing frequency or increasing wavelength.
Radio waves:
It has the longest wavelength and minimum frequency. Its source is the accelerated motion of charges in wires or oscillating circuits. It is used in radio and TV communication systems.
Wavelength range: 600 m to 0.1 m
Frequency range: 5$ \times {10^5}$Hz to ${10^9}$Hz
Microwave:
Its source is the oscillating current in vacuum tubes like klystrons or Gunn diodes. It is used in aircraft navigation, in long distance communication systems and in microwave ovens.
Wavelength range: 0.3 m to ${10^{ - 3}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^9}$ Hz to ${10^{12}}$ Hz
Infrared waves:
Its source is hot bodies and molecules and it produces heating effects, so they are also called thermal radiation or heat waves. It is used in greenhouses to keep the plants warm, in remote controls, in haze photography, in study of molecule structure and in reading ancient secret text.
Wavelength range: $5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ m to ${10^{ - 6}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{11}}$ Hz to $5 \times {10^{14}}$ Hz
Visible light:
Its source is radiated by excited atoms in ionised gas. It provides the information around us and can cause chemical reactions.
Wavelength range: $8 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m to $4 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m
Frequency range: $4 \times {10^{14}}$ Hz to $7 \times {10^{14}}$ Hz
Ultraviolet light:
Its source is a high voltage discharge tube and the sun. It is used in food preservation and it has harmful effects on human beings.
Wavelength range: $3.5 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m to $1.5 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{16}}$ Hz to ${10^{17}}$ Hz
X- rays:
Its source is the abrupt deceleration of electrons by a metal. It is used in medical diagnosis, in the study of crystal structure, in radiotherapy to cure skin, to detect explosive, diamond, gold etc.
Wavelength range: ${10^{ - 8}}$ m to ${10^{ - 11}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{18}}$ Hz to ${10^{20}}$ Hz
$\gamma $ rays:
Its source is radioactive nuclei and nuclear reactions. It is used for the treatment of tumours, initiating nuclear reactions, and preserving food for a long time.
Wavelength range: ${10^{ - 14}}$ m to ${10^{ - 10}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{18}}$ Hz to ${10^{22}}$ Hz
Note:
All electromagnetic waves travel in vacuum with the same speed.
The difference is in their wavelengths or frequencies.
Due to this, the electromagnetic waves interact differently with matter.
Complete step by step solution:
The orderly distribution of the electromagnetic waves in the accordance of their wavelength or frequency is divided into different groups, which have different properties and are known as electromagnetic spectrum.

The main parts of the electromagnetic spectrum are $\gamma $rays, X rays, ultraviolet rays, visible light, infrared rays, microwaves and radio waves in the order of decreasing frequency or increasing wavelength.
Radio waves:
It has the longest wavelength and minimum frequency. Its source is the accelerated motion of charges in wires or oscillating circuits. It is used in radio and TV communication systems.
Wavelength range: 600 m to 0.1 m
Frequency range: 5$ \times {10^5}$Hz to ${10^9}$Hz
Microwave:
Its source is the oscillating current in vacuum tubes like klystrons or Gunn diodes. It is used in aircraft navigation, in long distance communication systems and in microwave ovens.
Wavelength range: 0.3 m to ${10^{ - 3}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^9}$ Hz to ${10^{12}}$ Hz
Infrared waves:
Its source is hot bodies and molecules and it produces heating effects, so they are also called thermal radiation or heat waves. It is used in greenhouses to keep the plants warm, in remote controls, in haze photography, in study of molecule structure and in reading ancient secret text.
Wavelength range: $5 \times {10^{ - 3}}$ m to ${10^{ - 6}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{11}}$ Hz to $5 \times {10^{14}}$ Hz
Visible light:
Its source is radiated by excited atoms in ionised gas. It provides the information around us and can cause chemical reactions.
Wavelength range: $8 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m to $4 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m
Frequency range: $4 \times {10^{14}}$ Hz to $7 \times {10^{14}}$ Hz
Ultraviolet light:
Its source is a high voltage discharge tube and the sun. It is used in food preservation and it has harmful effects on human beings.
Wavelength range: $3.5 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m to $1.5 \times {10^{ - 7}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{16}}$ Hz to ${10^{17}}$ Hz
X- rays:
Its source is the abrupt deceleration of electrons by a metal. It is used in medical diagnosis, in the study of crystal structure, in radiotherapy to cure skin, to detect explosive, diamond, gold etc.
Wavelength range: ${10^{ - 8}}$ m to ${10^{ - 11}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{18}}$ Hz to ${10^{20}}$ Hz
$\gamma $ rays:
Its source is radioactive nuclei and nuclear reactions. It is used for the treatment of tumours, initiating nuclear reactions, and preserving food for a long time.
Wavelength range: ${10^{ - 14}}$ m to ${10^{ - 10}}$ m
Frequency range: ${10^{18}}$ Hz to ${10^{22}}$ Hz
Note:
All electromagnetic waves travel in vacuum with the same speed.
The difference is in their wavelengths or frequencies.
Due to this, the electromagnetic waves interact differently with matter.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




