
Explain the double helix structure of DNA with a labeled diagram.
Answer
528.9k+ views
Hint: The structure was discovered by Watson and Crick in which two strands of polynucleotide chains are linked together by base pairing. The backbone of the chain is constituted by sugar-phosphate and the nitrogenous bases are placed inside.
Complete answer:
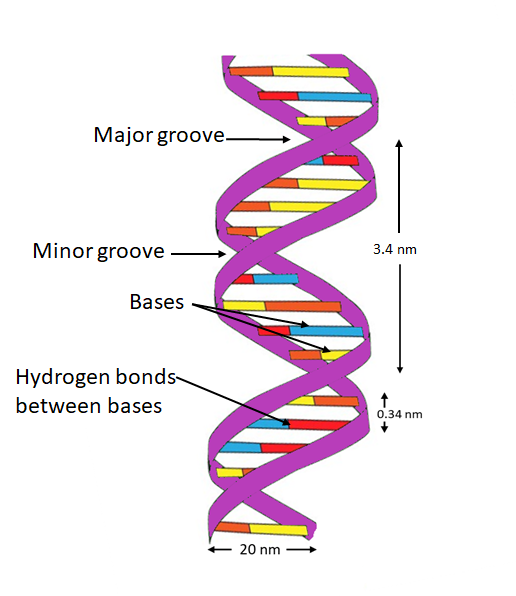
The double helix is a structure that is made up of two right-handed polynucleotide chains. The polynucleotide chains are coiled on the same axis and run alongside each other forming a double helix. Both the polynucleotide chains are complementary to each other. So, if the sequence of bases in one strand is known then the sequence of bases in other strands can be predicted.
The salient features of double-helix DNA are as follows:
-Both strands are antiparallel to each other means if one strand was oriented in 3’ to 5’ direction then the other was oriented 5’ to 3’ direction.
-Both strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between base pairs.
-Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine from the opposite strand and vice versa. Similarly, Guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with Cytosine.
-Both the chains are coiled in a right-handed manner.
-The pitch of the double helix DNA is 3.4nm.
-Each turn contains approximately 10 base pairs.
-The DNA bases are stacked with a regular spacing of 3.4 Å.
-Approximately 25 Hydrogen bonds are present in each complete turn in that provide the stability to the double-helical structure as strong as a covalent bond.
Note:
-Unlike DNA, RNA has uracil instead of thymine.
-RNA has an additional –OH group present at 2' -position in the ribose in every nucleotide residue.
-Lower organisms have simpler bodies and thus their genetic code is smaller compared to larger complex organisms.
Complete answer:
The double helix is a structure that is made up of two right-handed polynucleotide chains. The polynucleotide chains are coiled on the same axis and run alongside each other forming a double helix. Both the polynucleotide chains are complementary to each other. So, if the sequence of bases in one strand is known then the sequence of bases in other strands can be predicted.
The salient features of double-helix DNA are as follows:
-Both strands are antiparallel to each other means if one strand was oriented in 3’ to 5’ direction then the other was oriented 5’ to 3’ direction.
-Both strands are held together by hydrogen bonds between base pairs.
-Adenine forms two hydrogen bonds with Thymine from the opposite strand and vice versa. Similarly, Guanine forms three hydrogen bonds with Cytosine.
-Both the chains are coiled in a right-handed manner.
-The pitch of the double helix DNA is 3.4nm.
-Each turn contains approximately 10 base pairs.
-The DNA bases are stacked with a regular spacing of 3.4 Å.
-Approximately 25 Hydrogen bonds are present in each complete turn in that provide the stability to the double-helical structure as strong as a covalent bond.

Note:
-Unlike DNA, RNA has uracil instead of thymine.
-RNA has an additional –OH group present at 2' -position in the ribose in every nucleotide residue.
-Lower organisms have simpler bodies and thus their genetic code is smaller compared to larger complex organisms.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




