
Draw a diagram of a flower and name the parts.
Answer
584.4k+ views
Hint: A flower is the main reproductive organ in flowering plants (angiosperms) and they ensure the continuity of several generations of the species. It has a complex structure having various whorls, with each whorl contributing to an important function.
Complete answer:
Given below is the well-labeled diagram of a complete flower:
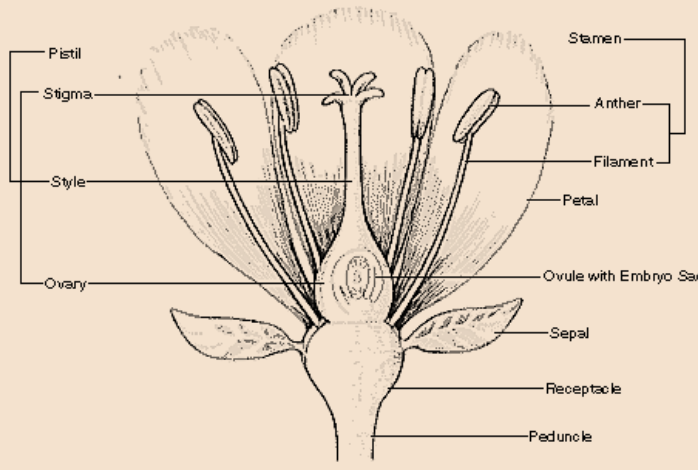
A flower is considered to be complete if all of these parts are present, otherwise, it is known as an incomplete flower.
The flower can be divided into four main parts: petals, sepals, stamen, and carpel (also known as a pistil).
Sepals: The outermost whorl consisting of sepals is known as calyx.
These are the exterior parts of a flower meant for protecting the inner whorls, during the bud stage.
They are typically green in color.
Petals: These are the units of the second whorl i.e. the corolla.
They are bright in color and attractive. Their purpose is to attract insect pollinators.
Stamen: It is the male reproductive part of a flower. Each stamen can be divided into two parts: the anther and the filament. The filament is the long cylindrical tendril part of the stamen, while the anther is a sac that sits at the top of the filament.
The filament holds the anther, exposing it to the pollinators.
The pollen is produced at the anther.
Carpel: This is also known as the pistil; the female reproductive organ of the flower. It contains a sac-like structure known as the ovary which is responsible for the production of seeds (or ovules). The extension of the ovary is known as the style, a tube-like structure ending in a swollen sticky structure called the stigma. A fertilized ovary swells to protect the developing seeds and transforms the flower into a fruit.
Pedicel: This structure is responsible to hold individual flowers in place and also expose the flowers to the sun and wind.
Pollen tube: It is a tube produced when the pollen grains land on the stigma and finally germinate. This tube carries the male gametes into the ovary.
Receptacle: Also known as the ‘torus’, it is a thick part of the stem from which the flower emerges.
Note: The flowers which are pollinated by the wind are generally dull in color and generally don’t release a strong odor, unlike insect-pollinated flowers.
They have a long feathery and extra sticky stigma, to increase the chances of receiving the pollen carried by the wind.
Complete answer:
Given below is the well-labeled diagram of a complete flower:

A flower is considered to be complete if all of these parts are present, otherwise, it is known as an incomplete flower.
The flower can be divided into four main parts: petals, sepals, stamen, and carpel (also known as a pistil).
Sepals: The outermost whorl consisting of sepals is known as calyx.
These are the exterior parts of a flower meant for protecting the inner whorls, during the bud stage.
They are typically green in color.
Petals: These are the units of the second whorl i.e. the corolla.
They are bright in color and attractive. Their purpose is to attract insect pollinators.
Stamen: It is the male reproductive part of a flower. Each stamen can be divided into two parts: the anther and the filament. The filament is the long cylindrical tendril part of the stamen, while the anther is a sac that sits at the top of the filament.
The filament holds the anther, exposing it to the pollinators.
The pollen is produced at the anther.
Carpel: This is also known as the pistil; the female reproductive organ of the flower. It contains a sac-like structure known as the ovary which is responsible for the production of seeds (or ovules). The extension of the ovary is known as the style, a tube-like structure ending in a swollen sticky structure called the stigma. A fertilized ovary swells to protect the developing seeds and transforms the flower into a fruit.
Pedicel: This structure is responsible to hold individual flowers in place and also expose the flowers to the sun and wind.
Pollen tube: It is a tube produced when the pollen grains land on the stigma and finally germinate. This tube carries the male gametes into the ovary.
Receptacle: Also known as the ‘torus’, it is a thick part of the stem from which the flower emerges.
Note: The flowers which are pollinated by the wind are generally dull in color and generally don’t release a strong odor, unlike insect-pollinated flowers.
They have a long feathery and extra sticky stigma, to increase the chances of receiving the pollen carried by the wind.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




