
Define angle of inclination (magnetic declination).
In the magnetic meridian of a certain place, the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is 0.25 gauss and the dip angle is 60°. At this place find the value of Earth’s magnetic field.
Answer
598.8k+ views
Hint: To know the definition of magnetic declination, we need to know about the magnetic Meridian and the geometrical Meridian. Then we will know about the dip angle and we will try to know about the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field. Then we can solve this problem easily.
Formula used:
$H=I.\cos\theta$
Complete step-by-step solution:
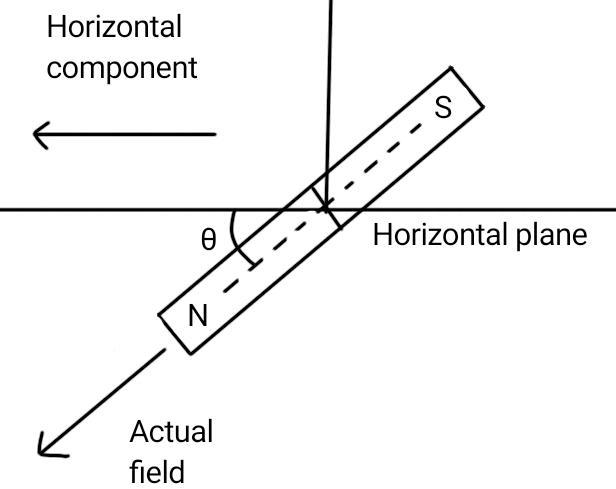
If a magnetic bar is tied with a thread exactly at its center of gravity, and then hanged, then it does not exactly point towards North and the South, but it is a little inclined. Now, the vertical plane through which the axis of this magnet passes is called the magnetic Meridian. And the vertical plane that passes through the geometrical North and South Pole is called the geometrical Meridian. So, the geometrical and magnetic Meridian are not the same, but they make an angle to each other.
The angle between the geometrical Meridian and the magnetic Meridian at a certain place is defined as the magnetic declination of that place.
Now, dip angle is the angle that the magnetic bar makes with the horizontal plane. Let this dip angle be $\theta$ . If I be the magnetic field of at a certain place, the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is given by,
$H=I.\cos\theta$
In this place we have, $\theta=60^\circ$. And I=0.25 gauss.
Putting these values in the above question, we easily obtain that I= 0.50 gauss.
So, the required answer of the given question is that, at the given place the value of Earth’s magnetic field is 0.50 gauss.
Additional information: The value of the vertical component of earth’s magnetic field is given by, $V=I.\sin\theta$. If one knows the vertical and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field at a certain place, then,
$I=\sqrt{V^2+H^2}$
Note: Never confuse between magnetic declination and the dip angle of Earth. Remember that geometrical meridian and magnetic Meridian is not the same. Also, Earth’s magnetic field, (I) will be in the same unit as the horizontal field, H.
Formula used:
$H=I.\cos\theta$
Complete step-by-step solution:
If a magnetic bar is tied with a thread exactly at its center of gravity, and then hanged, then it does not exactly point towards North and the South, but it is a little inclined. Now, the vertical plane through which the axis of this magnet passes is called the magnetic Meridian. And the vertical plane that passes through the geometrical North and South Pole is called the geometrical Meridian. So, the geometrical and magnetic Meridian are not the same, but they make an angle to each other.
The angle between the geometrical Meridian and the magnetic Meridian at a certain place is defined as the magnetic declination of that place.
Now, dip angle is the angle that the magnetic bar makes with the horizontal plane. Let this dip angle be $\theta$ . If I be the magnetic field of at a certain place, the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field is given by,
$H=I.\cos\theta$
In this place we have, $\theta=60^\circ$. And I=0.25 gauss.
Putting these values in the above question, we easily obtain that I= 0.50 gauss.
So, the required answer of the given question is that, at the given place the value of Earth’s magnetic field is 0.50 gauss.

Additional information: The value of the vertical component of earth’s magnetic field is given by, $V=I.\sin\theta$. If one knows the vertical and horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field at a certain place, then,
$I=\sqrt{V^2+H^2}$
Note: Never confuse between magnetic declination and the dip angle of Earth. Remember that geometrical meridian and magnetic Meridian is not the same. Also, Earth’s magnetic field, (I) will be in the same unit as the horizontal field, H.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




