
What is centripetal acceleration? Derive the expression for centripetal acceleration.
Answer
572.4k+ views
Hint: In circular motion centripetal force is perpendicular to velocity. Also if the particles decrease or increase their speeds in circular motion then acceleration is generated which deviates the net acceleration from pointing towards the centre.
Formula used:
$a=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
Complete answer:
We know that the motions are two types: one is straight motion and the circular motion. Then we know that circular motion, though the magnitude of velocity is a constant, the direction of velocity is changing. A circle. It is also defined as rotation of an object along a circular path. It can be of two forms, uniform circular motion, with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed, or non-uniform circular motion with a changing rate of rotation.
Consider a body of mass $m$ moving along the circumference of a circle. the radius of a circle $r$ with velocity $v$,as shown in the figure. Then if a small force $F$ is applied on the body, then we know that the force is given as $F=ma$.
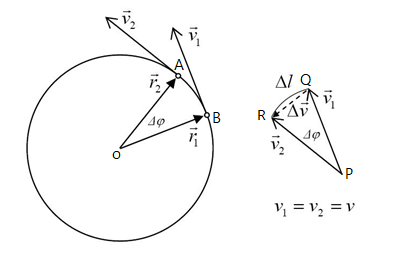
Where, $a$ is the acceleration and is given as the rate of change of velocity $\Delta v$ with respect to time.
Consider the \[\vartriangle OAB\] and $\triangle PQR$, then $\dfrac{\Delta v}{AB}=\dfrac{v}{r}$
Clearly, $AB=v\Delta t$
$\implies \dfrac{\Delta v}{v\Delta t}=\dfrac{v}{r}$
$\implies \dfrac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
$\implies a=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
Thus, the acceleration due to centripetal force is given by,$a=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$. Clearly as the velocity $v$ and the radius $r$ of the circle are constant, acceleration $a$ will also remain a constant.
Note:
Centripetal force is the force that acts on a body moving in a circular path and is directed towards the centre around which the body is moving. If the particles decrease or increase their speeds during the circular motion the net force deviates the particle from its initial path.
Formula used:
$a=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
Complete answer:
We know that the motions are two types: one is straight motion and the circular motion. Then we know that circular motion, though the magnitude of velocity is a constant, the direction of velocity is changing. A circle. It is also defined as rotation of an object along a circular path. It can be of two forms, uniform circular motion, with constant angular rate of rotation and constant speed, or non-uniform circular motion with a changing rate of rotation.
Consider a body of mass $m$ moving along the circumference of a circle. the radius of a circle $r$ with velocity $v$,as shown in the figure. Then if a small force $F$ is applied on the body, then we know that the force is given as $F=ma$.

Where, $a$ is the acceleration and is given as the rate of change of velocity $\Delta v$ with respect to time.
Consider the \[\vartriangle OAB\] and $\triangle PQR$, then $\dfrac{\Delta v}{AB}=\dfrac{v}{r}$
Clearly, $AB=v\Delta t$
$\implies \dfrac{\Delta v}{v\Delta t}=\dfrac{v}{r}$
$\implies \dfrac{\Delta v}{\Delta t}=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
$\implies a=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$
Thus, the acceleration due to centripetal force is given by,$a=\dfrac{v^{2}}{r}$. Clearly as the velocity $v$ and the radius $r$ of the circle are constant, acceleration $a$ will also remain a constant.
Note:
Centripetal force is the force that acts on a body moving in a circular path and is directed towards the centre around which the body is moving. If the particles decrease or increase their speeds during the circular motion the net force deviates the particle from its initial path.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




