
What is the Brewster angle for air to glass transition? (Refraction index of glass is 1.5)
Answer
599.1k+ views
Hint: When a ray of light is incident on an air glass interface at a particular angle the reflected light will be linearly polarized. The tangent of this incident angle (polarizing angle) gives the refractive index.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know when a ray of light is incident on an air glass interface, (glass has higher refractive index) some light reflects and other refract.
When light strikes at a particular angle known as the brewster's angle the reflected and refracted rays will be perpendicular to each other and also the reflected ray will be linearly polarised.
 .
.
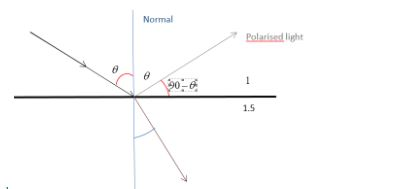
Snell’s law: It describes the relation between the angle of incidence and refraction .The law states that the ratio of sine of incident angle and sine of refracted angle will be equal to the ratio of refractive index($n_{2} $)and incident index ($n_{1}$) Using Snell’s law,
${n_1}sin{\theta _1} = .{n_2}sin{\theta _2}.$ since this is air glass interface ${n_1} = 1$ and ${n_2} = 1.5$.
From figure we can understand that
$1 \times sin\theta = 1.5 \times sin(90 - \theta )$
$1 \times sin\theta = 1.5 \times cos\theta $
$tan\theta = 1.5$
$\theta = ta{n^{ - 1}}(1.5)$
Therefore Brewster angle is equal to 56.30degrees.
Note: The incident ray will be unpolarised when it hits the air glass interface. It is temporarily absorbed by the medium. Electrons there oscillate in the direction of electric field vectors which are perpendicular to the refracted ray.These atoms re-emit the light to give the reflected and refracted rays. Since it is an electromagnetic wave the electric field vectors (which have the same direction in which the electrons where oscillating) will be perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
The only possible direction for the electric field vector of the reflected wave is perpendicular to the plane since it should be perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave .That’s the reason the reflected ray is linearly polarized. The refracted ray will be partly polarized as there are more electric field vectors in the plane than perpendicular to the plane.
For all other angles than 0 degrees and Brewster angle the reflected ray also will be partly polarized.
Complete step-by-step answer:
We know when a ray of light is incident on an air glass interface, (glass has higher refractive index) some light reflects and other refract.
When light strikes at a particular angle known as the brewster's angle the reflected and refracted rays will be perpendicular to each other and also the reflected ray will be linearly polarised.

Snell’s law: It describes the relation between the angle of incidence and refraction .The law states that the ratio of sine of incident angle and sine of refracted angle will be equal to the ratio of refractive index($n_{2} $)and incident index ($n_{1}$) Using Snell’s law,
${n_1}sin{\theta _1} = .{n_2}sin{\theta _2}.$ since this is air glass interface ${n_1} = 1$ and ${n_2} = 1.5$.
From figure we can understand that
$1 \times sin\theta = 1.5 \times sin(90 - \theta )$
$1 \times sin\theta = 1.5 \times cos\theta $
$tan\theta = 1.5$
$\theta = ta{n^{ - 1}}(1.5)$
Therefore Brewster angle is equal to 56.30degrees.
Note: The incident ray will be unpolarised when it hits the air glass interface. It is temporarily absorbed by the medium. Electrons there oscillate in the direction of electric field vectors which are perpendicular to the refracted ray.These atoms re-emit the light to give the reflected and refracted rays. Since it is an electromagnetic wave the electric field vectors (which have the same direction in which the electrons where oscillating) will be perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave.
The only possible direction for the electric field vector of the reflected wave is perpendicular to the plane since it should be perpendicular to the direction of propagation of the wave .That’s the reason the reflected ray is linearly polarized. The refracted ray will be partly polarized as there are more electric field vectors in the plane than perpendicular to the plane.
For all other angles than 0 degrees and Brewster angle the reflected ray also will be partly polarized.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE

In a human foetus the limbs and digits develop after class 12 biology CBSE

AABbCc genotype forms how many types of gametes a 4 class 12 biology CBSE

The correct structure of ethylenediaminetetraacetic class 12 chemistry CBSE




