
Blue eye colour is recessive to brown eye colour. A brown eyed man whose mother was blue-eyed marries a blue eyed woman.The children shall be
A) Both blue eyed and brown eyed 1:1
B) All brown eyed
C) All blue eyed
D) Blue eyed and brown eyed 8:1
Answer
569.1k+ views
Hint:There are two variants of one gene, brown (B) and blue (b). Green (G) and blue (G) are the other genes (b). If one gene is capable of causing brown eyes, another that causes blue will dominate. Probably, that is what happens in the older model with green eyes. On the green one the brown gene dominates, resulting in brown eyes.
Complete answer:
The genotype Bb must be a brown-eyed man whose mother was blue-eyed, where B represents brown-eye colour and b represents blue-eye colour. If a man with such a genotype is married to a woman with a blue eye, the children must be
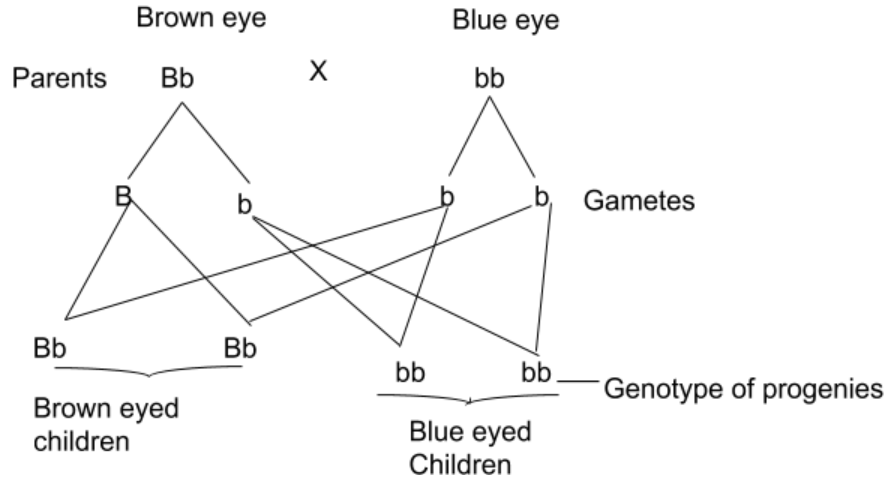
When a heterozygous brown-eyed male marries a homozygous blue-eyed woman, 50 percent of children are brown-eyed in the next generation and 50 percent of children are blue-eyed. The ratio of children with brown eyes to blue eyes is 1:1. It's known as the test cross.
OCA2 and HERC2 are two of the most important genes in eye colour. Both are available in variants that can cause blue eyes. And to work, they need each other. One reason for how blue-eyed parents may have a brown-eyed child is given by these two evidence.
People have the bulk of their genes in two copies. They're getting one copy out of mom and one copy out of dad. These genes will come in various versions (or alleles).
The correct answer is option (A) i.e, Both blue eyed and brown eyed 1:1.
Note:A model for the genetics of eye colour was created in 1907 by Charles and Gertrude Davenport. The colour of human eyes, skin and hair is mainly influenced by the quantity and form of a pigment called melanin. Melanin is produced by specialised cells known as melanocytes, which store it in intracellular compartments known as melanosomes.For all individuals, the total number of melanocytes is approximately equal, but the amount of melanin within each melanosome varies, and the number of melanosomes within a melanocyte varies. What defines the spectrum of hair, eye and skin colours is the total amount of melanin.
Complete answer:
The genotype Bb must be a brown-eyed man whose mother was blue-eyed, where B represents brown-eye colour and b represents blue-eye colour. If a man with such a genotype is married to a woman with a blue eye, the children must be

When a heterozygous brown-eyed male marries a homozygous blue-eyed woman, 50 percent of children are brown-eyed in the next generation and 50 percent of children are blue-eyed. The ratio of children with brown eyes to blue eyes is 1:1. It's known as the test cross.
| b | b | |
| B | BbBrown eyed | BbBrown eyed |
| b | bbBlue eyed | BbBlue eyed |
OCA2 and HERC2 are two of the most important genes in eye colour. Both are available in variants that can cause blue eyes. And to work, they need each other. One reason for how blue-eyed parents may have a brown-eyed child is given by these two evidence.
People have the bulk of their genes in two copies. They're getting one copy out of mom and one copy out of dad. These genes will come in various versions (or alleles).
The correct answer is option (A) i.e, Both blue eyed and brown eyed 1:1.
Note:A model for the genetics of eye colour was created in 1907 by Charles and Gertrude Davenport. The colour of human eyes, skin and hair is mainly influenced by the quantity and form of a pigment called melanin. Melanin is produced by specialised cells known as melanocytes, which store it in intracellular compartments known as melanosomes.For all individuals, the total number of melanocytes is approximately equal, but the amount of melanin within each melanosome varies, and the number of melanosomes within a melanocyte varies. What defines the spectrum of hair, eye and skin colours is the total amount of melanin.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




