
(a). State the principle of an AC generator and explain its workings with the help of a labeled diagram. Obtain the expressions for emf induced in a coil having \[N\] turns each of cross sectional area \[A\], rotating with constant angular speed \[\omega \] in a magnetic field \[B\], directed perpendicular to the axis of rotation.
(b). An aeroplane is flying horizontally from west to east with a velocity of \[900km\,h{{r}^{-1}}\]. Calculate the potential difference developed between the ends of its wings having a span of \[20m\]. The horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field is \[5\ times {{10}^{-4}}T\] and the angle of dip is \[{{30}^{o}}\].
Answer
571.2k+ views
Hint: (a). The AC generator is a device used to produce alternating current by moving an armature with a number of turns in the presence of a magnetic field.
(b). As the aeroplane is flying it experiences a change in magnetic flux due to the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field. Emf induced can be calculated by substituting the corresponding values in the formula from emf.
Complete step by step answer:
(a).
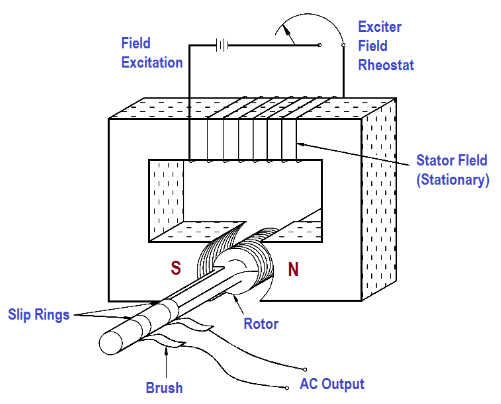
An AC generator is a machine which converts mechanical energy to electrical energy and the current produced is in the form of alternating current varying sinusoidally. The principle on which AC generators work is the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction which states that when a current carrying conductor moves in a magnetic field, a potential difference is developed across its ends,
The different parts of an AC generator are-
1. Stator field
2. Armature
3. Prime mover
4. Rotor
5. Stator
6. Slip rings
Working- When the armature is made to rotate between the poles of a magnet along an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field the flux associated with the armature changes continuously. Due to change in flux an emf is developed and current flows through the galvanometer, brushes and slip rings.
Due to flow of current, the galvanometer deflects between the negative and positive values which indicate that there is an alternating current flowing in the setup.
Let the coil have \[N\] number of turns and the area of the cross section of the armature be \[A\], let the armature be rotated at a constant angular velocity \[\omega \]. When armature rotates, it makes an angle \[\theta \] with the magnetic field of flux intensity \[B\]. The flux through the coil is given by-
\[\begin{align}
& \phi =NBA\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow \phi =NBA\cos \omega t \\
\end{align}\]
The emf developed is given by-
\[e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}\]
\[\begin{align}
& e=-\dfrac{d(NBA\cos \omega t)}{dt} \\
& e=-NBA\dfrac{d}{dt}(\cos \omega t) \\
& e=NBA\omega \sin \omega t \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the emf induced in the circuit is given by \[NBA\omega \sin \omega t\].
(b). As the aeroplane is travelling from east to west, it flies perpendicular to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field. So emf induced along its wings is due to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field.
We know, formula for induced emf is given by-
\[e=Blv\] ---- (1)
Here,\[B\]is the magnetic field
\[l\] is the length which cuts the magnetic field
\[v\]is velocity
We know that,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{{{B}_{v}}}{{{B}_{H}}}\]
Here, \[\theta \] is the angle of dip
\[{{B}_{v}}\] is vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field
\[{{B}_{H}}\] is horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
\[\therefore {{B}_{v}}={{B}_{H}}\tan \theta \]
Substituting in eq (1), we get,
\[\begin{align}
& e=({{B}_{H}}\tan \theta )lv \\
& e=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\times 20\times \left( \dfrac{900\times 1000}{3600}m{{s}^{-1}} \right) \\
& e=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\times 20\times 250 \\
& e=1.46V \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the emf induced along the wings of the aeroplane is \[1.46V\]
Note: In the AC generator either the magnet is made to rotate or the armature. It is always easier to rotate the magnet than the armature. Voltage cannot be induced in a conductor kept in a magnetic field if the magnetic field is in the direction of the area vector. The aeroplane is flying parallel to the horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field, therefore no emf is induced by it.
(b). As the aeroplane is flying it experiences a change in magnetic flux due to the vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field. Emf induced can be calculated by substituting the corresponding values in the formula from emf.
Complete step by step answer:
(a).

An AC generator is a machine which converts mechanical energy to electrical energy and the current produced is in the form of alternating current varying sinusoidally. The principle on which AC generators work is the Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction which states that when a current carrying conductor moves in a magnetic field, a potential difference is developed across its ends,
The different parts of an AC generator are-
1. Stator field
2. Armature
3. Prime mover
4. Rotor
5. Stator
6. Slip rings
Working- When the armature is made to rotate between the poles of a magnet along an axis perpendicular to the magnetic field the flux associated with the armature changes continuously. Due to change in flux an emf is developed and current flows through the galvanometer, brushes and slip rings.
Due to flow of current, the galvanometer deflects between the negative and positive values which indicate that there is an alternating current flowing in the setup.
Let the coil have \[N\] number of turns and the area of the cross section of the armature be \[A\], let the armature be rotated at a constant angular velocity \[\omega \]. When armature rotates, it makes an angle \[\theta \] with the magnetic field of flux intensity \[B\]. The flux through the coil is given by-
\[\begin{align}
& \phi =NBA\cos \theta \\
& \Rightarrow \phi =NBA\cos \omega t \\
\end{align}\]
The emf developed is given by-
\[e=-\dfrac{d\phi }{dt}\]
\[\begin{align}
& e=-\dfrac{d(NBA\cos \omega t)}{dt} \\
& e=-NBA\dfrac{d}{dt}(\cos \omega t) \\
& e=NBA\omega \sin \omega t \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the emf induced in the circuit is given by \[NBA\omega \sin \omega t\].
(b). As the aeroplane is travelling from east to west, it flies perpendicular to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field. So emf induced along its wings is due to the horizontal component of Earth’s magnetic field.
We know, formula for induced emf is given by-
\[e=Blv\] ---- (1)
Here,\[B\]is the magnetic field
\[l\] is the length which cuts the magnetic field
\[v\]is velocity
We know that,
\[\tan \theta =\dfrac{{{B}_{v}}}{{{B}_{H}}}\]
Here, \[\theta \] is the angle of dip
\[{{B}_{v}}\] is vertical component of Earth’s magnetic field
\[{{B}_{H}}\] is horizontal component of earth’s magnetic field
\[\therefore {{B}_{v}}={{B}_{H}}\tan \theta \]
Substituting in eq (1), we get,
\[\begin{align}
& e=({{B}_{H}}\tan \theta )lv \\
& e=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\times 20\times \left( \dfrac{900\times 1000}{3600}m{{s}^{-1}} \right) \\
& e=5\times {{10}^{-4}}\times \dfrac{1}{\sqrt{3}}\times 20\times 250 \\
& e=1.46V \\
\end{align}\]
Therefore, the emf induced along the wings of the aeroplane is \[1.46V\]
Note: In the AC generator either the magnet is made to rotate or the armature. It is always easier to rotate the magnet than the armature. Voltage cannot be induced in a conductor kept in a magnetic field if the magnetic field is in the direction of the area vector. The aeroplane is flying parallel to the horizontal component of the Earth’s magnetic field, therefore no emf is induced by it.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




