
What is a rectifier? Explain with a neat and clean diagram the action of a semiconductor diode as a full wave rectifier.
Answer
594.6k+ views
Hint: A rectifier is a device or arrangement of electrical instruments which is used to convert AC (Alternating current) to DC (Direct current). The semiconductor diode, also called p-n junction diode, plays a major role in the working of a rectifier as it allows current flow only in a single direction and blocks the current in the other direction. Conversion of AC to DC is a very important part of many instruments which we use in our day to day life.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Rectification basically means the separation of a particular type of item from another type. In electrical systems, it means the device that changes the direction of current for some part of the AC wave.
The need for rectification: As AC waves consist of both positive and negative parts, the average power taken over a cycle is zero. Hence it’s not possible to store electricity as AC. Hence we have to convert AC to DC to store the power for later use.
p-n junction diode: It is a semiconductor device that allows current in a particular direction only. It is made up of a p-type semiconductor and a n-type semiconductor. If the current is passed from a bigger end towards the smaller end, only then the passage is allowed. In short, for the passage of the current, the bigger side must be at high potential.
The action of semiconductor rectifier as a full-wave rectifier:
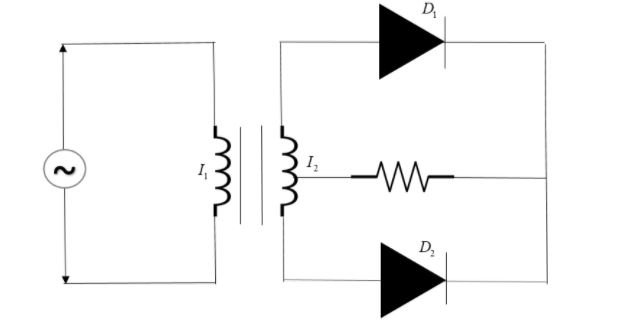
A full-wave rectifier consists of two inductors ($I_{1}$ & $I_{2}$), two diodes ($D_{1}$ & $D_{2}$), and a resistor, across which output is taken. The inductor connected to the main supply is used to induce a current in other circuits by mutual inductance. For the first half cycle, the upper end of $I_2$is at a higher potential. Hence current passes through $D_1$ and not through $D_2$. Hence for the first half cycle, the current is passed through the resistor. For the second half cycle, the lower end of $I_2$ is higher potential. Hence only though $D_2$ the current will pass. Hence we see that for both the cycles, the current is passing through the resistor.
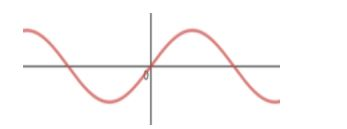
AC before rectification:
AC after rectification:
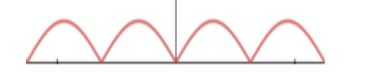
Note: It is important to note that ideally, there is no change in amplitude or frequency of the original wave. Chance of mistake is that a student might think that the second wave is also AC, but ac doesn’t mean fluctuating amplitude. If the current changes its direction, i.e. from positive to negative, or above x-axis to lower x-axis, then only we can say that the current is alternating.
Complete step-by-step answer:
Rectification basically means the separation of a particular type of item from another type. In electrical systems, it means the device that changes the direction of current for some part of the AC wave.
The need for rectification: As AC waves consist of both positive and negative parts, the average power taken over a cycle is zero. Hence it’s not possible to store electricity as AC. Hence we have to convert AC to DC to store the power for later use.
p-n junction diode: It is a semiconductor device that allows current in a particular direction only. It is made up of a p-type semiconductor and a n-type semiconductor. If the current is passed from a bigger end towards the smaller end, only then the passage is allowed. In short, for the passage of the current, the bigger side must be at high potential.
The action of semiconductor rectifier as a full-wave rectifier:

A full-wave rectifier consists of two inductors ($I_{1}$ & $I_{2}$), two diodes ($D_{1}$ & $D_{2}$), and a resistor, across which output is taken. The inductor connected to the main supply is used to induce a current in other circuits by mutual inductance. For the first half cycle, the upper end of $I_2$is at a higher potential. Hence current passes through $D_1$ and not through $D_2$. Hence for the first half cycle, the current is passed through the resistor. For the second half cycle, the lower end of $I_2$ is higher potential. Hence only though $D_2$ the current will pass. Hence we see that for both the cycles, the current is passing through the resistor.
AC before rectification:

AC after rectification:

Note: It is important to note that ideally, there is no change in amplitude or frequency of the original wave. Chance of mistake is that a student might think that the second wave is also AC, but ac doesn’t mean fluctuating amplitude. If the current changes its direction, i.e. from positive to negative, or above x-axis to lower x-axis, then only we can say that the current is alternating.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




