
A Galilean telescope measures 9 cm from the objective to the eye-piece. The focal length of the objective is 15 cm. Its magnifying power is
A. $2.5$
B. $\dfrac{2}{5}$
C. $\dfrac{5}{3}$
D. $\dfrac{3}{5}$
Answer
585.6k+ views
Hint: In a Galilean telescope, the focal length of the objective lens is equal to the difference between the length between the two lenses and the focal length of the eye-piece, ${f_o} = L + {f_e}$, where ${f_o},{f_e}$ are the focal lengths of objective lens and eye-piece, L is the distance between them. Substitute the values of L and focal length of the objective lens to find the value of focal length of the eye-piece. Magnification is the negative ratio of focal length of the objective lens and focal length of the eye-piece.
Complete step by step answer:
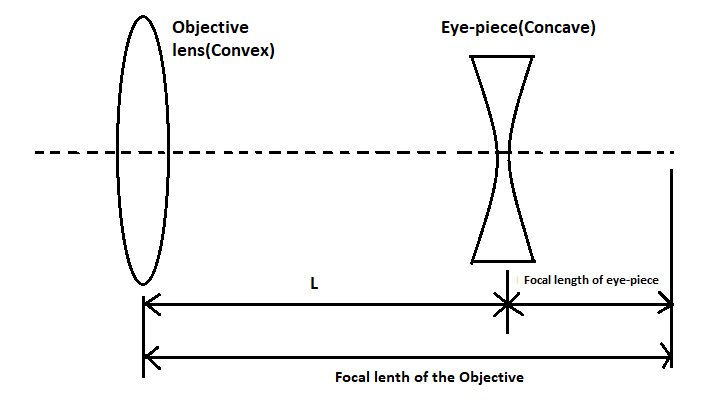 We are given that a Galilean telescope measures 9 cm from the objective to the eye-piece and the focal length of the objective is 15 cm.
We are given that a Galilean telescope measures 9 cm from the objective to the eye-piece and the focal length of the objective is 15 cm.
We have to find its magnifying power.
As we can see in the above figure, the objective is a convex lens and the eye-piece is a concave lens.
So the focal length is negative for the concave (eye-piece) lens.
As we can see, the focal length of the objective lens is the sum of the focal length of the eye-piece and the distance between them.
${f_o} = L + {f_e}$, where ${f_o},{f_e}$ are the focal lengths of objective lens and eye-piece, L is the distance between them and ${f_e}$ should be taken negatively.
$
{f_o} = L + \left( { - {f_e}} \right) \\
\implies {f_o} = L - {f_e} \\
\implies {f_e} = L - {f_o} \\
$
Substitute the values of the L and ${f_o}$ as they are given in the question.
$
{f_o} = 15cm,L = 9cm \\
\implies {f_e} = L - {f_o} \\
= 9 - 15 \\
\therefore {f_e} = - 6cm \\
$
Magnification is the negative ratio of focal length of the objective lens and focal length of the eye-piece.
$
m = \dfrac{{ - {f_o}}}{{{f_e}}} \\
{f_o} = 15cm,{f_e} = - 6cm \\
m = \dfrac{{ - 15}}{{ - 6}} \\
\implies m = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\therefore m = + 2.5 \\
$
The magnifying power of the given Galilean telescope is 2.5.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The objective lens is concave, which is a spherical lens and focuses the light rays passed through it to a specific point. Eye-piece is a convex lens, which is a spherical lens and diverges the light rays refracted from it. The lenses used in objective and eye-piece are not the same in a Galilean telescope. Be careful in considering the lenses.
Complete step by step answer:

We have to find its magnifying power.
As we can see in the above figure, the objective is a convex lens and the eye-piece is a concave lens.
So the focal length is negative for the concave (eye-piece) lens.
As we can see, the focal length of the objective lens is the sum of the focal length of the eye-piece and the distance between them.
${f_o} = L + {f_e}$, where ${f_o},{f_e}$ are the focal lengths of objective lens and eye-piece, L is the distance between them and ${f_e}$ should be taken negatively.
$
{f_o} = L + \left( { - {f_e}} \right) \\
\implies {f_o} = L - {f_e} \\
\implies {f_e} = L - {f_o} \\
$
Substitute the values of the L and ${f_o}$ as they are given in the question.
$
{f_o} = 15cm,L = 9cm \\
\implies {f_e} = L - {f_o} \\
= 9 - 15 \\
\therefore {f_e} = - 6cm \\
$
Magnification is the negative ratio of focal length of the objective lens and focal length of the eye-piece.
$
m = \dfrac{{ - {f_o}}}{{{f_e}}} \\
{f_o} = 15cm,{f_e} = - 6cm \\
m = \dfrac{{ - 15}}{{ - 6}} \\
\implies m = \dfrac{5}{2} \\
\therefore m = + 2.5 \\
$
The magnifying power of the given Galilean telescope is 2.5.
So, the correct answer is “Option A”.
Note:
The objective lens is concave, which is a spherical lens and focuses the light rays passed through it to a specific point. Eye-piece is a convex lens, which is a spherical lens and diverges the light rays refracted from it. The lenses used in objective and eye-piece are not the same in a Galilean telescope. Be careful in considering the lenses.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




