This World of Things Class 3 Questions and Answers - Free PDF Download
FAQs on NCERT Solutions For Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 This World of Things (2025-26)
1. What are the main topics covered in NCERT Solutions for Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 This World Of Things?
The NCERT Solutions for Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 focus on the different objects found in daily life, the materials they are made of, the distinction between natural and artificial things, and how to classify objects by their uses or properties as per the CBSE 2025-26 syllabus.
2. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 explain the difference between natural and artificial things?
According to the NCERT Solutions, natural things are those found in nature and not made by humans (like trees, water, and animals), while artificial things are man-made objects (like tables, clothes, and shoes). Students learn to identify and list items in both groups.
3. What materials are most everyday objects made of, as discussed in Chapter 10 NCERT Solutions?
Most everyday objects, as covered in the solutions, are made of wood, metal, plastic, glass, cloth, rubber, and clay. The solutions help students recognize these materials in their environment and understand their uses.
4. Why is it important for students to know what materials objects are made of?
Learning about materials helps students understand why certain materials are chosen for specific uses. For example, metal is used for utensils because it is strong and durable, while wood is used for furniture for its strength and appearance. This assists in developing observation and reasoning skills.
5. How do NCERT Solutions for Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 help students practise observation skills?
NCERT Solutions encourage students to identify, list, and group objects around them, testing properties like transparency, texture, and sound, which sharpens their observation and classification abilities.
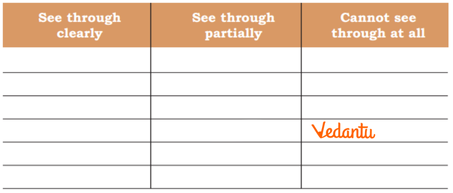
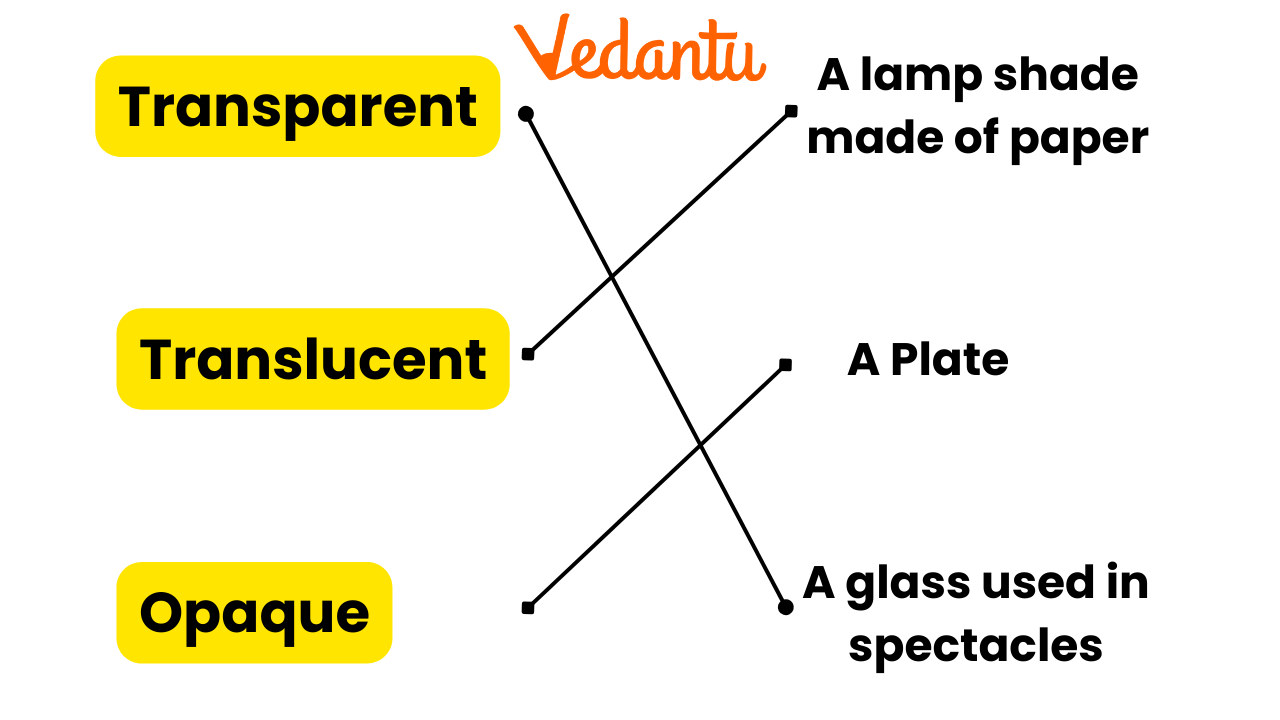
6. What are “transparent,” “translucent,” and “opaque” materials, as described in the solutions?
The solutions define:
- Transparent materials: Allow light to pass through completely (e.g., glass pane).
- Translucent materials: Allow light to pass through partially (e.g., butter paper).
- Opaque materials: Do not allow light to pass through (e.g., metal utensils).
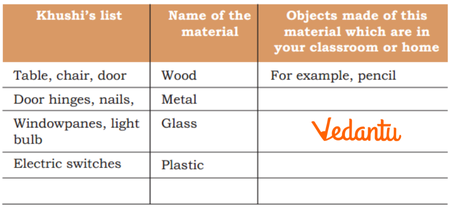
7. Can you give examples of objects made from more than one material as per NCERT Solutions for this chapter?
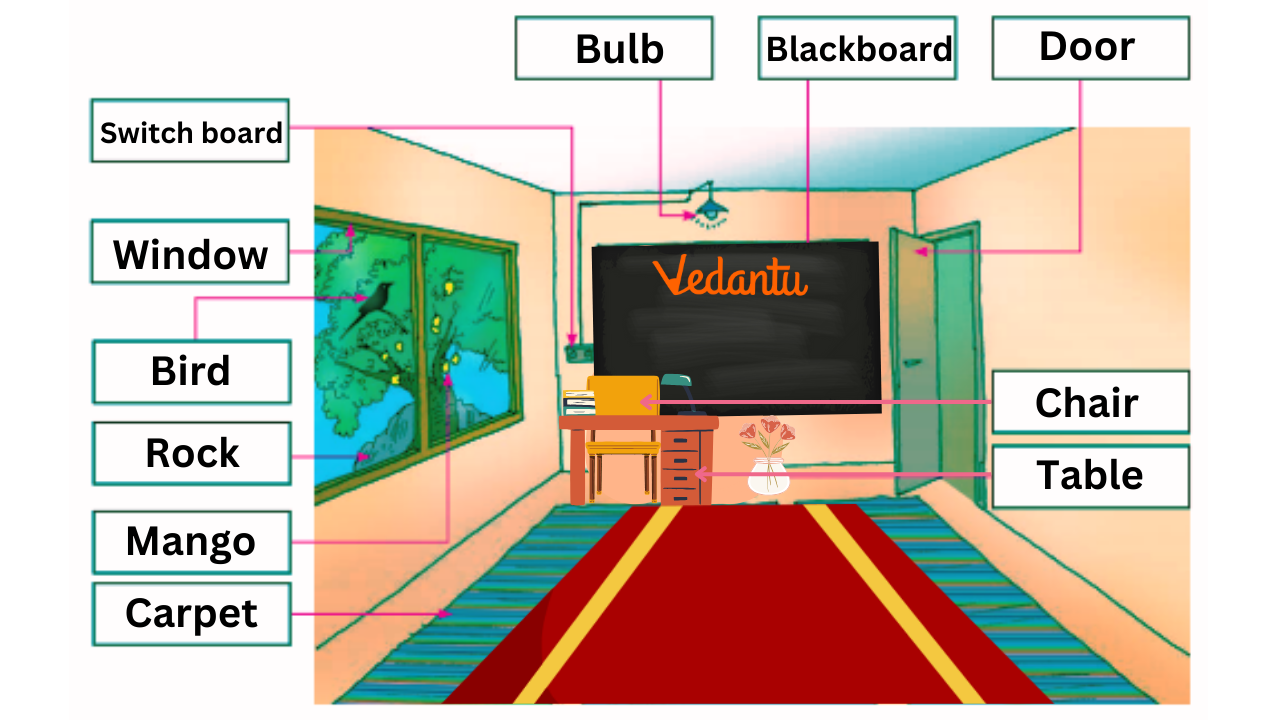
Yes, many objects use multiple materials. For example, electric switches are made using plastic and metal; bulbs use glass and metal; windows may use wood (frame), glass (pane), and metal (hinges).
8. What kinds of higher-order thinking (HOTS) questions are included in Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 NCERT Solutions?
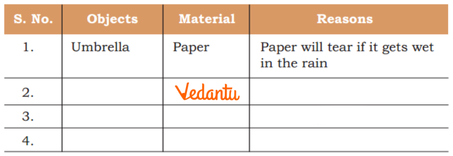
The solutions include HOTS questions such as why certain materials are unsuitable for specific objects (e.g., why umbrellas cannot be made of paper), and scenario-based problem-solving like grouping confusing objects or explaining what if objects were made using the wrong material.
9. How do the NCERT Solutions for this chapter encourage interaction with family or elders?
The solutions suggest students talk to grandparents about how materials used in everyday objects have changed over time, helping students understand historical changes and generational perspectives in daily life.
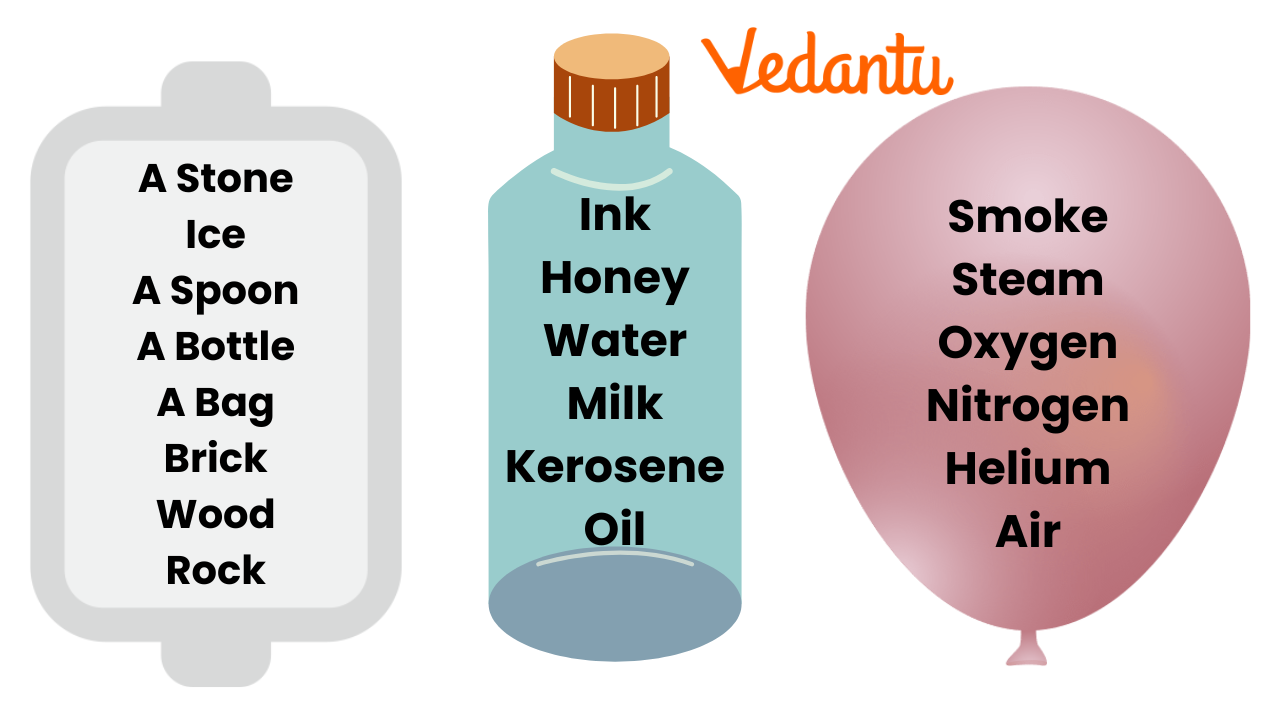
10. What is the importance of classifying objects as solids, liquids, or gases, as covered in the solutions?
Classification helps students understand states of matter and develop scientific thinking. For example, water is a liquid, stone is a solid, and air is a gas, all serving different roles in the environment and in usage.
11. How do the NCERT Solutions for Chapter 10 build reasoning about the selection of materials in everyday life?
By comparing and matching objects with their suitable materials, the solutions help students reason why certain materials are preferable (e.g., metal for cooking utensils due to heat resistance) and why others would not work (e.g., glass for tyres).
12. What “chain game” or grouping activities are given in NCERT Solutions for Class 3 EVS Chapter 10?
The solutions introduce chain games or grouping activities where students must connect objects to materials (like matching a spoon to metal), and extend groupings to new objects, encouraging active learning and critical thinking.
13. How does this chapter in NCERT Solutions introduce the concept of artificial and natural objects with examples?
The solutions use real-life, simple examples—for instance, a mango or a bird for natural, and a chair or bottle for artificial—to make the difference clear and relatable for Class 3 students.
14. What practical activities from Chapter 10 Solutions help students understand properties of materials?
Students are asked to look through materials to see transparency, knock on objects for sound differences, and investigate with magnets to check if an object is metal, learning via hands-on experience.
15. How do the NCERT Solutions for Class 3 EVS Chapter 10 enable exam preparation as per CBSE 2025-26 patterns?
The solutions offer CBSE-aligned structure, clear stepwise answers for all textbook questions, and exposure to application-based questions and activities that can appear in 2025-26 exams, ensuring conceptual clarity and practice for Class 3 students.