




Essential Subtraction Properties Every Student Should Know
According to the algebraic concept known as the "subtraction property of equality," if a value is subtracted from two equal quantities, the resulting differences are also equal.
The subtraction property of equality states that in order to maintain equality if we take a number away from one side of equality, we must also take that same amount away from the other side.
Comparable to the equality's addition property is this property. The properties of equality range from the addition property to the division property to the reflexive property to the multiplication property, among others. By applying the identical mathematical operation of subtraction to both sides of an equality, the subtraction property of equality seeks to balance an equation.
Let's look at an illustration to comprehend this better. There are two bags with ten balls each. Now, if we remove three balls from bag 1, we must remove three from bag 2 to maintain the same number of balls in bags 1 and 2. Thus, after releasing three balls from each bag, there are seven balls left in each bag.
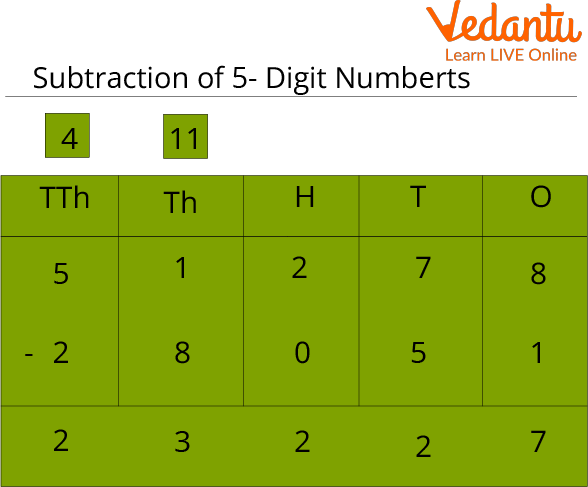
Subtraction of 5-Digit Number
Properties of Whole-Number Subtraction
Property 1:
If two whole numbers a and b are such that A > B or A = B, then A - B is also a whole number. If A < B, then it is impossible to subtract B from A in whole numbers.
For instance,
10 - 5 = 5
23 - 12 = 11
100 - 99 = 1
Property 2: Commutative Property of Subtraction
Whole numbers cannot be subtracted cumulatively, hence even if a and b are both whole numbers, a - b does not always equal (B - A).
Verification:
We are aware that 9 – 5 = 4, however, 5 – 9 is illogical. Additionally, 125 - 75 = 50, but 75 - 125 is impractical. In other words, if A > B, then A - B is a whole number but B - A is not feasible, and if B > A, then B - A is a whole number but A - B is not possible for two whole numbers A and B. This is the Commutative property of subtraction.
Therefore, (A -B) is generally not equal to (B - A).
Property 3:
A - 0 equals A if a is any whole number other than zero, but 0 - A is not defined.
Verification:
Although 0 - 15 is not feasible, we know that 15 - 0 equals 15.
Property 4: Associative Property of Subtraction
Whole number subtraction is not associative. In other words, if A, B, and C are three whole numbers, A - (B - C) is generally not equivalent to (A - B) - C. This is the Associative Property of Subtraction.
Verification:
Associative Property of Subtraction Example
10 - (9 - 3) = 10 - 6 = 4,
thus, (10 - 9) - 3 = 1 - 3 = - 2
Now because of that 10 - (9 - 3) (10 - 9) - 3.
Zero Property of Subtraction
When a number is subtracted from zero, the result is the original number.
For instance,
(i) 5645 - 0 = 5645;
(ii) 987 - 0 = 987
Properties of a Number Subtracted from Itself
The difference is zero when a number is subtracted from itself, according to the properties of subtraction.
For instance,
323 - 323 = 0
12 - 12 =0
Properties of Subtraction Worksheet
Children can practise from properties of subtraction worksheets.
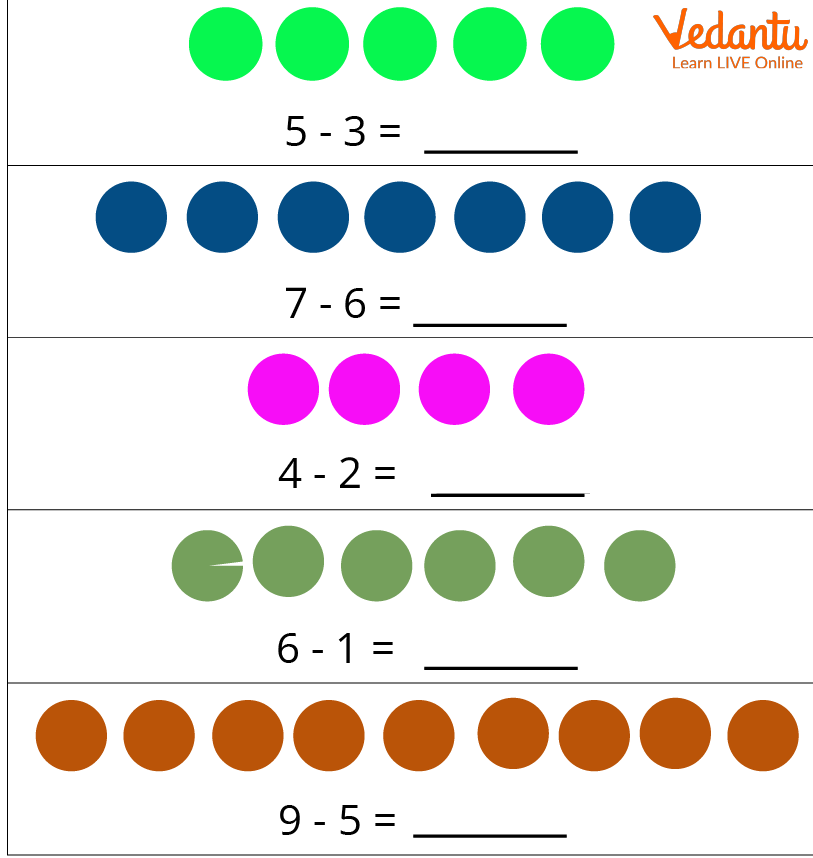
Properties of Subtraction Worksheet
Summary
A mathematical process called subtraction involves taking a portion of one value and subtracting it from another. You subtract two numbers when you do subtraction. The minuend is the initial digit in a subtraction equation. This is the figure from which we deduct. The subtraction is the name of the second number. We take away this from the minute. When we subtract, the result is the difference.
FAQs on Properties of Subtraction Explained
1. What are the main properties of subtraction?
The main properties of subtraction are:
- Non-commutative property (changing order changes result),
- Non-associative property (grouping numbers changes result),
- Identity property (subtracting zero leaves number unchanged).
2. What is the non-commutative property of subtraction?
The non-commutative property means changing the order of numbers in subtraction gives different results. For example, $8 - 5 = 3$, but $5 - 8 = -3$. In subtraction, the sequence of numbers is always important to the answer.
3. Is subtraction associative like addition?
No, subtraction is non-associative. Grouping numbers differently changes the result. For instance, $(10 - 3) - 2 = 5$ but $10 - (3 - 2) = 9$. This is called the non-associative property of subtraction.
4. What is the identity property of subtraction?
The identity property of subtraction states that subtracting zero from any number does not change its value. Mathematically, for any number $a$, $a - 0 = a$. Zero is called the identity element in subtraction because it keeps numbers the same.
5. How does subtraction differ from addition in terms of properties?
Subtraction and addition have different properties.
- Addition is commutative and associative,
- Subtraction is non-commutative and non-associative.
6. What happens when you subtract any number from itself?
Subtracting a number from itself always gives zero. Mathematically, for any number $a$, $a - a = 0$. This important property of subtraction shows that removing all parts of a quantity will leave nothing.
7. Can subtraction be performed in any order?
No, subtraction cannot be performed in any order because of its non-commutative property. Switching the order of numbers changes the answer. Carefully following the correct order is necessary for accurate subtraction results.
8. Does subtracting zero change a number?
No, subtracting zero from any number does not change its value. For example, $42 - 0 = 42$. This demonstrates the identity property of subtraction, where zero does not affect the outcome in subtraction problems.
9. Is there a closure property in subtraction for whole numbers?
The closure property does not hold for subtraction with whole numbers. For example, $5 - 7 = -2$ is not a whole number. So, subtracting two whole numbers can result in a number outside the set of whole numbers.
10. Why is order important in subtraction?
Order is important in subtraction because of its non-commutativity. Changing the order changes the result. For instance, $9 - 4 = 5$, but $4 - 9 = -5$. Always subtract the correct way to get the intended answer.
11. What is the difference between subtraction and inverse operations?
Subtraction is the inverse operation of addition. If $a + b = c$, then $c - b = a$. This means subtraction undoes what addition does, helping solve equations and check work in mathematics.
12. How is the property of subtraction used in real life?
The properties of subtraction are used in daily life for activities like calculating change, measuring differences in scores, or comparing quantities. Remembering the order and identity properties helps ensure correct results in everyday subtraction tasks.











