




Why Is the Multiplicative Identity Important in Math?
Have you ever heard about the answer obtained when any number is multiplied by 1? When any number is multiplied by 1 the product is always the number itself. In the below-discussed article, children would gain knowledge about the steps involved in solving multiplication problems, which is considered one of the basic and most widely used mathematical and arithmetical operations. Generally, it is represented using the symbol '×' or '*' in between the two numbers. Now, let us start with our topic here:
What is Multiplication?
Multiplication is a process of calculating the product of two quantities or numbers by multiplying them together. '×' is used to depict the product of two quantities. The number multiplied by the multiplier is called the multiplicand and the number by which the multiplicand is multiplied is called the multiplier. It can also be stated as a way of adding a number repeatedly to acquire their product.

Showing Terms Used in the Multiplication of Two Numbers
Steps Involved in Solving Multiplication Queries
The steps required to follow in the multiplication of two numbers are given below:
Write the given multiplicand and multiplier in the column form by taking into consideration their place values
Then put the multiplication sign (×) preceding the multiplier
Start the multiplication from the right-hand side of the multiplier and move to the left side.
Count the number of digits in multiplier quantity and place the zeroes 1 less than the number of digits in the multiplier from the right side
Finally, add up all the products respective to each digit of the multiplier.
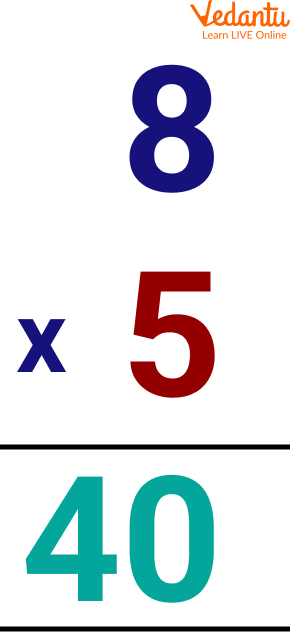
Multiplication of 8 and 5
Multiplicative Identity Property
Multiplicative identity property states that "Any number multiplied by 1 is the number itself". It means that when any number is multiplied by 1 the answer is always the number. It serves as a user identity in solving various problems. 1 is the identity of itself i.e. 1 × 1 = 1. It is also called the Identity Property of Multiplication because of the reason, here the identity of a number remains unaltered.

Showing Identity Property of Multiplication
Solved Examples
Q 1. 12 × 1
Ans: Steps to be followed to calculate the product using Multiplicative Identity
Align the given numbers in columns or rows to calculate the product
Multiplying 1 with the given number and noting the result
Thus, we can conclude that when any number is multiplied by 1 the answer is the number itself.
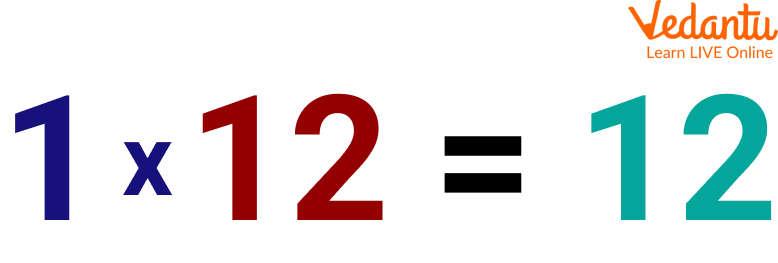
Showing Any Number Multiplied by 1
Q 2. 65 × 31
Ans: Steps to calculate the result of this statement are given below:
Write the given multiplier and multiplicand in columns format
Now, using multiplicative identity, any number multiplied by 1 is the number, for multiplying 65 and 1
Calculate the number of digits of the multiplier and put zeroes one less than the calculated number of digits
Further, multiplying the tens digit of the multiplier with the multiplicand
Adding the two obtained partial products i.e. 65 + 1950 = 2015
Hence, the required result of the multiplication of 65 × 31 is 2015.
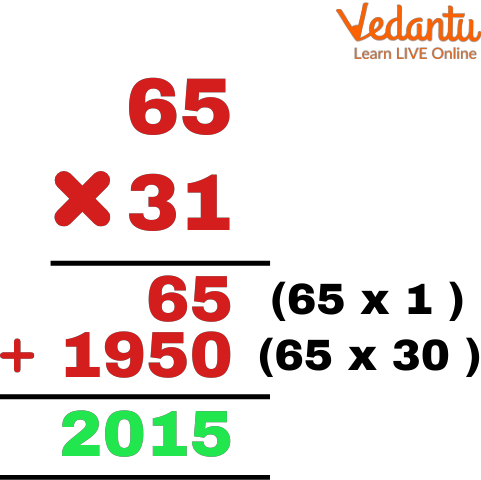
Showing the Multiplication of Two Digit Number Whose One Digit is 1
Practice Problems
Some practice problems based on the concept, any number multiplied by 1 is the number itself are given below. These should be solved by the children on their own for a better understanding of the concepts.
Q 1. 59 × 1
Ans: 59
Q 2. 84 × 1
Ans: 84
Q 3. 1 × 18
Ans: 18
Q 4. 34 × 1
Ans: 34
Q 5. 1 × 32
Ans: 32
Summary
To wrap up here with the topic of number multiplication. The main motive of this article is to impart knowledge of multiplication by covering every topic including, what is multiplication, the steps involved in solving mathematics problems, whether any number multiplied by 1 is the number, etc. It is formed using the solved examples and images which makes learning interesting and exciting. Hoping the writing helped you in capturing the concept of multiplication and you enjoyed reading it. Feel comfortable to ask about your problems.
FAQs on What Is the Multiplicative Identity Property?
1. What is the multiplicative identity property?
The multiplicative identity property states that any number multiplied by 1 will result in the original number itself. The number's value or identity remains unchanged after the multiplication. For instance, if you multiply any number like 15 by 1, the product is still 15.
2. How can the multiplicative identity property be represented as a formula?
The multiplicative identity property is represented algebraically with a simple formula. If 'n' represents any number (like a whole number, integer, or fraction), the formula is: n × 1 = n. This clearly shows that the outcome of multiplying 'n' by 1 is 'n' itself.
3. What are some examples of the multiplicative identity property in action?
The multiplicative identity property applies across all types of numbers. Here are a few examples:
- For Whole Numbers: 25 × 1 = 25
- For Integers: -8 × 1 = -8
- For Fractions: (5/6) × 1 = 5/6
- For Decimals: 9.75 × 1 = 9.75
4. Why is the number 1 specifically called the 'multiplicative identity'?
The number 1 is called the multiplicative identity because it is the unique number that does not change the identity (the value) of any number it multiplies. Think of it as a neutral element for multiplication. Just as your own identity makes you who you are, the number 1 leaves any number it interacts with through multiplication exactly as it was before.
5. How does the multiplicative identity property differ from the additive identity property?
The primary difference lies in the mathematical operation involved.
- The multiplicative identity is 1, because any number multiplied by 1 stays the same (for example, a × 1 = a).
- The additive identity is 0, because any number added to 0 stays the same (for example, a + 0 = a).
6. What is the difference between the multiplicative identity of 1 and the multiplicative property of 0?
The difference is in the result of the multiplication. The multiplicative identity property of 1 preserves the original number (e.g., 54 × 1 = 54). In contrast, the multiplicative property of 0 states that any number multiplied by 0 becomes 0, effectively losing its original value (e.g., 54 × 0 = 0).
7. Is the multiplicative identity always 1, even for different number systems like rational numbers or complex numbers?
Yes, the multiplicative identity is consistently 1 across various number systems taught in the CBSE/NCERT syllabus. For rational numbers (fractions), the identity is 1 (or 1/1). For real numbers (including decimals and irrationals), it is 1. Even in more advanced topics like complex numbers, the multiplicative identity is 1 (represented as 1 + 0i).























