




How to Convert Kilometres: Step-by-Step Guide with Practice Questions
Introduction to Kilometre for Kids
Everyone loves taking long walks or bicycling around a park. But have you ever wondered how the distance that we travel during these walks or bicycling is measured? How can we measure the distance between our home and school? We measure the distance in kilometres. But now we often hear or read on maps that the turn is 10 metres away or the destination metres. What does it mean? Well, the metre is also a term used to quantify the distance.
In this article, we will learn about the metre and kilometre definitions in Maths and their conversion.
What is the Metric System?
A Metric system is an international system that deals with the use of metric units. These units are used to measure height, weight, distance, or length. The metric system also has units like kilometres and metres that are used to measure the length or the distance of the object. Another example of a metric unit is kilograms, this is used to quantify the mass of a body. Grams is a smaller metric unit that is also used to quantify the mass of an object. The image illustrated below represents the different units that are used to measure length.
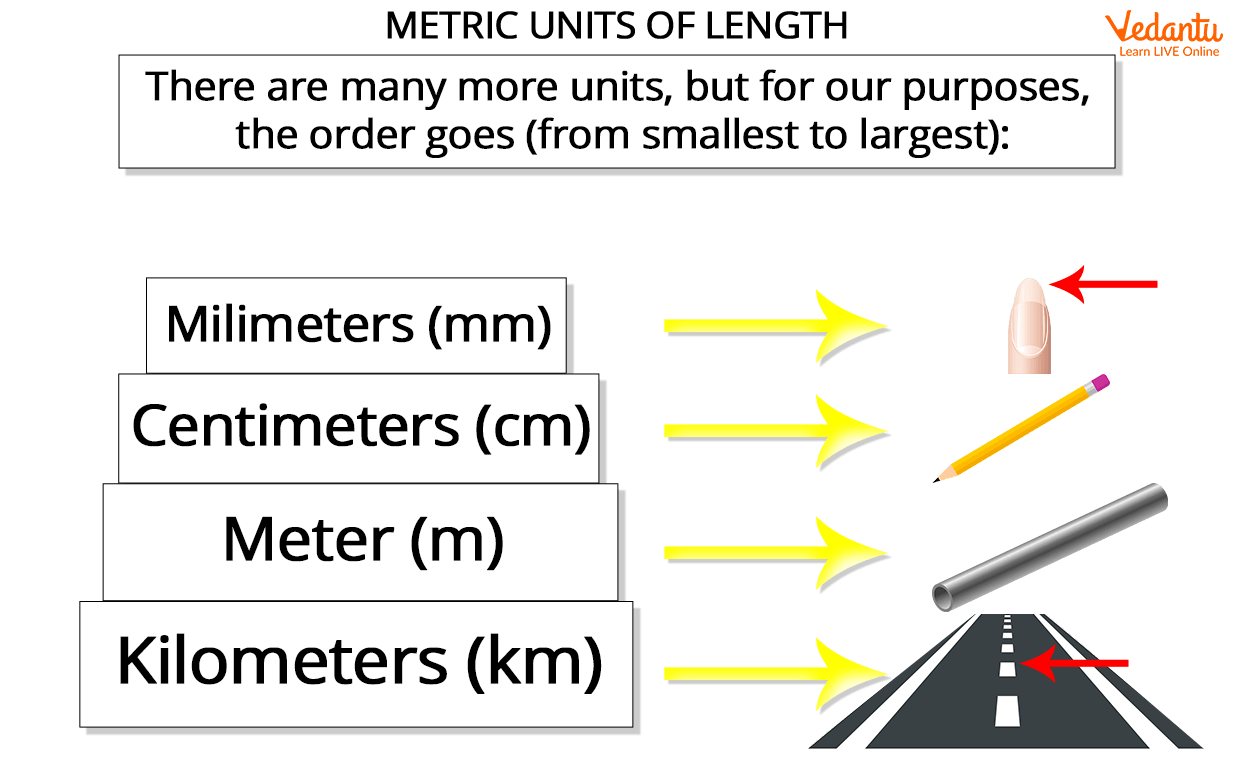
Metric units used to measure the length
What is a Kilometre?
Since we have learnt about the metric system, we can now discuss the kilometre definition in Maths. A kilometre is a SI unit that is used to measure distance. The term is abbreviated as km. The prefix kilo is derived from Greek which refers to a thousand. This interesting fact can help kids in understanding the conversion of metric units. Let us look into some examples where kilometres can be used.
The distance between the school and my home is 2 km.
The distance between Delhi and Bangalore is 2147 km.
I go for a 3 km walk every morning.

Distance from home to school
What is a Metre?
A metre is defined as the metric unit that is used to measure smaller distances and lengths. It is abbreviated as (m). The term metre is commonly used to measure lengths that are smaller than 1000 metres. For example, the term is used to measure the length of the table or the length of a Christmas tree. The term is also used to quantify small distances, for instance:
The turn is 10 metres away.
There is a basketball court 60 m from the school playground.
Relation Between Metres and Kilometres
As we have learnt the kilometre definition in Maths and the metre definition as well, let us look into the relationship between them. As km and m are metric units, they can be converted into each other. 1 kilometre is equal to 1000 metres. That means we can express the values of a given distance in both units. The following examples can help students understand the conversion.
Example 1
If a car travels 20 km to reach points A to B, what is the distance travelled by car in metres?
Solution: Since 1 km is equal to 1000 m, to convert the 20 km, we need to multiply 20 by 1000.
20 x1000 = 20000 metres.
Example 2
What is the distance in kilometres if the distance travelled is 3 metre?
Solution: The distance travelled is 3 m.
1 km = 1000 m
1 m = 11000 km
31000=0.003 km
The distance travelled is 0.003 km.
Conclusion
This was the complete discussion on the kilometre and metre. We have learnt the kilometre definition in Maths as well as its relation with metres. We have also learnt how to convert the length into metres and kilometres. Students can practise more questions to develop a better understanding of the concept.
FAQs on What Is a Kilometre? Definition, Facts & Conversion in Maths
1. What exactly is a kilometre in Maths?
A kilometre, often abbreviated as km, is a standard unit of length in the metric system used to measure long distances. According to the CBSE/NCERT curriculum, one kilometre is defined as being equal to exactly 1,000 metres. It provides a practical way to express the distance between cities, the length of a river, or the distance covered in a race.
2. What is the basic formula to convert kilometres to metres?
To convert kilometres (km) to metres (m), you multiply the number of kilometres by 1,000. The formula is:
Metres = Kilometres × 1,000.
For example, to find out how many metres are in 5 kilometres, you would calculate 5 × 1,000, which equals 5,000 metres.
3. Can you give some real-world examples of distances measured in kilometres?
Kilometres are used for measuring large-scale distances that would be impractical to measure in metres. Common examples include:
- The distance between two cities, such as the approximately 1,400 km distance between Delhi and Mumbai.
- The total length of a major highway or a river.
- The distance covered during a marathon race, which is officially 42.195 km.
- The altitude of an airplane flying in the sky.
4. How do you convert metres back to kilometres?
To convert metres (m) back to kilometres (km), you do the opposite of converting from kilometres to metres: you divide the number of metres by 1,000. The formula is:
Kilometres = Metres ÷ 1,000.
For instance, if you have a distance of 7,500 metres, you would calculate 7,500 ÷ 1,000 to get 7.5 kilometres.
5. How does a kilometre compare to a centimetre?
A kilometre is significantly larger than a centimetre. There are 100,000 centimetres in just one kilometre. This is because 1 kilometre contains 1,000 metres, and each metre contains 100 centimetres. Therefore, you multiply 1,000 by 100 to establish the relationship. We use centimetres for small items like a pencil and kilometres for vast distances.
6. Why do we need a separate unit like the kilometre instead of just using metres?
Using only metres for very long distances would result in extremely large and impractical numbers. For example, saying the distance between two towns is '50,000 metres' is cumbersome compared to saying it is '50 kilometres'. The kilometre was introduced as part of the metric system to provide a convenient, easy-to-understand unit for expressing these large-scale distances, making calculations and communication much simpler.
7. How can I decide when to use kilometres, metres, or centimetres for measurement?
Choosing the right unit depends on the scale of what you are measuring. A good rule of thumb is:
- Use centimetres (cm) for small objects you can hold or that fit on a desk, like a pen or a book.
- Use metres (m) for larger objects or short distances, like the length of a room, the height of a building, or a 100m sprint.
- Use kilometres (km) for very long distances that you would typically travel by car, bus, or train, such as the distance between cities or the length of a journey.
8. What is the difference between a kilometre and a mile?
A kilometre and a mile are both units for long distances, but they belong to different measurement systems. The kilometre is part of the metric system, used globally, while the mile is from the imperial system, primarily used in countries like the USA. A kilometre is shorter than a mile. Here's the conversion:
- 1 kilometre ≈ 0.62 miles
- 1 mile ≈ 1.61 kilometres
9. What does the prefix 'kilo' mean in the metric system?
The prefix 'kilo-' is a standard part of the metric system and always means 'one thousand' (1,000). This is not exclusive to kilometres. It applies to other units as well, which makes the system very logical and consistent. For instance:
- A kilogram (kg) is 1,000 grams (for mass).
- A kilolitre (kl) is 1,000 litres (for volume).























