




Key Differences Between Proper, Improper, and Mixed Fractions
An Introduction to Types of Fractions
A fraction is defined as a part or portion of any quantity out of a whole, where the whole can be any number, a specific value, or a thing.
Types of fractions are categorised mostly on the basis of their numerator and denominator. A fraction is composed of two parts; these are the numerator and the denominator. The number placed on the top of the fractional bar is known as the numerator and the number placed at the bottom is known as the denominator. The numerator shows the number of parts that are being considered while the denominator indicates the total number of parts in the whole.
Types of Fractions with Examples
There are many types of fractions but the three main types of fractions which are differentiated on the basis of the numerator and the denominator are given below.
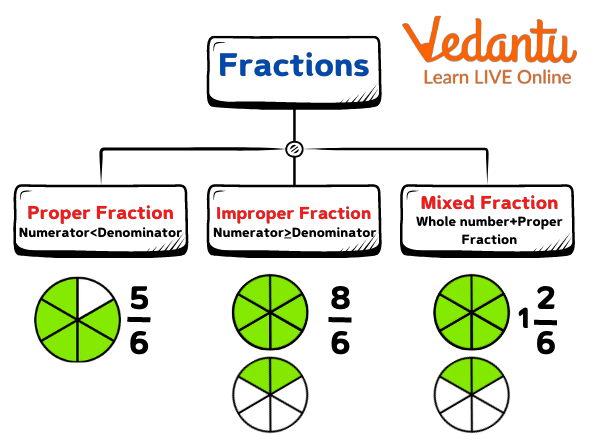
Proper fractions
Improper fractions
Mixed fractions
Let’s understand each type of fraction in detail.
1. Proper Fractions
A proper fraction is defined as a fraction whose numerator is less than its denominator. The examples of the proper fractions are $\frac{4}{7}$ and $\frac{8}{15}$ because 4 < 7 and 8 < 15. Example: Rohan took a stick and he broke it into 3 equal parts. He took 1 part and gave 2 parts to his friend. We can represent Rohan's portion as 1/3 and his friend’s portion as 2/3. Both of these fractions are proper fractions here.
2. Improper Fractions
An improper fraction is defined as a fraction whose numerator is greater than or equal to its denominator.
For example, $\frac{7}{2}$ and $\frac{8}{15}$ are improper fractions because 7 > 2 and 19>7.
3. Mixed Fractions
A mixed fraction is a combination of a whole number and a proper fraction. For example, $1\frac{4}{9}$ and $2\frac{4}{17}$ are mixed numbers or mixed fractions. In the first example, 1 is the whole number part and $\frac{4}{9}$ is the proper fraction. In the second example, 2 is the whole number part and $1\frac{4}{17}$ is the proper fraction.
Group of Fractions
There are some types of fractions that are classified into groups. Groups of fractions are helpful in comparing fractions. These are as follows.
Like fractions
Unlike fractions
Equivalent fractions
1. Like Fractions
In like fractions, the denominators of two or more fractions are the same. For example $\frac{1}{8}$, $\frac{3}{8}$, $\frac{7}{8}$, $\frac{19}{8}$ are like fractions. Mathematical operations such as addition and subtraction can be easily performed on like fractions.
2. Unlike Fractions
In unlike fractions, the denominators of two or more fractions are different. For example $\frac{2}{7}$, $\frac{1}{3}$, $\frac{5}{7}$, $\frac{1}{6}$ etc. In order to perform mathematical operations in unlike fractions we may convert them into like fractions.
3.Equivalent Fractions
When equivalent fractions are simplified or reduced they give the same value while these fractions have different numerators and different denominators. For example, $\frac{12}{24}$, $\frac{6}{12}$, $\frac{4}{8}$ are all equivalent fractions because they all get reduced to $\frac{1}{2}$.
Important Points
Some important points related to the different types of fractions are given below.
A mixed fraction is a fraction which is the combination of a fraction and a whole number. The conversion of a mixed fraction can be converted into an improper fraction and vice versa. For example, $3\frac{1}{4}=\frac{3х4+1}{4}=\frac{13}{4}$
In an improper fraction, we know that the value of a numerator is greater than or equal to its denominator. So its value will always be greater than unity.
In a proper fraction, the numerator is less than its denominator so its value is always less than unity.
Do You Know?
Units fractions are those fractions where the value of the numerator is 1 and the denominator is a positive integer. For example,$\frac{1}{3}$, $\frac{1}{8}$, $\frac{1}{19}$, $\frac{1}{23}$ and so on are known as unit fractions.
Conclusion
Fraction and its types are important and basic concepts of mathematics. In this article, we have learnt about how many types of fractions are there with examples, such as proper and improper fractions, mixed fractions, equivalent fractions, like and unlike fractions.
FAQs on How Many Types of Fractions Are There?
1. How many types of fractions are there in mathematics?
There are three main types of fractions in mathematics:
- proper fractions
- improper fractions
- mixed fractions
2. What is a proper fraction?
A proper fraction is a type of fraction where the numerator is less than the denominator. For example, $\frac{3}{5}$ is proper because 3 is less than 5. Proper fractions always have a value less than one.
3. What is an improper fraction?
An improper fraction occurs when the numerator is equal to or greater than the denominator. For example, $\frac{7}{4}$ is improper because 7 is more than 4. Improper fractions represent numbers that are one or greater.
4. What is a mixed fraction?
A mixed fraction combines a whole number and a proper fraction, like $2\frac{1}{3}$. It is used to represent quantities that are greater than one but not whole, making it common in measuring and cooking.
5. Are there other types of fractions besides proper, improper, and mixed?
Yes, besides the main three, fractions can also be described as like fractions (same denominators), unlike fractions (different denominators), and unit fractions (numerator is 1). This helps when comparing or adding fractions in math problems.
6. What are like and unlike fractions?
In like fractions, the denominators are the same, while in unlike fractions, the denominators differ. For example, $\frac{2}{7}$ and $\frac{5}{7}$ are like fractions, while $\frac{2}{7}$ and $\frac{3}{8}$ are unlike fractions. Understanding this helps with fraction operations.
7. What is a unit fraction?
A unit fraction is any fraction with numerator 1 and a positive integer as denominator, like $\frac{1}{6}$. Unit fractions are the simplest form of fractions and are important as building blocks in fraction understanding and problem solving.
8. Can fractions be classified based on their denominators?
Yes, fractions are often categorized as like or unlike fractions based on their denominators. When adding or comparing, like fractions are simpler since their denominators match, while unlike fractions require finding a common denominator for calculations.
9. Do fractions always have a whole number numerator and denominator?
Yes, in standard fractions the numerator and denominator are both whole numbers, with the denominator never zero. This basic rule helps keep operations with fractions consistent and prevents mathematical errors like division by zero.
10. Why are there different types of fractions?
There are different types of fractions to represent various relationships between numbers.
- Proper fractions
- improper fractions
- mixed fractions
11. How do you know which type of fraction you have?
To identify the type of fraction:
- Compare numerator and denominator.
- If numerator is less, it’s proper.
- If numerator equals or exceeds denominator, it’s improper.
- If there’s a whole number and fraction together, it’s mixed.























