




Essential Map Symbols: Meaning, Examples & Practical Tips
Reading maps using symbols is an essential part of the map. It provides a lot of information in a limited space. Map symbols are easy to draw and read even if you can't ask someone for directions because you don't know the local language. You may use symbols to collect information from maps.
What are Symbols?
A symbol is a shape or object used to represent something else. Symbols are often used to refer to different things in different situations. Different symbols and colors are used on maps to mark important places such as hospitals, train stations, and schools.

Symbols Used on a Map
What are Maps?
A map is a pictorial representation of all or part of an area, usually displayed on a flat surface. A map is an image that provides information about a place. For example, a map of bedrooms might show where beds, dressing tables, and wardrobes are located. A map of a city or region shows streets, highways, schools, or places of interest.
Maps are very useful and important to us. They help us navigate different places and give us directions to different places with the help of directions symbols present on the maps.
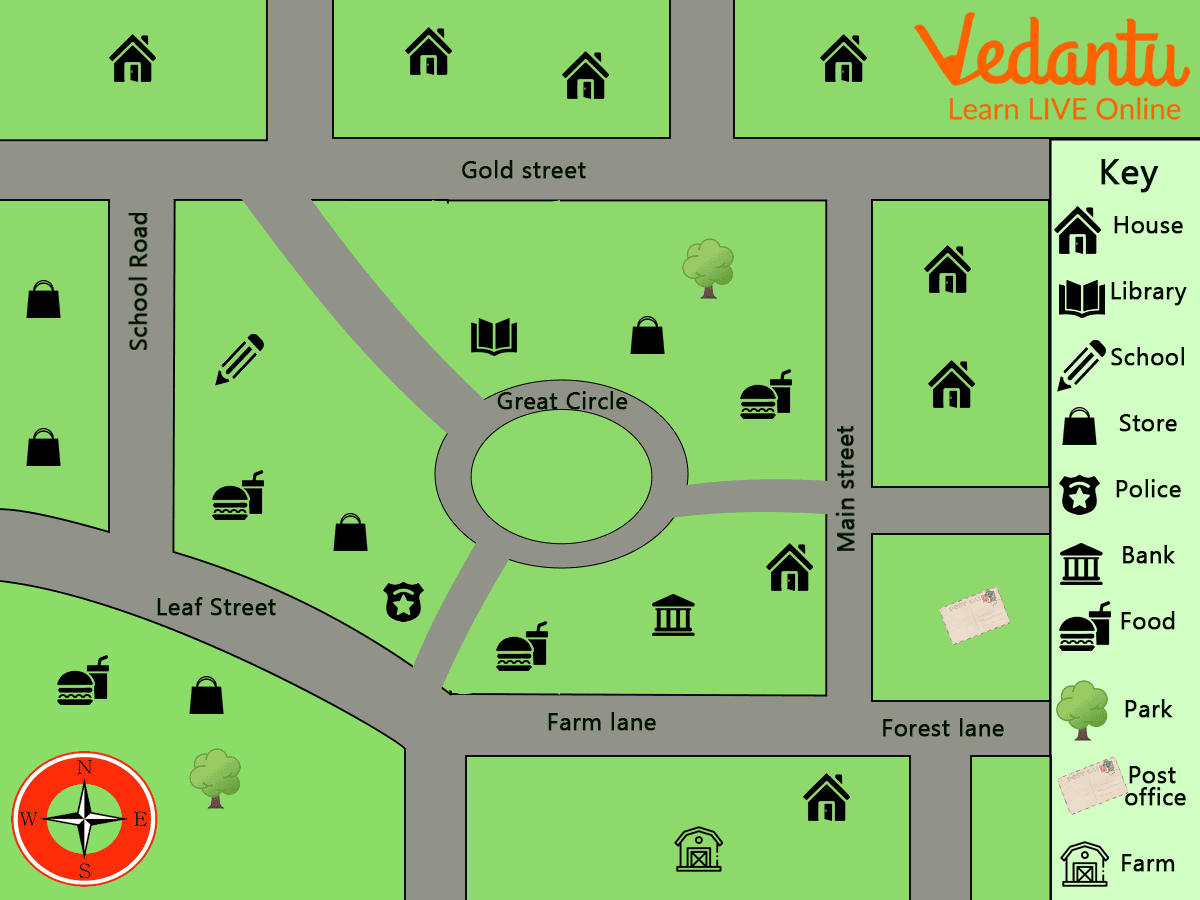
Map of a Community
Map Reading
Reading a map is the process of looking at a map to see what is being displayed and how the cartographer(a person who draws or makes maps) described the map. This includes identifying the objects or phenomena depicted, the symbols and labels used, and information about the map that may not appear on the map.
Map Reading
How do Symbols Help in Reading Maps?
Maps are easy to draw with symbols and are easy to understand without asking anyone for directions as we don't know the language of the area. Symbols are made up of individual points, lines, or shaded areas on the map. They have size, shape, and (usually) color. Map symbols collectively represent details that lead to shape, relative location, distribution, and structure.
The best way to read a map or directions is to use symbols. You can use symbols such as lines, shapes, shades, or colors to easily find specific landmarks or directions. Buildings, roads, rivers, bridges, trees, railroads, and many other elements make it impossible to draw a map in real shape and size. So we use specific symbols, shades, colors, images, etc. to display the map line. This symbol provides a lot of information and helps to read the card.
Summary
We have learnt about maps, their types, the symbols used on a map and how these symbols can help us to find directions. Map reading is an exercise which can help us in many ways. When you grow up and learn to drive, this reading will help you locate many places across the world. You can practice what you learnt till now with the help of a worksheet given at the end of this article.
Map Symbols Worksheet
Use Maps and answer the questions
1. Answer the following using the given maps.
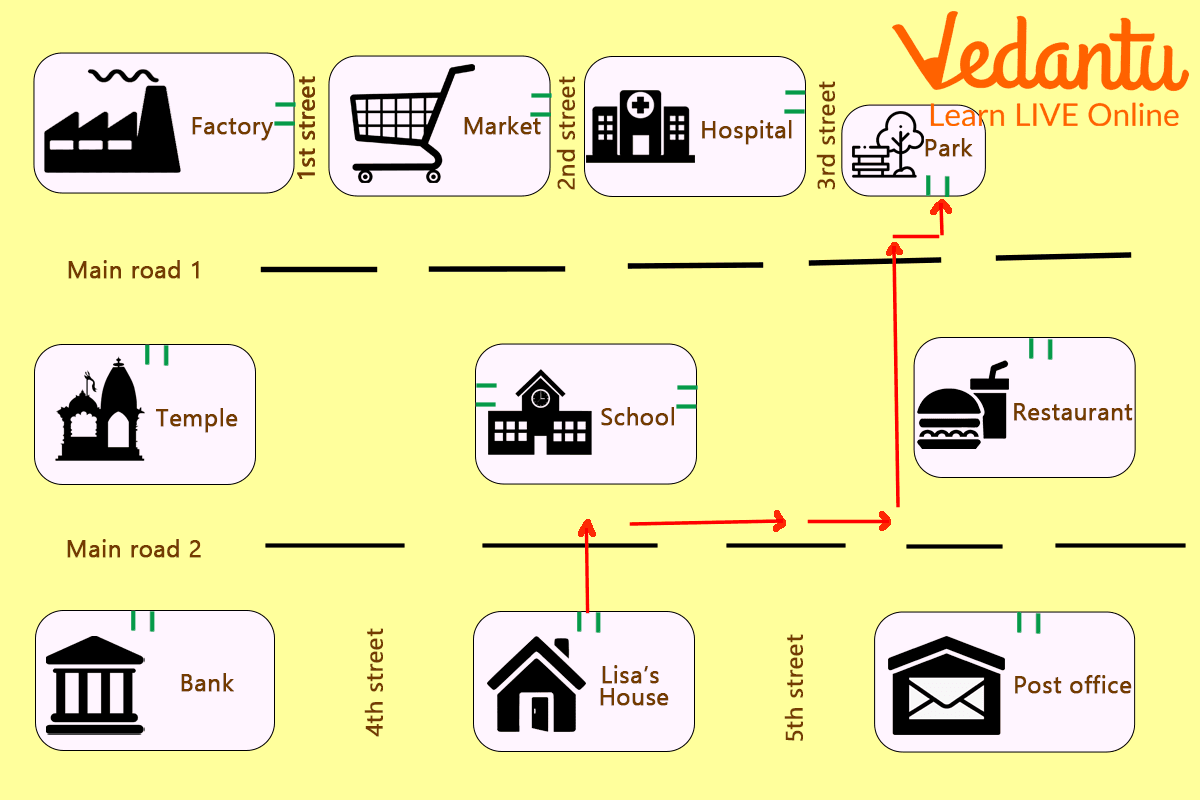
Directions on a Map
(i) In which direction a hospital is situated?
(ii) What is situated between 1st and 2nd street?
(iii) How to reach the restaurant from main road 2?
(iv) By what symbol hospital is represented?
Answers:
(i) Hospital situated right to 2nd street.
(ii) Market lies between 1st and 2nd street.
(iii) More straight on main road 2 then reaching in front of 3rd street turn right to reach the restaurant.
(iv) Hospital is represented by a plus(+) symbol.
FAQs on How Do Symbols Help in Reading Maps?
1. What is the use of symbols in a map?
The use of symbols in a map is to visually represent different features or elements such as landmarks, roads, rivers, and cities. By using easily understood map symbols, readers can quickly identify important geographical information without lengthy descriptions. These symbols enable efficient communication of data, making it simple for students and learners to interpret maps—a skill emphasized throughout Vedantu’s interactive geography sessions.
2. What do symbols on a map help people to do when reading a map?
Symbols on a map help people to identify and locate various features swiftly, making maps more comprehensible. They act as a visual shorthand for physical and cultural elements such as mountains, schools, hospitals, and roads. In Vedantu’s education programs, learning how to interpret these symbols sharpens students’ map-reading abilities and supports their overall geographical understanding.
3. How do signs and symbols help the reader?
Signs and symbols serve as essential tools for readers by:
- Simplifying complex information into easily recognizable images
- Guiding navigation across different regions and terrains
- Reducing language barriers, since symbols are universally understood
4. What is the use of symbols to present information on a map?
The use of symbols to present information on a map allows cartographers to convey vast amounts of data in a compact and visually appealing format. For instance, a tree symbol may represent a forest, while a blue line may indicate a river. Vedantu’s live classes teach students how to interpret these symbols, promoting spatial awareness and data analysis skills essential for academic success in geography.
5. How can students learn to interpret map symbols effectively?
Students can learn to interpret map symbols effectively by:
- Referring to the map legend or key, which explains the meaning of each symbol
- Practicing with various types of maps
- Engaging in guided exercises and quizzes offered by Vedantu
6. Why is understanding map symbols essential for geography students?
Understanding map symbols is vital because it enables geography students to:
- Interpret information quickly and accurately
- Compare different locations or regions
- Develop strong spatial thinking and analytical abilities
7. What are some common map symbols used in educational resources?
Some common map symbols used in educational maps include:
- A star or dot for capitals and cities
- Wavy blue lines for rivers
- Triangles for mountains or peaks
- Parallel lines for railway tracks
8. How do map legends support accurate map reading?
A map legend (or key) explains the meaning of each symbol used on a map. By consulting the legend, learners accurately interpret symbols and make sense of the geographic data presented. Vedantu educators always guide students to read the legend first, reinforcing this essential technique for map reading proficiency.
9. Can students create their own map symbols for school projects?
Yes, students are often encouraged to create their own map symbols during school projects or assignments. This creative process, supported by Vedantu’s project-based learning approach, helps students understand symbol design, enhance visualization skills, and tailor maps for specific themes or purposes.























