




How to Calculate Cross Sectional Area with Step-by-Step Examples
In Geometry, a cross-section is a shape formed by intersecting a solid with a plane. A cross-sectional area is formed when we cut the solid object in a way that changes or takes the shape of a 2D figure, making it easier to calculate the formula. In Geometry and Physics, a cross-section is the non-empty intersection of a solid body in three-dimensional space with a plane or the equivalent in higher-dimensional environments.
What is the Area of Cross-Section?
To know about the area of cross-section let us understand it with an example. If we have a solid object like a sphere and have to find its area of cross-section then we need to cut it into two symmetrical halves. We can see that the new two-dimensional part of the sphere is like a circle. Now we can apply the formula of the area of the circle which would be the same as the area of the cross-section of the sphere.
When we cut a three-dimensional object in such a way that it becomes a two-dimensional object. This new area formed is the area of the cross-section of the given object.
The Cross-Sectional Area of Different Shapes
The Cross-Sectional Area of the Cylinder
A cylinder's cross-section will be equal to the area of the circle. Let us understand it in a simple way. Consider a circular item, such as a pipe, and cut it in a perpendicular slice to its length as shown in the picture. A thin cross-sectional slice of a cylinder is a circle. Hence the cylinder's cross-section area formula is the same as the formula for the area of a circle.
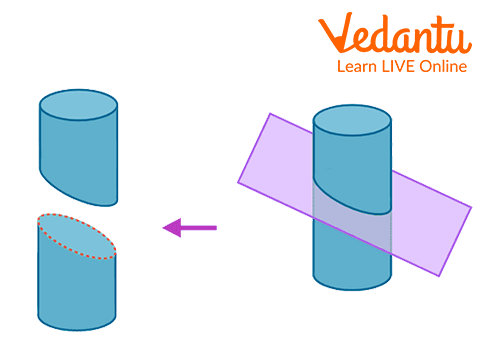
A Cross-Section of The Cylinder
The cross-section area of a cylinder is calculated by \[\pi {r^2}\] . The cross-sectional area of the rod formula is the same as that of the cylinder.
Let us understand this by an example. Determine the cross-section area of a cylinder having a radius of 2 cm and a height of 10 cm.
Thus, Radius = 2cm
The cross-sectional area formula of cylinder is \[\pi {r^2}\]
\[\begin{array}{l}area = 3.14 \times {2^2}\\ = 12.56c{m^2}\end{array}\]
The Cross-Sectional Area of Rectangle
The volume of any rectangular solid, including a cuboid, is equal to the area of its base multiplied by its height: \[V = l \times w \times h\].
As a result, if a cross-section is parallel to the top or bottom of the solid, its area is \[l \times w\] as there isn't any height needed so we do not need to use height in the formula. If the cutting plane is perpendicular to one of the two sets of sides, the cross-sectional area is given by \[l \times h\] or \[w \times h\]. Let us solve an example to better understand it.
Determine the cross-sectional area of the plane perpendicular to the base of the \[27{m^3}\] cube.
As \[l = w = h\], the cube must be 3m long.
The cross-sectional area of the square of 3m is \[9{m^2}\].
The Cross-Sectional Area of Cone
A cone is a pyramid with a circular cross-section. Depending on the connection between the plane and the slant surface, the cross-section, often called a conic section (for a cone), could be a circle, a parabola, an ellipse, or a hyperbola.
How to Calculate Cross-Sectional Area?
The area of the cross-section can be calculated using the area of the cross-section formula of different shapes and figures. In the question, you would be given the data like length, height, radius, or diameter of the shape from which you can calculate the area of the cross-section. There are different cross-sectional area formulas that you need to use carefully according to the shape mentioned in the questions.
Uses of Cross-Sectional Area
The cross-section of a series of water pipes determines the speed and pressure at which the water goes through the pipe.
When constructing hydroelectric dams - notably penstocks - for hydroelectric power generation, the cross-sectional area of pipes must be considered.
Changes in a pipe's cross-sectional area can be used to calculate how other factors, such as water pressure and speed, must change to account for the pipe change.
Sample Questions
1. Consider a 6-meter-high cylinder with a radius of 3 meters. What will the cylinder's cross-sectional area be?
a. 27.43-meter sq
b. 63.75-meter sq
c. 748-meter sq
d. 28.27- meter sq
Ans. 28.27-meter sq
Explanation: The cross-section formula of cylinder is \[\pi {r^2}\]
So, \[\begin{array}{l}\pi {r^2} = 3.14 \times {(3)^2}\\ = 28.27\end{array}\]
The area of a cylinder is 28.27meter sq.
2. A plane is abruptly inserted through the Earth at the North Pole, removing a 10 m chunk of the globe. What is the cross-sectional area of this icy sliver of the planet?
a. 8.64
b. 46.64
c. 9.43
d. 7.96
Ans: 7.96
Explanation: Circumference \[2\pi r = 10\]m
\[r = \frac{{10}}{{2\pi }} = 1.59\]
\[\begin{array}{l}Area = \pi {r^2}\\ = 3.14 \times {1.59^2}\\ = 7.96{m^2}\end{array}\]
3. Determine the cross-sectional area of a plane perpendicular to the cube's base with a volume of \[64{m^3}\]
a. 9 unit
b. 23 unit
c. 56 unit
d. 16 unit
Ans: 16 units
Explanation: Volume of the cube \[ = sid{e^3}\]
The volume of the cube given is \[64{m^3}\]
Side of the cube \[ = 4cm\]
Area of cube \[\begin{array}{l}area = sid{e^2}\\ = {4^2}\\ =16\\\end{array}\]
Conclusion
A three-dimensional solid object when changed into two dimensional can be used to take the cross-sectional area of the object. When a solid object is cut through a surface this new surface is taken into consideration when calculating the cross-sectional area. The area of an object is taken when an object is present at a place whereas, the cross-sectional area is taken when the 3D object is cut perpendicularly.
FAQs on Cross Sectional Area: Concepts & Solutions
1. What is the cross-sectional area?
Cross-sectional area refers to the area of a specific section cut across an object, typically perpendicular to its length. In mathematics and physics, it is a key measurement used to determine properties such as strength, flow rate, and resistance in various fields. For example, the cross-sectional area of a cylinder can be found by slicing it perpendicular to its axis and measuring the area of the resulting circle. This concept is widely used in engineering, science classes, and competitive exams, and is often explained with clear examples in Vedantu’s online math sessions.
2. How to calculate for cross-sectional area?
To calculate the cross-sectional area, identify the shape of the section you are measuring. The formula depends on the shape:
- Rectangle: Area = width × height ($A = w \times h$)
- Circle: Area = $\pi r^2$
- Triangle: Area = $\frac{1}{2} \times$ base $\times$ height
3. How to identify cross-sectional area?
To identify the cross-sectional area, visualize cutting the object perpendicular to its longest dimension (axis or flow direction). The exposed face of this slice is the cross section. Then, determine the geometric shape of this face (such as circle, square, rectangle, etc.), so you can apply the appropriate area formula. Vedantu’s expert educators often use diagrams and real-life objects during online sessions to help students understand and recognize cross sections more easily.
4. What is an example of cross-sectional area?
An example of cross-sectional area is the area of the circular face at the end of a cylindrical pipe. If a pipe has a radius of $5$ cm, the cross-sectional area, $A$, is calculated as $A = \pi r^2 = \pi \times 5^2 = 78.54$ cm$^2$ (approx). Vedantu provides many such practical examples and practice questions to reinforce this concept for students at all academic levels.
5. What are common shapes for cross-sectional area calculations?
The most common shapes used in cross-sectional area calculations include:
- Circle (e.g., pipes, wires)
- Rectangle (e.g., beams, rods)
- Square (a special case of rectangle)
- Triangle (e.g., structural supports)
6. Why is cross-sectional area important in physics and engineering?
Cross-sectional area is crucial because it affects the strength, flow, and other physical properties of objects. For example:
- In physics, it determines the amount of force an object can withstand or the rate of flow through a pipe.
- In engineering, structural elements are designed based on required cross-sectional areas for safety and efficiency.
7. How is cross-sectional area related to volume calculation?
The cross-sectional area is directly related to the volume of a prism or cylinder. The formula for the volume of such objects is:
$$\text{Volume} = \text{Cross-sectional Area} \times \text{Length (or Height)}$$
This principle is frequently demonstrated in Vedantu’s online classes using diagrams and real-life examples to reinforce conceptual understanding.
8. What units are used for measuring cross-sectional area?
Cross-sectional area is measured in square units (such as m$^2$, cm$^2$, mm$^2$). The specific unit depends on the size of the object and the measurement system used (SI or metric). Vedantu instructors trains students to always include the correct units in their answers to ensure accuracy in exams and assignments.
9. How do you find the cross-sectional area of irregular shapes?
For irregular shapes, the cross-sectional area can be found by:
- Dividing the shape into simpler geometric sections, calculating their areas, and summing them up.
- Using graph paper to estimate the area by counting the squares covered.
10. Can cross-sectional area affect current in an electrical wire?
Yes, the cross-sectional area of an electrical wire determines the maximum current it can safely carry. According to the formula $R = \rho \frac{L}{A}$, where $R$ is resistance, $\rho$ is resistivity, $L$ is length, and $A$ is cross-sectional area, a larger area lowers resistance and allows more current. Vedantu’s physics courses explain this relationship in detail, helping students relate mathematical principles to practical electrical scenarios.























