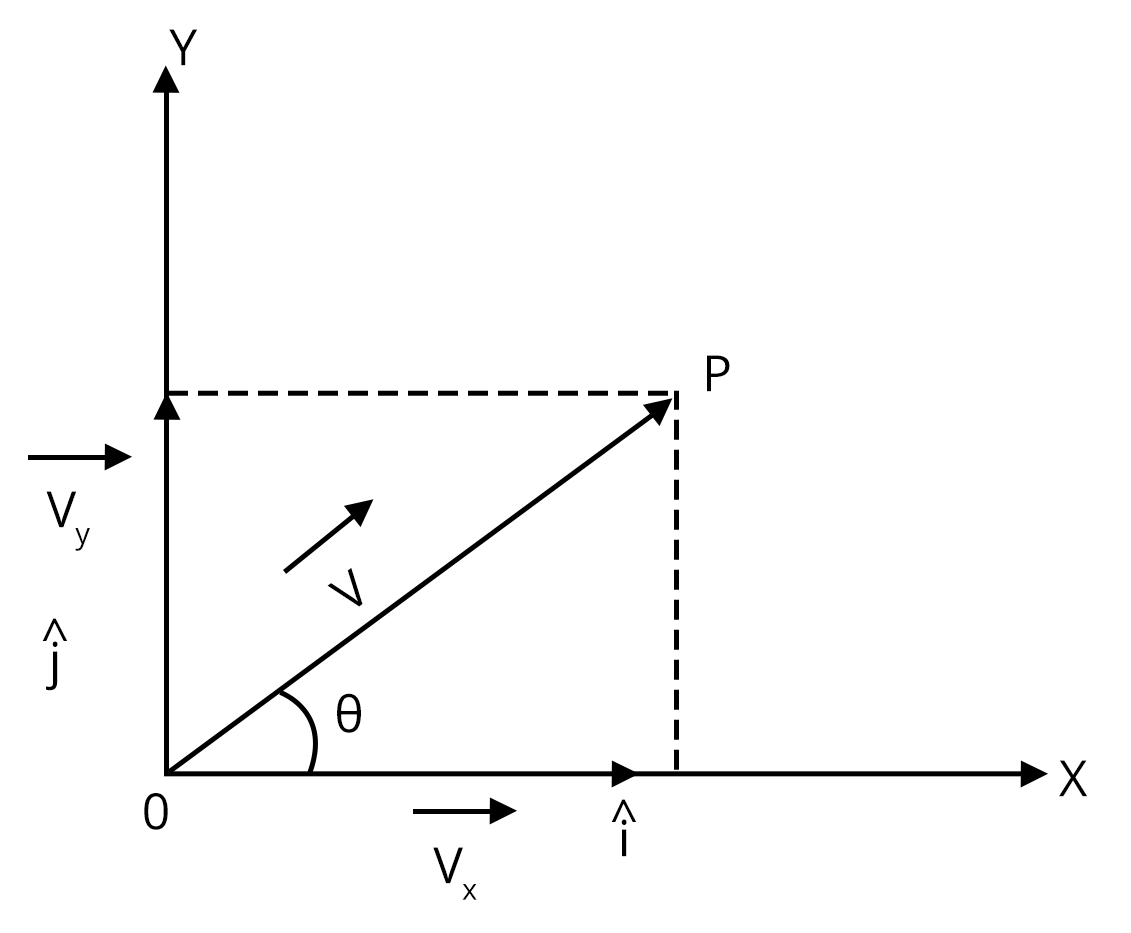
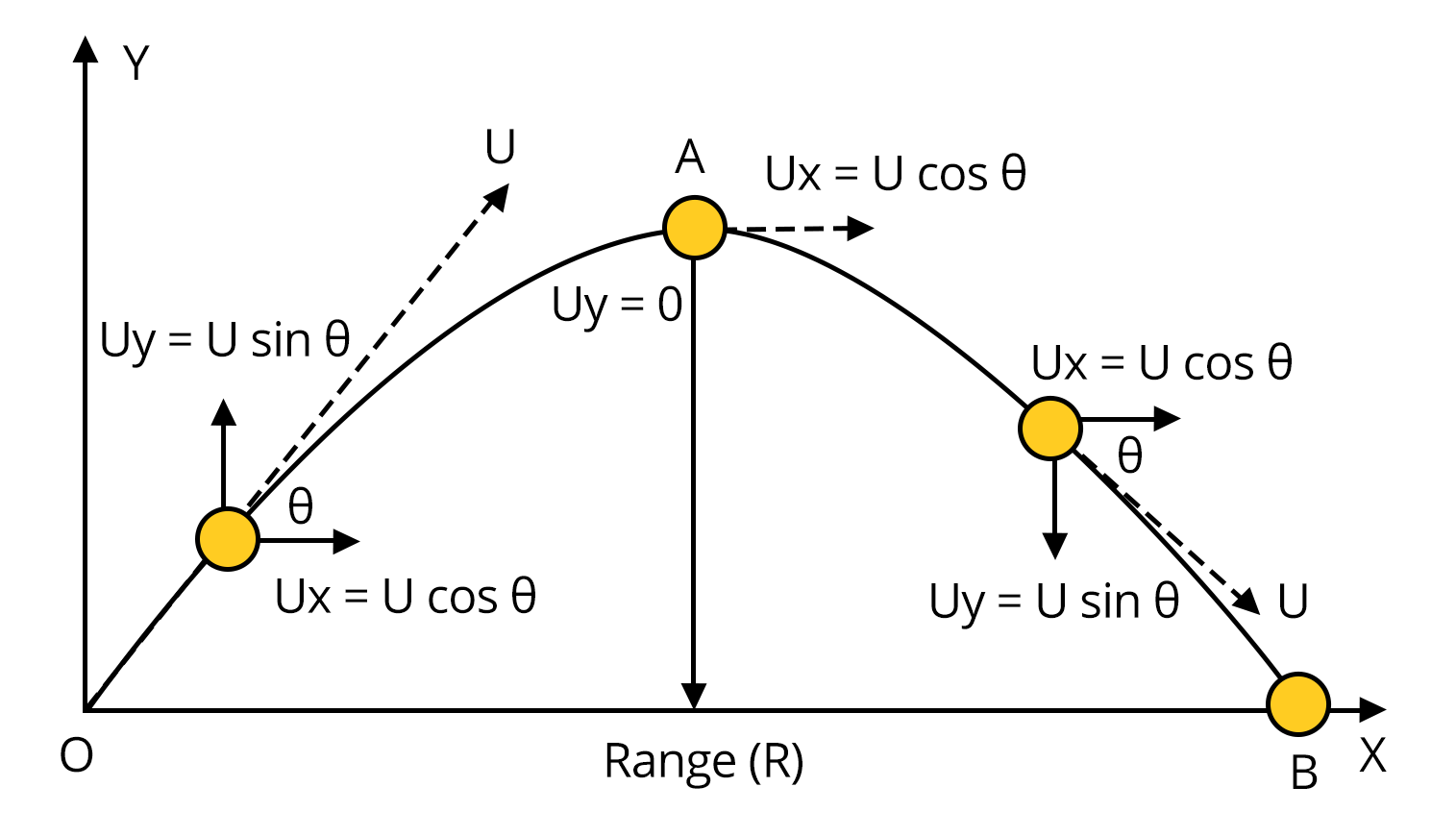
Essential Kinematics Formulas, Graphs, and Example Problems for Exams
FAQs on Kinematics Revision Notes for JEE Main: Formulae & Key Concepts
1. What is kinematics in physics?
Kinematics in physics is the study of the motion of objects without considering the forces that cause the motion. It includes key concepts such as displacement, velocity, acceleration, and equations of motion. Main features of kinematics are:
- Describes one-dimensional, two-dimensional, and three-dimensional motion.
- Focuses on position, speed, and acceleration as a function of time.
- Does not deal with the forces or masses that affect the motion (which is covered in dynamics).
2. How do I revise kinematics for JEE Main efficiently?
To revise kinematics for JEE Main efficiently, focus on understanding core concepts and practicing as many numerical problems as possible. A successful strategy includes:
- Reviewing all key formulas and equations of motion regularly.
- Solving step-by-step worked examples for conceptual clarity.
- Practicing past year JEE Main questions and MCQs.
- Using revision notes and formula sheets for quick memorisation.
- Clarifying doubts regarding kinematics graphs and real-life applications.
3. What are the three equations of motion in kinematics?
The three equations of motion relate displacement (s), initial velocity (u), final velocity (v), acceleration (a), and time (t) for uniformly accelerated motion:
- v = u + at
- s = ut + (1/2)at²
- v² = u² + 2as
4. Is kinematics difficult for class 11 students?
Kinematics can seem challenging initially due to its use of equations and graphical analysis, but becomes easier with focused practice. Key points for students:
- Conceptual clarity is more important than rote memorisation.
- Practice with plenty of numericals and diagram-based questions.
- Kinematics forms the base for other topics like dynamics and projectile motion.
- Referring to concise revision notes and solved examples helps boost confidence.
5. Where is kinematics applied in real life?
Kinematics has several practical real-life applications, including:
- Analyzing the motion of vehicles on roads (cars, trains, airplanes).
- Studying trajectories in sports (ball throw, cricket, basketball).
- Understanding the motion of projectiles and satellites.
- Designing roller coasters and amusement park rides.
- Calculating travel time and speed for logistics and travel planning.
6. Can I download free kinematics revision notes PDF?
Yes, you can download free kinematics revision notes PDF from trusted educational platforms. These revision notes usually include:
- Key concepts and formula sheets.
- Stepwise solved examples and shortcut tips.
- Important practice questions and common mistakes to avoid.
7. How do you solve kinematics numericals stepwise?
To solve kinematics numericals stepwise, follow these simple steps:
- Identify what quantities are given (initial velocity, final velocity, displacement, acceleration, time).
- Write down the appropriate equation of motion that connects these variables.
- Substitute the known values and solve for the unknown variable.
- Ensure correct units are used throughout the calculation.
- Check if the obtained answer is reasonable and matches the context.
8. Why do students often confuse displacement with distance in kinematics?
Students frequently confuse displacement and distance because both describe movement, but differ fundamentally:
- Distance is the total length of the path travelled, regardless of direction.
- Displacement measures the straight-line change in position from the initial to the final point, including direction.
- For a round trip, distance can be large but displacement may be zero.
9. What common mistakes should I avoid while solving kinematics numericals?
When solving kinematics numericals, students should avoid these common mistakes:
- Confusing velocity with speed.
- Ignoring units or mismatching SI and CGS systems.
- Applying the wrong equation for the situation (use correct equations for uniform or non-uniform acceleration).
- Not considering direction (a negative sign can indicate a change in direction).
- Overlooking initial conditions or missing given data.
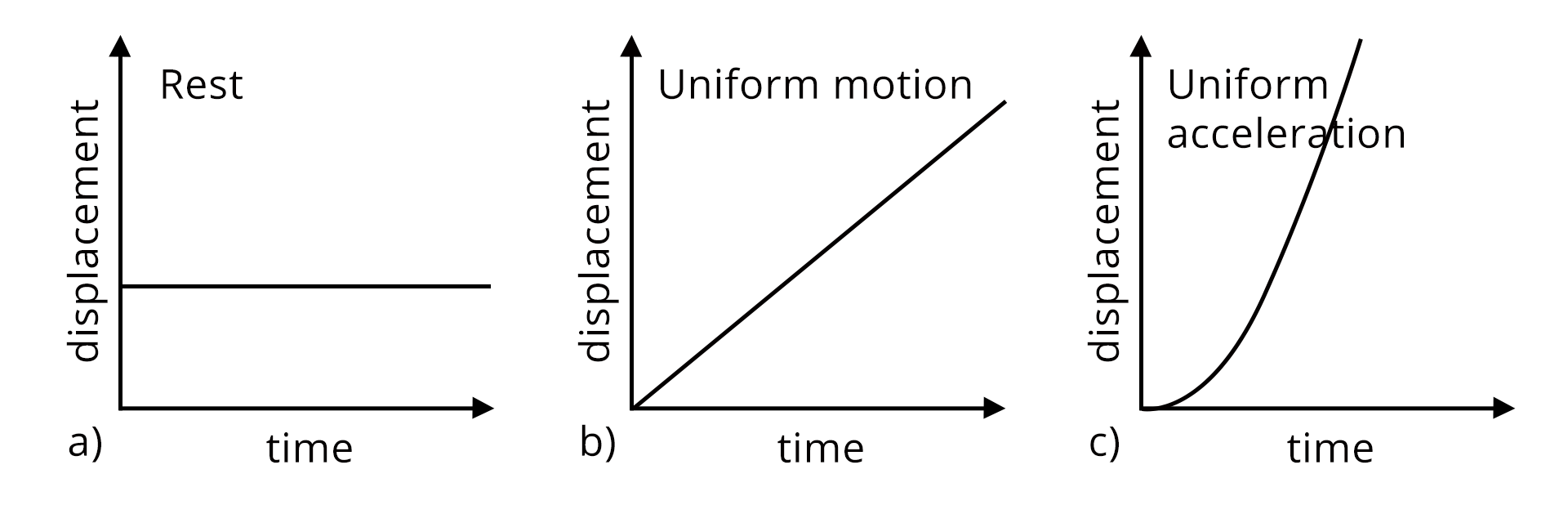
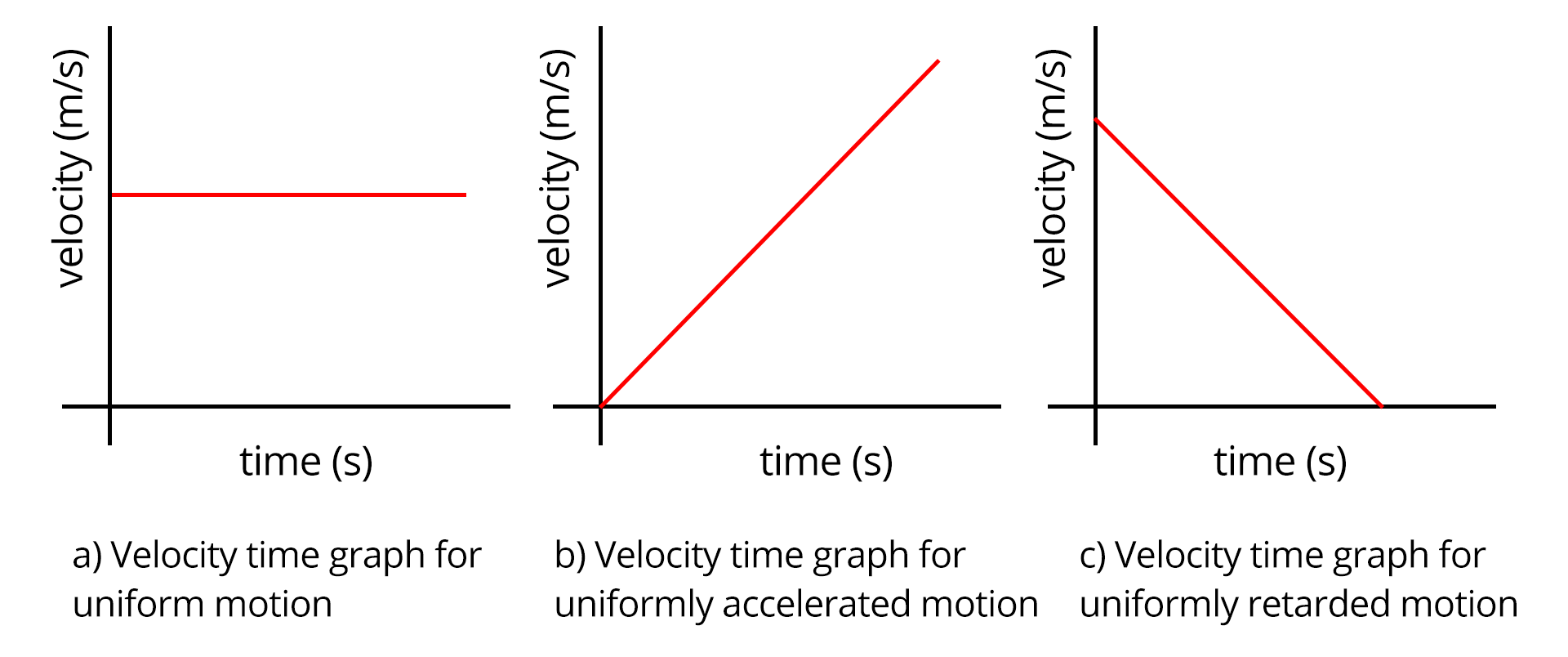
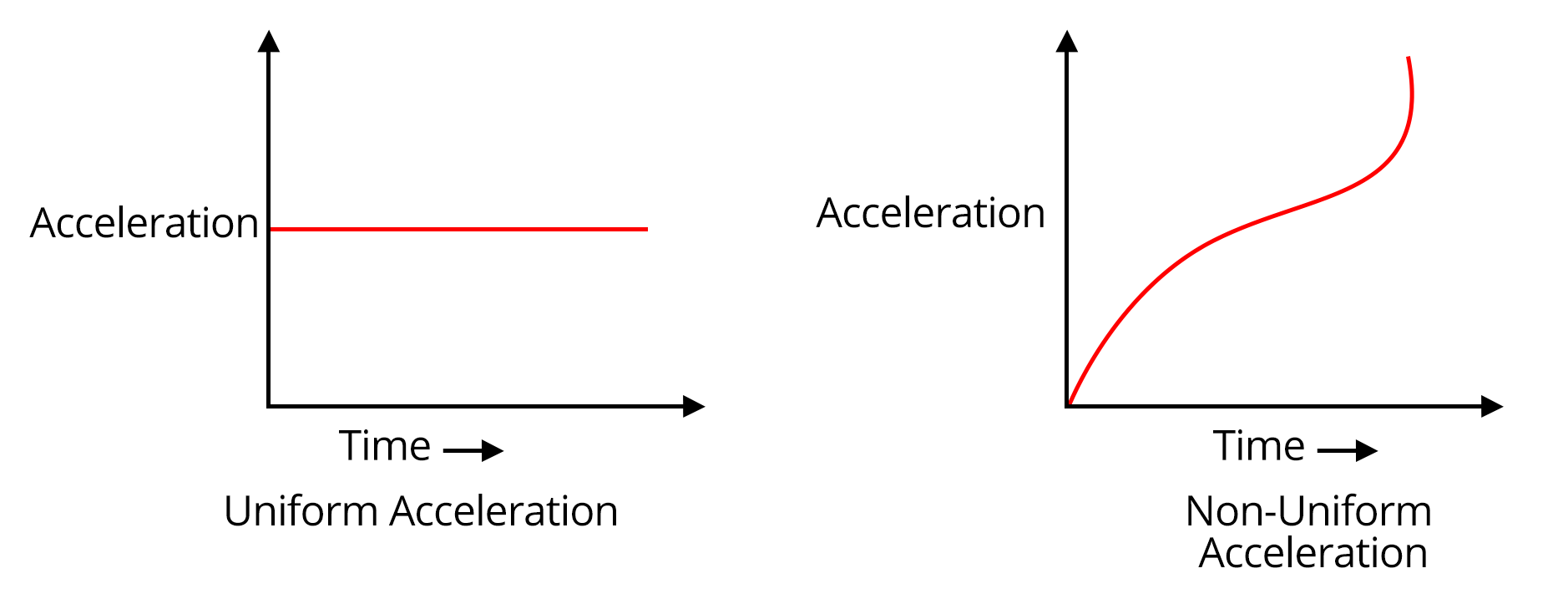
10. Are kinematics graphs important for scoring in JEE/NEET?
Kinematics graphs are very important for scoring in JEE and NEET as they often appear in questions on interpretation and analysis. Main reasons include:
- They test understanding of position-time, velocity-time, and acceleration-time relationships.
- Graph-based questions quickly assess your conceptual clarity.
- Mastery helps avoid traps in multiple-choice and assertion-reasoning questions.