




Introduction
An AC motor is a piece of electrical equipment that turns alternating current into mechanical movement. AC motor uses range from converting large amounts of electrical power to mechanical power in factories to small amounts of power in homes. AC motors can be either single-phase or three-phase. Three-phase motors are mainly used to convert large amounts of power. Synchronous and induction are the two kinds of AC motors. In this article, let's briefly discuss what an AC motor is and how it works.
What is an AC Motor?
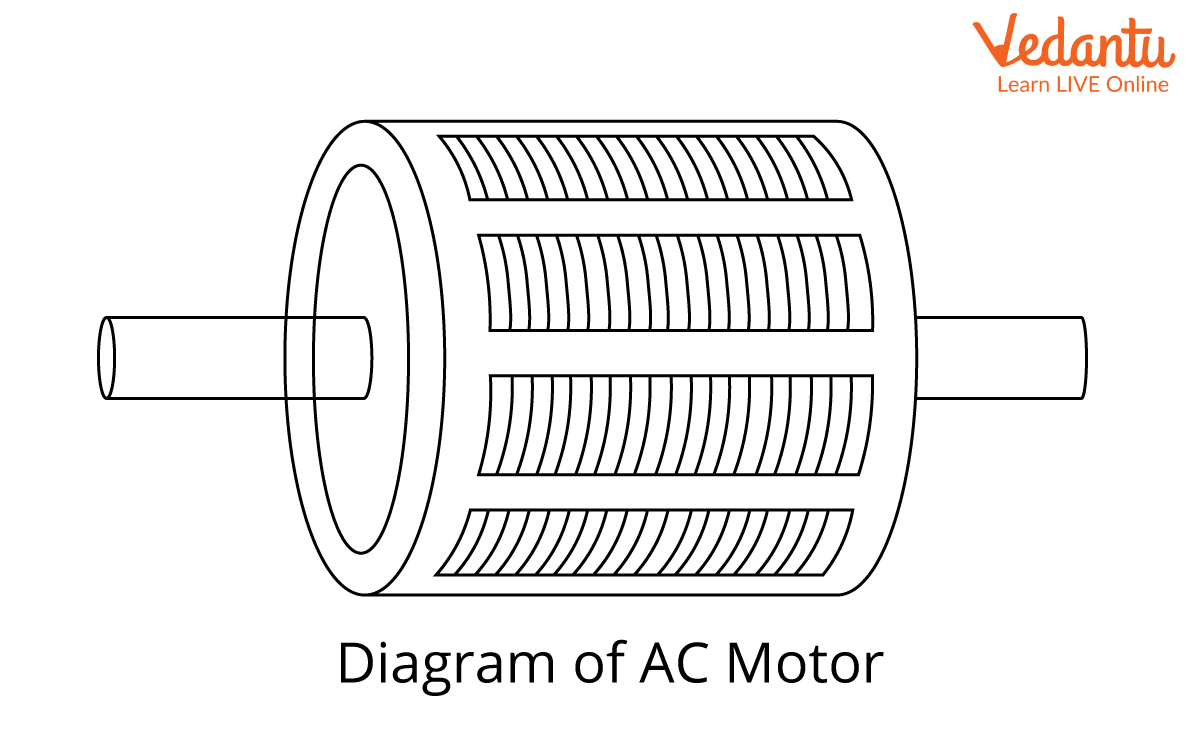
AC Motor
A motor that turns alternating current (AC) into mechanical power is called an AC motor. The stator and the rotor are both essential parts of an AC motor. The amount of the motor that doesn't move is called the stator. The part that moves is called the rotor. AC motors can have either one phase or three phases. In 1887, Nikola Tesla came up with the first AC induction motor.
How Do AC Motors Work?
AC motor is a term for several types of motors, such as single-phase, three-phase, brake, synchronous, asynchronous, customized, two-speed, and three-speed single-phase. The difference between the different types is based on the work that needs to be done. For example, some AC motors are simple and used for small jobs, while others are made for more significant, challenging assignments.
One big difference is that the phase of the electrical feed is different for homes and factories.
Single or double-phased electricity is used in homes, while three-phased electricity is used in factories. This difference makes an industrial AC motor different from a residential one. AC motors are called "induction motors" because the torque they make comes from the electromagnetic induction of the magnetic field of the stator.
Uses of AC Motors
AC motors can be used for many things, from running appliances to powering significant machinery.
Their low cost and high efficiency make them useful in many situations.
AC motors are the main part of any situation where electric motors are needed.
AC motors are stronger than other engines because and ac motors are used in industries as they can use strong currents to make more torque.
They come in many different shapes, sizes, and power levels to meet the needs of any industry.
Application of AC Motor
Here are some uses for AC motors:
AC motors are used in home appliances like water pumps, drills, and other tools.
AC motors are also used in refrigerators, washing machines, grinders, and other household items.
AC motors are also used in compressors and other industrial areas.
Electric cars also use AC motors.
AC motors are used in many real-world situations because they are simple and last a long time.
The Different Types of AC Motor
The Types of Motor
The different kinds of AC motors are explained in detail below. Based on how they work, AC motors can be put into the following categories:
Synchronized Motor- A synchronous motor is a motor that runs at the same speed as another motor. Synchronous speed is the constant speed at which the motor creates electromotive force. When an electromagnet is in a rotating magnetic field, it magnetically locks onto the field and turns at the same speed as the field.
Induction Motor- The most common type of motor is an induction motor. Induction motors are also called asynchronous motors because they always run slower than synchronous.
Conclusion
AC motors use alternating current and magnetism to create mechanical energy. The main benefit of an AC motor is that it can keep putting out the same amount of torque up to the speed it is rated for. The main parts of an AC motor are the stator, the outer drum that stays still, and the rotor, which is the inner part that spins and is attached to the shaft of the motor.
AC motors are used in various industrial settings because they are strong, flexible, durable, and easy to maintain due to their simple design.
FAQs on Uses of AC Motors
1. Where can we find AC motors used in our homes and daily life?
AC motors are extremely common in household appliances because they are reliable and efficient. You can find them in:
- Refrigerators and Air Conditioners: To run the compressors.
- Washing Machines: To spin the drum.
- Ceiling Fans and Table Fans: To rotate the blades.
- Water Pumps: To move water throughout the house.
- Mixer Grinders and Blenders: To power the blades for chopping and blending.
2. What are the main types of AC motors and what is each used for?
AC motors are broadly classified into two main types:
- Synchronous Motors: These motors run at a constant speed synchronised with the frequency of the power supply. They are used in applications requiring precise speed control, like clocks, timers, and industrial robotics.
- Induction Motors (or Asynchronous Motors): These are the most common type. Their speed varies slightly with the load. They are used in almost all major appliances like fans, pumps, and industrial machinery due to their simple and robust design.
3. What are the key advantages of an AC motor over a DC motor?
AC motors are often preferred over DC motors for many applications due to several key advantages:
- Less Maintenance: Most AC motors are brushless, which means there are no brushes to wear out or replace.
- More Durable: Their construction is generally more rugged and simpler, leading to a longer operational life.
- Cost-Effective: They are typically cheaper to manufacture and maintain.
- Safety: The absence of brushes eliminates the sparking that can occur in DC motors.
4. Which type of AC motor is the most common and why?
The three-phase squirrel cage induction motor is the most widely used AC motor in the world, especially in industrial settings. Its popularity comes from its incredibly simple, rugged, and reliable design. It has no brushes or slip rings, making it very low-maintenance and cost-effective to produce and operate.
5. What is the function of the rotor in an AC motor?
The rotor is the rotating part of the motor. Its main function is to convert the electrical energy from the stator's rotating magnetic field into mechanical energy. As the magnetic field of the stator rotates, it induces a current in the rotor, creating another magnetic field that tries to catch up with the stator's field, causing the rotor to spin and turn the motor shaft.
6. Why are bearings important in an AC motor?
Bearings are critical components in an AC motor for several reasons. They support the rotor and keep it perfectly centred, which is essential for maintaining a consistent air gap between the rotor and the stator. Most importantly, they reduce friction, allowing the rotor to spin freely and efficiently with minimal wear and tear.
7. How does the working principle of an AC motor make it so versatile for different uses?
The versatility of an AC motor comes from its use of a rotating magnetic field, which is generated directly by the alternating current supply. This clever principle eliminates the need for a physical connection (like brushes) to deliver power to the rotor. This simple, contactless power transfer allows for designs that are robust, highly reliable, and can be scaled for everything from small fans to massive industrial machines.
8. Why are three-phase induction motors the top choice for heavy industrial machinery?
Three-phase induction motors are ideal for heavy industry because they are self-starting and produce a high and constant amount of torque. They can handle heavy loads without stalling and operate with high efficiency and reliability under harsh conditions. Their simple construction means they require very little maintenance, which is a huge advantage for factories and industrial plants.
9. Can you use a standard AC motor for a small, battery-powered device like a toy car?
No, it is not practical. An AC motor is designed to run on alternating current (AC), the type of electricity that comes from a wall socket. A battery, like the one in a toy car, provides direct current (DC). For battery-powered devices, a DC motor is the correct and necessary choice as it is designed to work with that type of power source.









