




How Did Michael Faraday’s Inventions Shape Modern Science?
Have you ever wondered who invented the electric city generator that provides electricity to the area you live in or the entire City that you live in? Or have you ever imagined How our life would have been if carbon-related hydrocarbon compounds had not been found? All these important discoveries were made by Michael Faraday; he was a well-known scientist and chemist.
In this article, we will learn everything about Michael Faraday from his biography to what struggles he faced during his journey and then we will look at what contributions he made to the scientific society. Along with all this, we will also look at facts related to Michael Faraday's inventions. So let's start learning.

Michael Faraday
Who is Michael Faraday?
Michael Faraday was a well-known scientist and physicist who made a number of important advances in both the field of chemistry and electricity.
Biography of Michael Faraday
Michael Faraday was born in England on the 22nd of September in 1791. He was a son of a black Smith and was very interested in reading scientific books from the shop where he used to work as an apprentice at the age of 14. He used to attend all the lectures of the scientist he blindly followed and took notes and later he also wrote a letter to him seeking employment. The professor welcomed him to his laboratory as an assistant after being moved by his enthusiasm.
After following the instructions and footprints of his master he succeeded in liquifying gasses by the means of compression. In 1825 he discovered a hydrocarbon named benzene and later was called the father of organic chemistry. In 1833 he formulated his loss of electrolysis which was linked with the fields of chemistry and electricity.
Michael Faraday has been a very popular name in the field of Physics and he was well known for his experiments and discoveries that contributed to the growth of Physics. Amongst his inventions are the very first electric motor and the first electromagnetic generator that contributed in the growth of Physics and its application for the help of the entire world.
Michael Faraday Inventions
In this section of the article are listed all the Michael faraday inventions
One of his greatest Discoveries was the discovery of electromagnetic induction. He formulated his laws of electromagnetic induction in 1831 when he saw that when he moves the magnet through a coil of wire a current is produced in the wire.
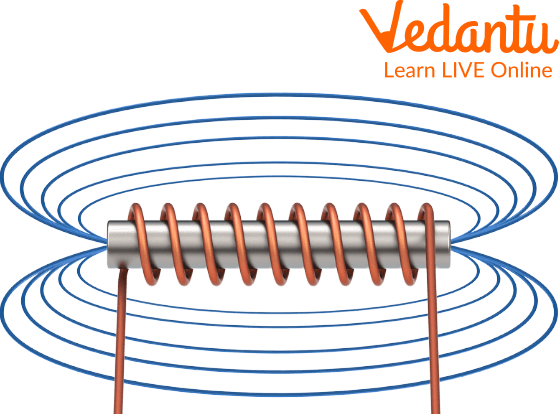
Electromagnetic Induction Through Coil
Through this Discovery he later discovered the electric generator which was later called as the heart of modern electrical equipment.

Primitive Electric Generator
In the last days of his career, Faraday discovered polarization or rotation of plane polarization of light in magnetic fields. His work in the field of electromagnetism leads Maxwell to link his theories of electricity magnetism to light with the founding of Faraday. In conclusion, there came the invention of the radio.
Michael Faraday Facts for Kids
Below are listed some Michael Faraday Facts For Kids
He created inflatable balloons.
He was the one who helped Albert Einstein to get his first employment.
The option of being cremated at Westminster Abbey alongside all the renowned monarchs and queens was presented to Michael Faraday, however, he rejected it.
Summary
To conclude all the learnings from this article we can say that Michael Faraday was an important human being for the entire world. The world would not have been the same without his discoveries of electromagnetism, organic chemistry and much more. All though he was a very famous scientist but was still a very down-to-earth and humble person. With this, we would like to end this article. And hope that you all also get inspired by the story of Michael Faraday and aim to achieve something big in your lives. If you have any further doubts you can write them in the comment section below, we hope we were easy and understandable enough, in case of any other doubts feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Michael Faraday’s Inventions: Discoveries, Impact & Applications
1. What are the main inventions and discoveries of Michael Faraday?
Michael Faraday, a key figure in the history of science, is credited with several revolutionary inventions and discoveries. His most significant contributions include the first electric motor, which demonstrated the conversion of electrical energy into mechanical motion, the electric generator, based on his principle of electromagnetic induction, and the Faraday cage, an enclosure that blocks electromagnetic fields.
2. What is the principle of electromagnetic induction discovered by Michael Faraday?
The principle of electromagnetic induction, discovered by Faraday in 1831, is a fundamental law of physics. It states that a changing magnetic field within a closed circuit will induce an electromotive force (voltage), which in turn creates an electric current. This discovery is the foundational principle behind modern transformers, inductors, and electric generators.
3. How did Michael Faraday's findings change the world?
Michael Faraday's findings, particularly the discovery of electromagnetic induction, were world-changing because they provided a practical method to convert mechanical energy into electricity. This led to the development of the electric generator, making it possible to produce and distribute electricity on a massive scale. Modern power grids, electric lighting, and countless industrial and domestic technologies are all built upon Faraday's foundational work.
4. What were Michael Faraday's most important contributions to chemistry?
Beyond physics, Michael Faraday made several crucial contributions to chemistry. His main chemical discoveries include:
- The discovery of Benzene: He isolated and identified this fundamental aromatic compound.
- Laws of Electrolysis: He formulated two quantitative laws that govern the process of electrolysis.
- Liquefaction of Gases: He was the first to liquefy several gases, including chlorine and ammonia, by applying pressure.
- Invention of Oxidation Numbers: He developed the system of assigning oxidation states to elements.
5. What is a Faraday Cage and what are some of its real-world examples?
A Faraday cage is an enclosure made of a conductive material that blocks external electromagnetic fields. It works by distributing the electrical charge or radiation around the exterior of the cage, preventing it from penetrating the interior. Common real-world examples include the metal body of a car protecting occupants from lightning, the mesh screen on a microwave oven door containing the microwaves, and shielded cables that prevent signal interference.
6. How is an electric motor different from an electric generator?
Although both devices rely on Faraday's principles of electromagnetism, they serve opposite functions. An electric motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, using current to produce motion. In contrast, an electric generator converts mechanical energy into electrical energy, using motion within a magnetic field to induce a current, as described by Faraday's law of induction.
7. Who was Humphry Davy and how did he influence Michael Faraday's career?
Sir Humphry Davy was an eminent chemist who hired a young, self-educated Michael Faraday as his laboratory assistant. Davy provided Faraday with access to a world-class laboratory and a scientific education he would not have otherwise received. This mentorship was crucial in launching Faraday's career. Though their relationship became strained, Davy later famously referred to Michael Faraday as his "greatest discovery."
8. What is the Faraday Effect?
The Faraday Effect, or Faraday rotation, was the first experimental evidence that light and magnetism are related. Discovered by Faraday in 1845, it describes the interaction between light and a magnetic field in a medium. Specifically, it is a magneto-optical phenomenon where the plane of polarization of light rotates when it passes through a material subjected to a magnetic field parallel to the direction of light propagation.









