




Information About Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton was born on Christmas Day, i.e. 25 December 1642 in Lincolnshire, England. The laws of motion ( more commonly known as Isaac Newton Laws of Motion or Isaac Newton Laws ) and the theory of gravity were developed by Newton. One of history's most important scientists is Sir Isaac Newton. He developed various theories and made contributions to physics, mathematics, and philosophy, among other subjects. In addition to creating the first functional reflecting telescope, Newton also created a complex theory of colour.
Sir Isaac Newton
Details and Achievements of Isaac Newton
Sir Isaac Newton was a brilliant mathematician, physicist, and astronomer.
On Christmas Day, 25 December 1642, in the English county of Lincolnshire, Isaac Newton was born.
Newton created the gravitational theory and the laws of motion.
He also studied optic ideas and produced a book on them.
He created a number of hypotheses and contributed to a number of fields, including physics, mathematics, and philosophy.
Newton developed the first practical reflecting telescope as well as a sophisticated understanding of colour.

Reflecting Telescope Invented by Isaac Newton
He wrote several books including the world-famous: ‘Principia’ and ‘Opticks’.
Fun Facts about Isaac Newton(Isaac Newton Facts)
Here are some interesting information about Newton :
In 1668, Isaac Newton developed the reflecting telescope.
The Philosophiae Naturalis Principia Mathematica, which he published in 1687, was his most significant contribution. There were three books in this work.
Although he was born on Christmas, his actual birthday is January 4.
A lab fire cost him 20 years' worth of research.
Although he participated in the parliament, Isaac Newton had relatively little of an impact.
He was a mediocre investor.
Originally, his mother had intended for him to become a farmer.
His study on gravity was motivated by an apple tree that is still around now.
Newton's Laws of Motion
The first person to really examine motion was Newton. He researched, refined, and created three motion laws regarding the interactions between force and motion. He later gave 3 very important laws regarding motion which have been known forever as Newton's laws of motion. There are 3 laws of motion according to newton:
Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)
Newton's Second Law of Motion (Law of Mass and Acceleration)
Newton's Third Law of Motion (Action-Reaction Law)
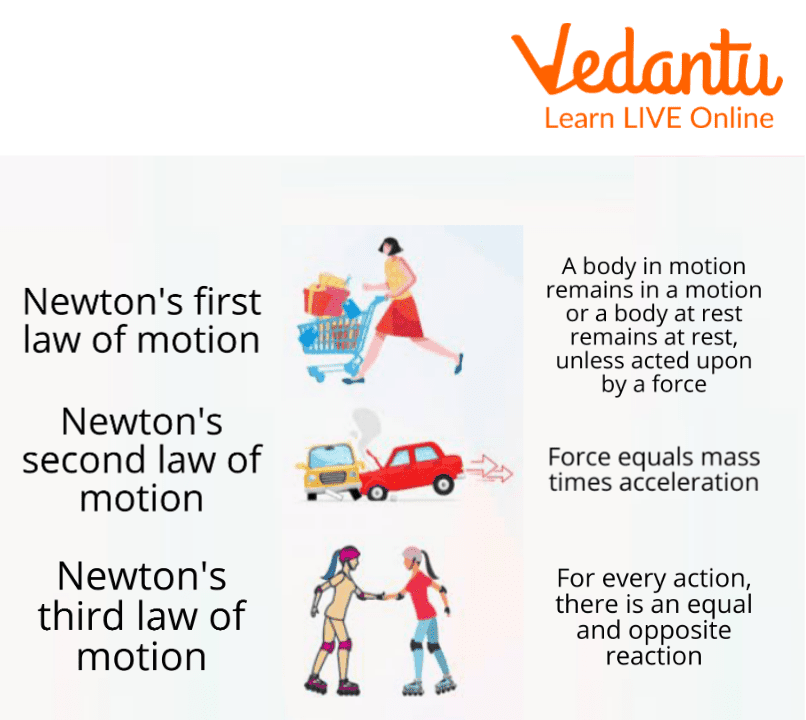
Newton’s 3 Laws of Motion
Solved Questions
1. Why is Newton considered the most significant scientist of all time?
Ans: Isaac Newton is considered the father of modern science and physics due to his contribution in the field of physics, calculus, optics, etc. He was also a pioneer engineer.
2. What are the 3 laws of motion?
Ans: The 3 laws of motion are:
Newton's First Law of Motion (Law of Inertia)
Newton's Second Law of Motion (Law of Mass and Acceleration)
Newton's Third Law of Motion (action-reaction law)
3. Name any 3 interesting facts about Isaac Newton.
Ans: 3 Isaac Newton Interesting Facts are:
Newton created the gravitational theory and the laws of motion.
He also studied optic ideas and produced a book on them.
Although he was born on Christmas, his actual birthday is January 4.
Summary
Sir Isaac Newton was an English mathematician, physicist, and astronomer who is regarded as one of the finest and most important mathematicians and physicists of all time. The laws of motion and the theory of gravity were given by Newton. In addition to creating the first functional reflecting telescope, Newton also created a complex theory of colour. He created the gravitational theory and the laws of motion. He also studied optic ideas and produced a book on them.
Newton created a number of hypotheses and contributed to a number of fields, including physics, mathematics, and philosophy. Newton developed the first practical reflecting telescope as well as a sophisticated understanding of colour. He wrote several books including the world-famous: ‘Principia’ and ‘Opticks’. He later gave three very important laws regarding motion which have been known forever as Newton's laws of motion.
FAQs on Facts About Isaac Newton for Kids
1. Who was Sir Isaac Newton?
Sir Isaac Newton was a highly influential English scientist, mathematician, and astronomer. He is celebrated as one of history's most important scientific minds for his groundbreaking discoveries, including the laws of motion and the universal law of gravity, which form the foundation of classical physics.
2. What are Isaac Newton's three laws of motion, explained simply for kids?
Isaac Newton's three laws of motion describe how things move. Here’s a simple way to understand them:
- The First Law (Inertia): An object stays still or keeps moving unless a force acts on it. A toy car won't move until you push it.
- The Second Law (Acceleration): It takes more force to move a heavier object than a lighter one. This is famously known as F=ma (Force = mass x acceleration).
- The Third Law (Action-Reaction): For every action, there's an equal and opposite reaction. When you push against a wall, the wall pushes back on you with the same force.
3. What is the real story about Isaac Newton and the falling apple?
The popular story is that an apple fell on Newton's head, giving him the idea for gravity. While he was inspired by watching an apple fall from a tree, it most likely did not hit him. The sight made him wonder why objects always fall straight down. This question led him to develop his theory that the same force, gravity, pulls everything towards the centre of the Earth.
4. What important books did Isaac Newton write?
Isaac Newton's most famous book is the 'Principia Mathematica' (full title: Philosophiæ Naturalis Principia Mathematica). This is where he published his laws of motion and the law of universal gravitation. He also wrote another significant book called 'Opticks', which detailed his experiments and discoveries about light and colour.
5. What other major discoveries is Newton known for, besides gravity?
Beyond gravity and motion, Newton made several other critical contributions. He discovered that white light is a mixture of all colours of the rainbow by experimenting with a prism. He also invented a new, powerful type of mathematics called calculus to help him solve complex scientific problems, and he built the first practical reflecting telescope.
6. Why was Newton's discovery of universal gravity so important for science?
Newton's discovery of gravity was revolutionary because it was a universal law. He proposed that the same force that pulls an apple to the ground is also the force that keeps the Moon in orbit around the Earth and the planets in orbit around the Sun. This single idea explained the workings of both heavenly bodies and objects on Earth, uniting astronomy and physics for the first time.
7. How did Isaac Newton's reflecting telescope improve on older designs?
Older telescopes (refractors) used lenses that bent light, which often created images with blurry, coloured edges (an issue called chromatic aberration). Newton's innovative reflecting telescope used a curved mirror to gather light instead. This mirror-based design avoided the colour-fringing problem, producing much clearer and sharper images of stars and planets and setting a new standard for astronomical observation.
8. If the apple story is a myth, how did Newton actually figure out his theory of gravity?
The falling apple was merely a starting point for a 'thought experiment'. Newton's theory of gravity was the result of many years of intense work, not a single moment of inspiration. He used his own laws of motion and the advanced mathematics of calculus (which he also invented) to calculate how a force from the Earth could extend all the way to the Moon. It was this combination of observation, mathematical proof, and brilliant thinking that led to his final theory.









