




Introduction
Remember when you injured yourself, and a deep red-coloured liquid gushed out of the wound; that red-coloured liquid is known as blood. It is the circulating fluid in our body; that is, it flows in the nerves throughout our body, reaching almost all the cells of our body. Thus, it helps in transporting various substances, such as nutrients in our body, from one cell to another. Thus we can conclude that blood is vital in our body. At this second, we have approximately 5 litres of blood circulating within our body!
Definition of Blood
The fluid circulating in the human body that collects in the heart through the veins and again circulates from the heart to the whole body through the arteries is called blood.
It is a liquid connective tissue. It regulates the temperature of the body and protects the body from diseases. It consists of four things – plasma, red blood cells (red blood cells or RBCs), white blood cells (white blood cells or WBCs) and platelets (platelets).
White Blood Cells and Red Blood Cells.
Interesting Facts About Blood
The amount of blood in the human body is 6-7% of the total body weight.
It is an alkaline solution with a pH of 7.4.
Women have half a litre of blood less than men.
Two types of substances are found in blood, plasma and blood.
About 60% of the blood is found in the form of plasma, and the remaining 40% is in the form of blood.
90% of plasma is water.
Blood cells have three parts: red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs), and blood platelets.
The red colour of blood is due to ferrous ions, which are the colour of haemoglobin (a type of protein found in red blood cells).
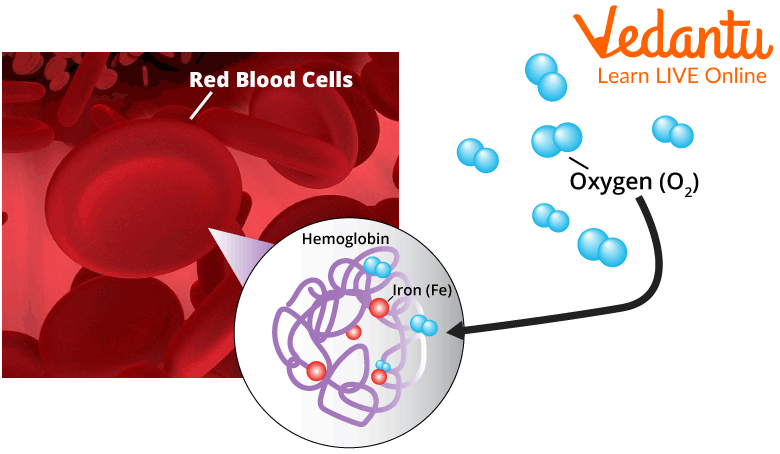
Haemoglobin Found in the Red Blood Cells.
The normal blood pressure in the human body is 120/80 mmHg. it happens.
The life span of red blood cells is 120 days.
Functions of Blood
The following are the main functions of blood in the body-
Blood regulates body temperature.
It takes oxygen from the lungs and transports it to other body parts.
It takes carbon dioxide from the cells of the body to exhale and transports it to the lungs.
It takes the digested food in the small intestine and carries it to all body parts.
It takes the waste product urea from the liver and takes it to the kidneys for excretion.
Red Blood Cells (RBCs)
One of the major components of blood are the red blood cells; they are responsible for the red colour of the blood. They have a lifespan of 120 days and then are destroyed and removed from our body, whereas simultaneously new red blood cells are formed in the bone marrow to replace the ones being destroyed. They have an important substance namely haemoglobin about which we will study in the next segment.
Role of Haemoglobin in Blood
The Red Blood Cells have an iron containing pigment named Haemoglobin. The haemoglobin is a very important molecule since it plays an important role in the transport of oxygen, the molecule essentially carries the oxygen molecule from the lungs to the other cells of the body and also carries the carbon dioxide from the cells and to the lungs from where it is discarded from our body.
Facts About Blood Vessels
What are Blood Vessels?
The circulation of blood in the body takes place through the vessels. Those are called blood vessels. There are three types of blood vessels in the human body:
Artery
Vein
Capillary
Artery: The vessels that carry pure blood from the heart to other parts of the body are called arteries. In these, the blood flow is fast and at high pressure. The aorta is the largest artery. Impure blood flows in the pulmonary artery.
Vein: The vessels that carry impure blood from different parts of the body to the heart are called veins. The pulmonary vein contains pure blood.
Capillaries: These are thin blood vessels, in which blood flows very slowly.
Facts:
It takes about 60 seconds for each blood cell to complete one cycle of the body.
There are 5 litres of blood in the normal human body; in each heartbeat, the heart produces about 70 ml. pumps blood.
The normal human heart beats 70-72 times in a minute (60 seconds).
Solved Questions
1. Write one main function of the blood.
Ans: The main function of blood (red blood cells) is to transport oxygen.
2. How many types of blood vessels are in the human body?
Ans: The human body has three types of blood vessels: Artery, Vein and Capillary.
3. Why is blood red?
Ans: Blood is red because the colour of the haemoglobin is red, which is found in red blood cells.
Learning By Doing
Write True or False.
10% of plasma is water.
Blood is a liquid connective tissue.
Blood cells have three parts: RBCs, WBCs and blood platelets.
Summary
Blood plays a very important role in the human body. Red blood cells are filled with haemoglobin and carry oxygen from our lungs to the rest of our bodies. In this chapter, we have studied many things about human blood. Now, you must have understood what is called blood and its facts, functions and many things related to blood.
FAQs on Interesting Facts about Blood
1. What are some surprising facts about human blood?
Our blood has many interesting characteristics that often go unnoticed. Here are a few surprising facts:
- About 8% of an adult's body weight is made up of blood.
- Blood is not just red cells; over half of it (about 55%) is a yellowish liquid called plasma.
- Not all animals have red blood. Insects, for example, have a clear or yellowish fluid called hemolymph.
- A single drop of blood contains millions of red blood cells and thousands of white blood cells.
- The human body produces about 17 million red blood cells every second in the bone marrow.
2. What is blood pressure?
Blood pressure is the force that your blood exerts against the walls of your arteries as your heart pumps it around your body. It is measured with two numbers: the systolic pressure (when the heart beats) over the diastolic pressure (when the heart rests between beats).
3. What is the main component of our blood?
The main component of blood is not red or white blood cells, but a fluid called plasma. Plasma makes up about 55% of the total blood volume. It is a pale yellow liquid that carries blood cells, platelets, nutrients, hormones, and waste products throughout the body.
4. What is the importance of haemoglobin in red blood cells?
Haemoglobin is an iron-rich protein found in red blood cells that is crucial for survival. Its primary function is to bind with oxygen in the lungs and transport it to all the tissues and organs in the body. It is also what gives blood its characteristic red colour.
5. How long does it take for blood to circulate the entire body?
On average, it takes about 45 to 60 seconds for a single red blood cell to leave the heart, travel through the entire circulatory system, and return to the heart. This rapid circulation ensures that all body cells receive a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients.
6. What is the study of blood called?
The branch of medicine and biology concerned with the study of blood, its disorders, and the blood-forming organs is called haematology. Specialists in this field are known as haematologists.
7. What is the process of blood formation called?
The process of creating new blood cells in the body is called hematopoiesis. This essential process occurs primarily in the bone marrow, where stem cells differentiate into red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets.
8. If blood is always red, why do veins look blue through our skin?
This is a common misconception based on an optical illusion. Blood is never blue. Veins appear blue because of the way light interacts with your skin and the tissues. Your skin scatters red light, while blue light is reflected back to your eyes, making the veins underneath look bluish or green.
9. Why is the O-negative blood type known as the 'universal donor'?
The O-negative blood type is called the 'universal donor' because its red blood cells lack the main antigens (A, B, and Rh factor) on their surface. Since there are no antigens to trigger an immune response, this blood type can be safely transfused to individuals with any other blood type in an emergency.
10. How is human blood different from the 'blood' of insects?
Human blood is fundamentally different from the fluid found in insects, called hemolymph. The key difference is that our blood uses iron-based haemoglobin to transport oxygen, making it red. Insect hemolymph does not transport oxygen; instead, it transports nutrients and waste. Insects breathe through a separate system of tubes called tracheae. Consequently, their 'blood' is typically clear, yellow, or green.
11. What makes blood so interesting from a scientific perspective?
From a scientific view, blood is fascinating because it acts as a complex, living tissue in liquid form. It is a unique transport system for oxygen, nutrients, and waste, a key part of the immune system fighting infections, and essential for regulating body temperature and pH. Its components work in perfect harmony to maintain homeostasis, the stable internal environment necessary for life.









