What are the 10 examples of perfect tense in English?
Perfect Tense Examples help learners understand how to express actions completed in the past, present, or future using correct forms. Learning the definition and rules for perfect tenses is essential for clarity in English communication. This guide explains all perfect tenses with rules, example sentences, common mistakes, tips, and practice activities suitable for all ages, including kids and students in class 6.
Perfect Tense Examples: Definition and Key Rules
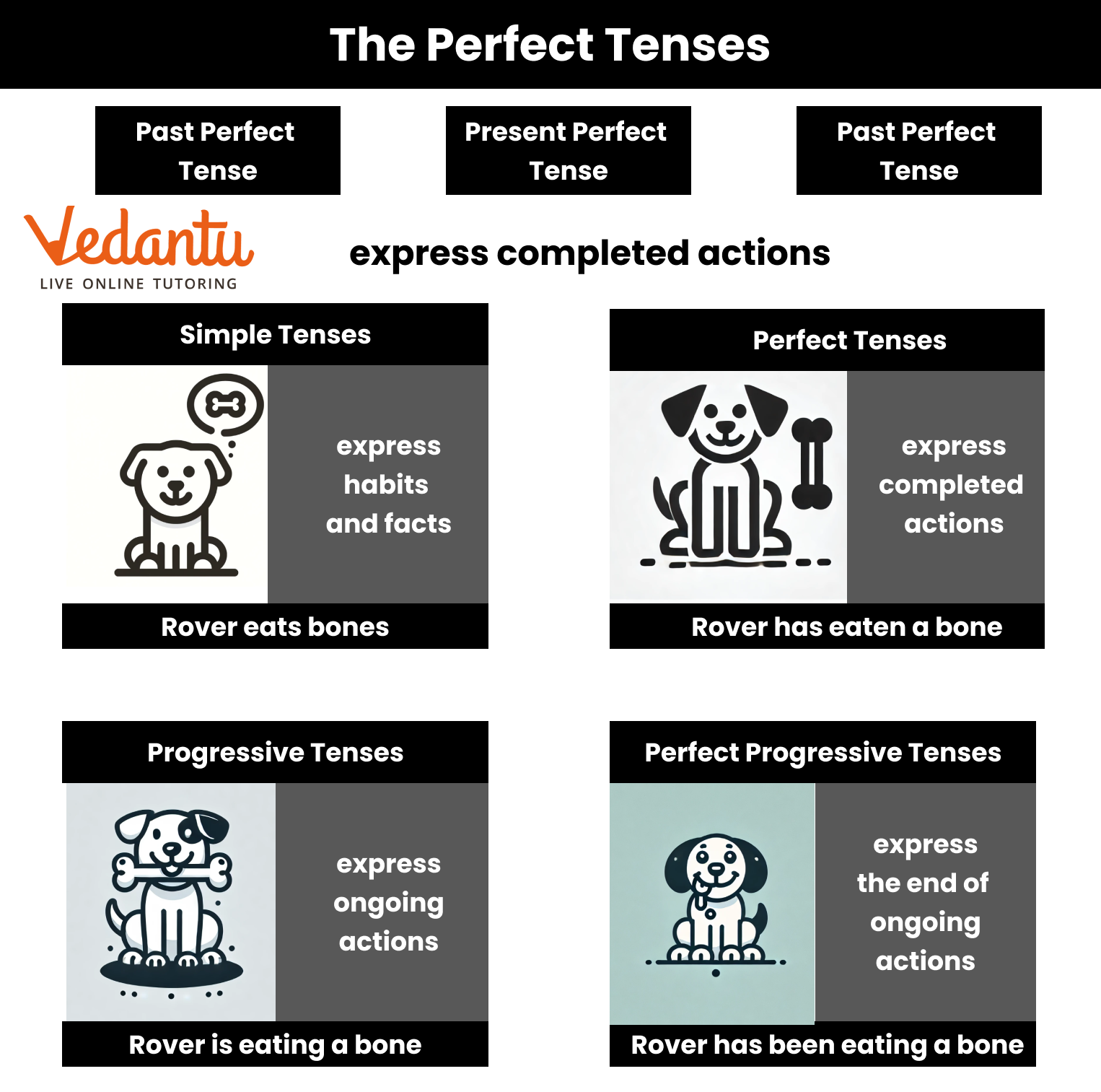
Perfect tense examples show actions that are complete or have been completed at a certain time. The perfect tense is formed by using auxiliary verbs—has, have, or had—with the past participle of the main verb. Understanding the difference between each perfect tense is important for constructing sentences about past experiences, ongoing actions, or things that will be finished in the future.
For details about different types of verbs, visit Verbs for Kids and Verb Questions and Answers from Vedantu’s English resources.
Types of Perfect Tense with Examples
| Tense | Form | Perfect Tense Examples (with sentences) |
|---|---|---|
| Present Perfect | Has/Have + Past Participle | She has finished her homework. |
| Past Perfect | Had + Past Participle | They had left before the rain started. |
| Future Perfect | Will have + Past Participle | I will have completed my project by tomorrow. |
Each perfect tense places an action at a specific time related to the present, past, or future. Using correct forms helps express sequences and relationships between actions.
Present Perfect Tense Examples and Usage
The present perfect tense is used for actions that happened at an unspecified time or started in the past and continue now. The form is has/have + past participle. For example: “I have visited London.” For more practice, see Present Perfect Tense and English Grammar on Vedantu.
She has eaten breakfast already.
We have finished the assignment.
He has not seen that movie.
Past Perfect Tense Examples and Practice
Past perfect tense uses had + past participle and is used for an action completed before another one in the past. For instance: “She had completed her work before dinner.” For detailed explanations and worksheets, explore Past Perfect Tense and Grammar Exercises.
They had gone home before it got dark.
He had already left when the teacher arrived.
She had studied French before moving to Paris.
Future Perfect Tense Examples Explained
Future perfect tense expresses actions that will be completed before a specified time in the future. The structure is will have + past participle. Example: “By next year, you will have graduated.” For additional examples and tips, check Future Perfect Tense and Uses of Tenses.
She will have completed her studies by March.
I will have read ten books by summer.
They will have reached home before sunset.
Perfect Tense Examples with Practice Questions and Answers
Practice helps understand perfect tense examples better. Try choosing the correct tense in these sentences to test your knowledge. Answers are provided for each.
-
Although Rahul (has/have/had) never seen a lion, he was brave at the zoo.
Answer: had never seen (Past perfect) -
Sana (has/have/had) finished her homework before dinner.
Answer: had finished (Past perfect) -
We (has/have/had) visited this museum many times.
Answer: have visited (Present perfect) -
He (will have/has/had) completed the course by this time next week.
Answer: will have completed (Future perfect)
To reinforce your learning, worksheets like Error Correction Exercises are highly useful.
Common Mistakes and Tips: Perfect Tense Examples
Common mistakes include using the wrong auxiliary verb or confusing tense types. For example, “She has went” is incorrect; it should be “She has gone.” Use the past participle form after has/have/had and match the subject with the correct auxiliary. For structured practice, try exercises from Basic Verb Tenses and Has, Have, Had Exercises.
Avoid double marking time (e.g., “I have finished yesterday” should be “I finished yesterday” or “I have finished”).
Check verb forms for irregular verbs (e.g., write/written, eat/eaten).
Auxiliary agreement: Use “has” with he/she/it, “have” with I/you/we/they.
Perfect Tense Exercises for Class 6 with Answers
The following exercise will help class 6 students and beginners master perfect tense usage. Answers are given below for instant checking. For more activities, visit Worksheets for Kids and Practice Questions for Kids.
I ________ (finish) reading the book already.
Answer: have finishedThey ________ (leave) before the party started.
Answer: had leftBy 7 PM, she ________ (cook) dinner.
Answer: will have cooked
Difference Between Perfect and Perfect Continuous Tenses
Perfect tenses focus on completed actions, while perfect continuous tenses emphasize ongoing actions up until a point. Example: “I have read” (present perfect) vs. “I have been reading” (present perfect continuous). The continuous form uses “has/have/had + been + verb-ing”.
For charts and differences, visit Present Perfect Continuous Tense and Future Perfect Continuous Tense.
Chart: Perfect Tense Examples vs. Perfect Continuous
| Tense | Perfect Tense Example | Perfect Continuous Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present | She has danced. | She has been dancing. |
| Past | She had danced. | She had been dancing. |
| Future | She will have danced. | She will have been dancing. |
Referring to such charts helps quickly understand usage and clear confusion between similar tenses.
Perfect Tense Examples for Kids
Perfect Tense Examples for kids must be simple and clear. For instance, “The cat has eaten its food,” or “We have played outside.” Children pick up tenses faster with engaging stories and fun exercises. Explore more kids’ grammar topics at Kids Topics.
I have built a sandcastle.
She has drawn a picture.
They have finished their puzzles.
Perfect Tense Examples Worksheet with Answers
Practice questions reinforce perfect tense examples effectively for all learners. Fill in the blanks using correct forms. Answers are provided below.
By evening, we ________ (complete) the project. Answer: will have completed
She ________ (never see) snow before.
Answer: has never seenMy parents ________ (visit) Paris twice.
Answer: have visitedHe ________ (finish) his homework before dinner.
Answer: had finished
Find worksheets for various tenses at Tenses Exercises and Grammar Vowels and Consonants.
Perfect Tense Examples MCQ with Answers
Choose the correct option in these MCQs about perfect tense examples:
She ________ to the show before it started. (has gone / had gone / will have gone)
Answer: had goneWe ________ breakfast already. (have eaten / had been eaten / will eat)
Answer: have eatenYou ________ the news by tomorrow. (had heard / have heard / will have heard)
Answer: will have heard
Perfect Tense Examples: Chart and Table
Charts and tables make it easier to remember rules and see patterns among perfect tense examples. Always check the auxiliary verb, the verb form, and the sequence of events. For more difference and usage notes, explore Elementary Idea of Tenses.
Summary of Perfect Tense Examples
Understanding perfect tense examples is crucial for expressing actions completed at different times, comparing sequences, and improving sentence accuracy. With clear rules, engaging activities, and real-world examples, learners can easily master perfect, perfect continuous, and their applications. Use Vedantu’s diverse grammar resources for further practice, explanations, and confidence in English communication.
FAQs on Perfect Tense Examples, Rules, and Usage in English
1. What is perfect tense with examples?
Perfect tense describes actions that have been completed at a specific time.
Examples include:
- Present Perfect: She has finished her homework.
- Past Perfect: I had left before it started raining.
- Future Perfect: They will have reached the station by noon.
2. What is the rule for forming perfect tense?
Perfect tense is formed by combining a suitable helping verb and the main verb’s past participle form.
- Present Perfect: Subject + have/has + past participle
- Past Perfect: Subject + had + past participle
- Future Perfect: Subject + will have + past participle
3. How do you identify perfect tenses?
You can identify perfect tenses by checking for the helping verbs have/has/had/will have before the past participle of a verb.
- Look for time words like already, yet, since, before, by, for.
- Check that the verb is in past participle form (e.g., eaten, finished, written).
4. What are the helping verbs used in perfect tense?
The main helping verbs for perfect tense are:
- have (I/you/we/they in present perfect)
- has (he/she/it in present perfect)
- had (all subjects in past perfect)
- will have (all subjects in future perfect)
5. What are some common examples of perfect tense?
Here are some clear, exam-friendly perfect tense examples:
- I have completed my homework. (Present Perfect)
- She had left before the class started. (Past Perfect)
- We will have finished the project by Friday. (Future Perfect)
6. What are the 10 examples of perfect tense?
Ten examples of perfect tense sentences are:
- She has finished her work.
- I have eaten lunch.
- They have travelled to Delhi.
- He had left the office before I called.
- We had completed the assignment.
- The train had departed before they arrived.
- She will have finished the test by noon.
- I will have read the book by tomorrow.
- They will have reached home by 8 PM.
- He has been studying for two hours. (Present Perfect Continuous)
7. Why is the perfect tense important?
The perfect tense is important because it shows:
- Actions that are completed before another action or now
- Clear sequence of events (useful in exams, essays, stories)
- Accurate time relationships in spoken and written English
8. What is the difference between perfect tense and perfect continuous tense?
The perfect tense shows completed actions, while the perfect continuous tense shows actions that started in the past and might still be continuing.
- Perfect: I have completed my task. (Finished)
- Perfect Continuous: I have been completing my task. (Ongoing)
9. What are time words used with perfect tense?
Common time words that signal perfect tense include:
- already, yet, just, ever, never
- since, for, before, by, so far
- recently, lately
10. Can you give perfect tense examples in Hindi and English?
Yes! Here are perfect tense examples:
- English: I have finished my homework.
- Hindi: Main apna kaam kar chuka hoon (मैं अपना काम कर चुका हूँ)
- Urdu: Mein kaam kar chuka hoon (میں کام کر چکا ہوں)