




What Are the Main Parts of Speech and Sentence Structure?
Basic English grammar is the method through which we connect words to form a meaningful sentence with the help of some general rules applied. To understand English Grammar better, we will try to break the sentence and stress the words which will help us gain the meaning of the sentences.
The rules are further divided as parts of speech which are the noun, pronoun, determiners, verbs into present, past, future tense, modals, active – passive voices, phrases and clauses, prepositions and many more, all of these make a correct sentence and are known as basic English grammar collectively. So, let’s dive in and learn easy English grammar with the help of this article.
Basic English Grammar
Let’s take a simple example and try to understand the importance of rules of easy English grammar and what happens if these rules don't exist.

Woman Driving a Car
We will try to write a sentence without the easy English grammar rules and one with the rules to see the difference in the meaning.
With Grammar Rules: A woman is driving a car
Without Grammar Rules: A car is driving a women
Now as the difference is clear, let’s learn a bit about some topics of English grammar as parts of speech and verbs and their tenses.
Parts of Speech
Let’s have a quick overview of parts of speech, there are eight parts of speech in English grammar. Parts of speech are the classes into which words are divided according to their function in a sentence, these are as follows :
Noun
A noun is observed as the name of a person, place, or thing.
Example: John, Anita, boy, girl, gold, table, Chennai
Pronoun
A pronoun is generally a word used instead of a noun
Example: I, we, he, she, it, mine, ours, yours, them, their
Adjective
An adjective is used to usually qualify or add something to the meaning of the existing noun.
Example: a beautiful flower, twenty soldiers, little food
Verb
A verb specifies an action, being, or possession.
For example, the girl sang, Raman is an intelligent boy.
Verbs have three chief forms
The present tense
The past tense
The past participle
Adverb
An adverb is a word that adds value to an existing verb, an adjective, or another adverb.
Example: Raman runs quickly.
Preposition
A preposition is a word used in a sentence to show its relationship with the noun and the pronoun.
Example: a cat hid under the table
Conjunction
A conjunction is a word as but, which is used to join together words, phrases, or sentences.
Example: Raman is clever but lazy.
Interjection
An interjection is an exclamatory word, which shows some sudden reactions of shock or excitement
Example: Hurrah! India won a gold medal.
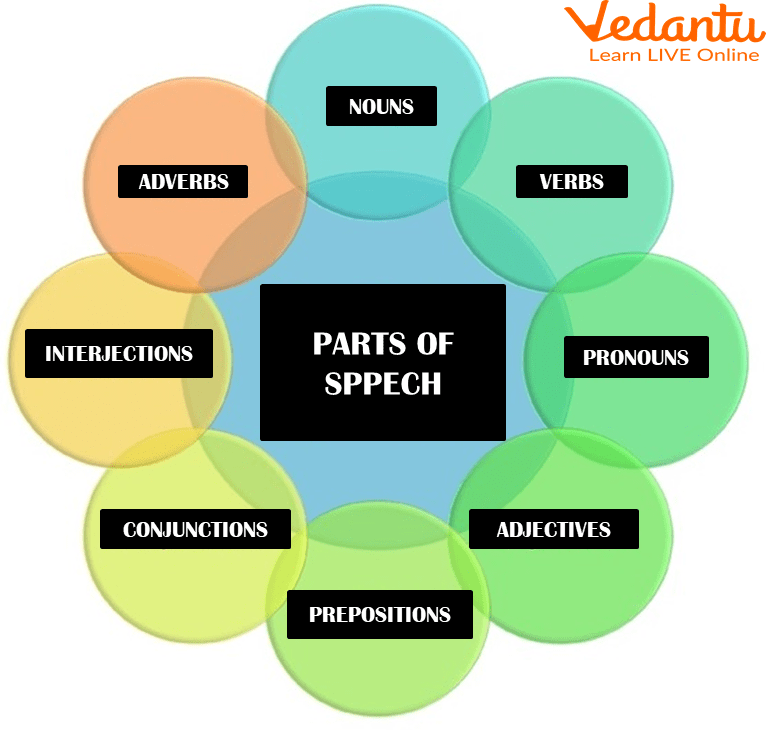
Parts of Speech
Verb: The Present Tense
The present tense like the past tense and future is divided into 4 further tenses :
Simple present, present continuous, present perfect tense, present perfect continuous
The present tense is used to express custom or habit as; I play badminton every evening.
To express what is happening at the present moment as; See, how it rains!
To express general truth; The earth moves around the sun.
Simple Present Tense Worksheet
Q1. Rewrite the passage using the simple present tense of the words given in the brackets. Complete the simple present tense worksheet.
Ans: At the new Delhi railway station, the kalam family (attract) attracts the attention of a large number of curious onlookers and media. Dr kalam (remain) remains untouched by the excitement of the masses. The day of the ceremony (start) starts like any other day with the regular 5 km walk at the Asiad village. He (take) takes a shower and (eat) eats a light south Indian breakfast consisting of Idli, sambhar, and buttermilk. He (dress) dresses immaculately in a suit and (step) steps out to acknowledge the greetings of the crowd.
Q2. Write 7 sentences about the things you like and 7 about the things you don’t like In simple present tense.
Ans: I like to eat chocolate.
I like to listen to music.
I like to draw sketches.
I like to watch tv.
I like -to dance.
I like to make friends.
I like to be at school.
I don’t like to have soup.
I don’t like to tell lies.
I don’t like to be disturbed.
I don’t like to fight.
I don’t like to play cricket.
I don’t like to cry a lot.
I don’t like my neighbour.
Summary
To summarise, grammar is a set of rules which apply to a language and result in making the sentence meaningful and correct in a sense, when these rules are applied to English as a language, it is known as English grammar. We often tend to speak informally in our daily life, which could be grammatically incorrect but by following the rules and by keeping in mind the eight parts of speech, we can form a correct sentence using English grammar topics and rules. In this article we learned about various different aspects of grammars like parts of speech as well as the basics of english grammar. We hope this article was helpful to you, however, in case of any other doubts, feel free to ask in the comments.
FAQs on Basic English Grammar Made Easy: Rules, Tips & Examples
1. What are the core components of basic English grammar?
The core components of basic English grammar are the foundational rules and structures that govern the language. These primarily include:
- Parts of Speech: Understanding the roles of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
- Sentence Structure: Knowing how to correctly form sentences with a subject and a predicate, and understanding phrases and clauses.
- Tenses: Correctly using verb tenses to indicate when an action occurs (past, present, future).
- Punctuation: Using commas, periods, question marks, and other symbols to give structure and clarity to writing.
2. What are the main types of nouns in English grammar?
In English grammar, nouns are primarily categorised into five main types based on their function and what they represent:
- Proper Noun: The specific name of a person, place, or thing (e.g., Rohan, Delhi).
- Common Noun: A general name for a person, place, or thing (e.g., boy, city).
- Collective Noun: A name for a group of individuals or things (e.g., team, flock).
- Material Noun: The name of a substance or material from which things are made (e.g., gold, wood).
- Abstract Noun: A name for a quality, idea, or feeling that cannot be touched (e.g., honesty, happiness).
3. How do you differentiate between 1st, 2nd, and 3rd person pronouns?
The differentiation is based on the speaker's point of view:
- First Person (1st): Refers to the person who is speaking. The pronouns are I, me, we, and us.
- Second Person (2nd): Refers to the person being spoken to. The main pronoun is you.
- Third Person (3rd): Refers to the person or thing being spoken about. The pronouns are he, she, it, they, him, her, and them.
4. What is the difference between a phrase and a clause?
The key difference lies in their structure. A clause is a group of words that contains both a subject and a verb, expressing a complete or near-complete thought (e.g., 'she is running'). An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence. In contrast, a phrase is a group of words that works as a single unit but does not have both a subject and a verb, so it cannot express a complete thought (e.g., 'on the table', 'running quickly').
5. Why is subject-verb agreement a fundamental rule in grammar?
Subject-verb agreement is fundamental because it ensures that a sentence is logically and grammatically clear. The rule states that a singular subject must take a singular verb, and a plural subject must take a plural verb. Following this rule prevents confusion and makes the relationship between the subject (who or what is doing the action) and the verb (the action) precise. For example, 'The dog barks' is clear, whereas 'The dog bark' is grammatically incorrect and confusing.
6. How does a strong grasp of basic grammar improve one's writing skills?
A strong grasp of basic grammar significantly enhances writing skills in two major ways. First, it brings clarity, ensuring that the writer’s intended meaning is conveyed accurately without ambiguity. Second, it builds credibility; correct grammar makes writing appear more professional and trustworthy, causing the reader to take the ideas presented more seriously. It is the foundation for effective and persuasive communication.
7. What are the four forms of the present tense with examples?
The four forms of the present tense describe actions happening at different moments in the present:
- Simple Present Tense: Used for habits, universal truths, or regular actions. Example: She reads every day.
- Present Continuous Tense: Used for actions happening right now. Example: He is playing outside.
- Present Perfect Tense: Used for actions that started in the past but are still relevant to the present. Example: They have finished their homework.
- Present Perfect Continuous Tense: Used for actions that started in the past, are still continuing, and may continue into the future. Example: I have been waiting for an hour.
8. Besides a verb, what other part of speech is essential to form a complete sentence?
Besides a verb, a subject is essential to form a complete sentence. A sentence must express a complete thought, and to do so, it needs a subject (a noun or pronoun that performs the action) and a verb (the action or state of being). For example, in the sentence 'Birds fly,' 'Birds' is the subject and 'fly' is the verb. Without both of these core components, you only have a fragment, not a complete sentence.















