The Basic Components of an Email System
E-mail stands for Electronic Mail or Electronic Mailer. The most commonly used feature of the networks in the field of communication is e-mail. Electronic mail in computer networks enables the exchange of messages and files between users through interconnected systems over the internet. Communication can take place between two to many users. It not only sends the message in text format, but also we can add images, and documents in the form of PDFs, videos, or other attachments.
The person who has to send a certain message is called the sender and the one who receives it is called the receiver. To have successful communication, each user should have a unique email address (it is just like posts, where each post is sent to persons with a unique home address). The e-mail address may look something like this, which is an electronic mail example.
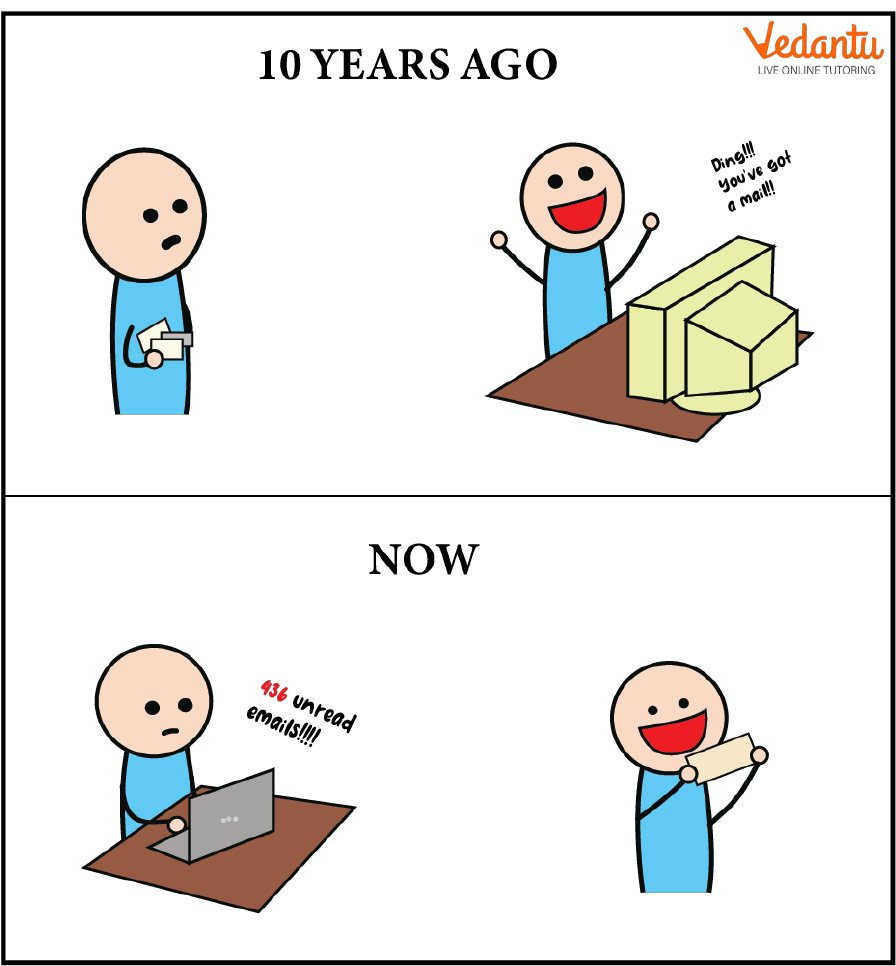
Copy of the Extent of Email Used Today
The Basic Components of an Email System
Electronic mail architecture refers to the system and components involved in sending, receiving, and storing email messages over a network.
User Agent (UA): It is the software or application (like Gmail, Outlook) that allows users to compose, read, and manage their emails. It provides a user-friendly interface to interact with the email system.
Message Transfer Agent (MTA): It is the system that transfers emails from the sender's server to the recipient's server.It ensures the email is routed correctly using protocols like SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
Mail Box: It is the storage space where incoming emails are stored on the server for a specific user. Each user has a unique mailbox to hold their emails until they access them.
Spool File: It is a temporary storage location where outgoing or undelivered emails are stored. The MTA processes emails in the spool file and sends them when the recipient’s server is available.
When was the First Email Sent?
E-mail is much older when compared to the internet. The first-ever e-mail was sent to computers in 1965 by using the MIT program called a mailbox. By using this program the user can type a message and send it. Whereas the receiver can see the message only after logging in to the computer.
Whereas in 1969 the first message using ARPANET was sent from computer to computer by the US Department of Defence.

The First Message was Sent using ARPANET
Who Invented Electronic Mail and What was the First Message Sent Using ARPANET?
Later in 1972, Ray Tomlinson developed the ARPANET into ARPANET’s networked e-mail system and invented electronic mail. It is the one that we use today. Here his contribution was “@” which indicated the destination address of the message to be sent. It got tremendous popularity as people wondered how one can send an electronic mail to the others who are completely not present in the same place.
In 1993, internet use increased and electronic mail was replaced by “E-mail”. Then Yahoo, Hotmail, AOL (America Online), and Echomail platforms were launched. Whereas the year 2004 completely changed the history of E-mail with the launch of Gmail (a platform to send an email).
The overall history of e-mail in computer networks can be something like this,

History of E-mail
Mailing Format
An electronic mail diagram illustrates the flow of messages, including key components like the envelope, header, and body of the email. The E-mail can be divided into three main components:
Message Envelope
Message Header
Message Body
Message Envelope
Message Header
Message Body

E-mail Format

Structure of Email
Types of Email
Emails are broadly classified into three categories:
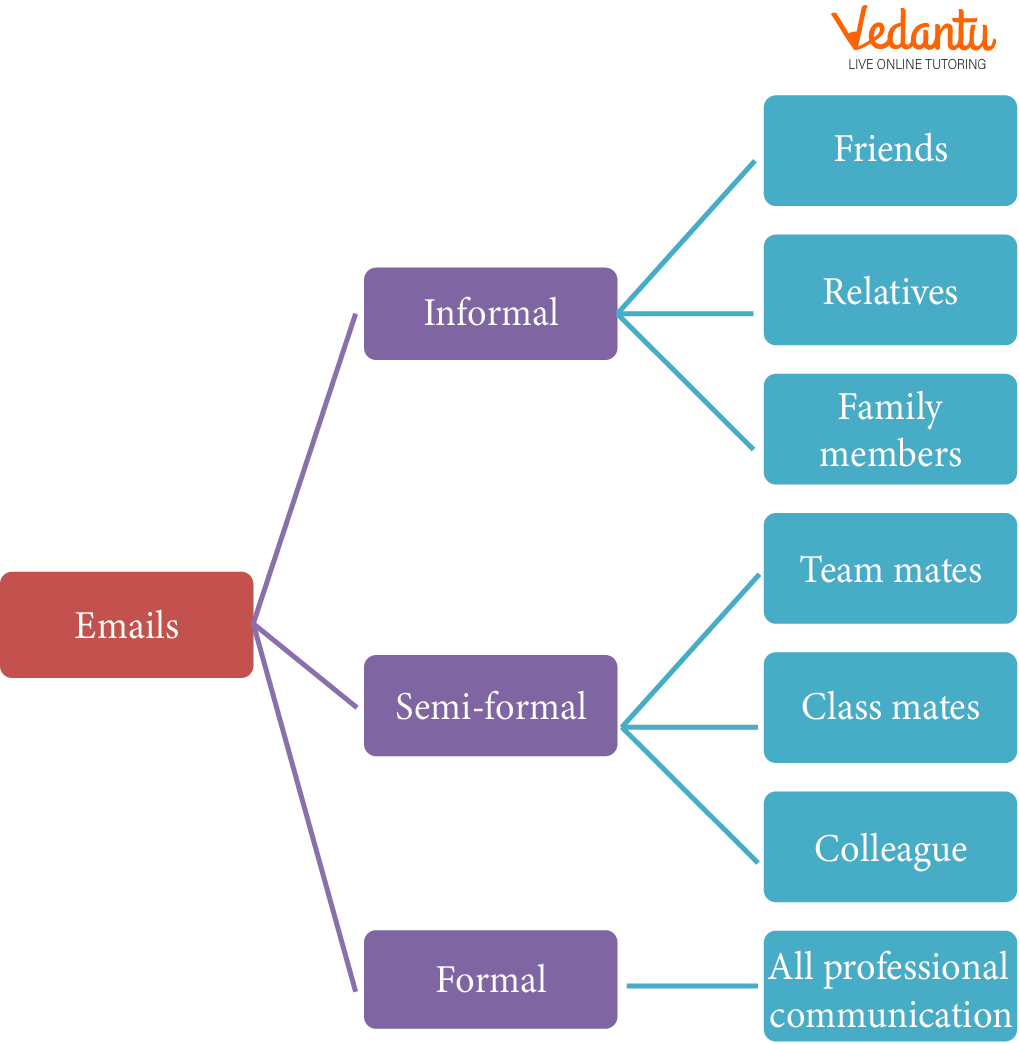
Types of Emails
Informal: It is sent to friends and family. There are no rules for writing an email of this type, and one can use any language.
Semi-formal: It is sent to colleagues and teammates. We can use simple language here, and the messages can be casual or friendly in nature.
Formal: It is used to communicate to the government department, schools, businesses, or any officers. Here certain rules have to be followed like text should be in respectful language. You shouldn’t add any unwanted things like jokes, funny text, etc. Writing a subject is always mandatory.
How to Send a E-Mail
Open Your Email App: Use an email app like Gmail, Outlook, or any other service you use.
Click on "Compose": Look for the "Compose" or "New Email" button to create a new email.
Enter the Recipient's Address: In the "To" field, type the email address of the person you want to send it to.
Add a Subject: Write a brief and clear subject line to let the recipient know the email's purpose.
Write the Email Body: Type your message in the main body section. Be polite and clear.
Add Attachments (Optional): If needed, click the paperclip icon to attach files, images, or documents.
Review Your Email: Check for any spelling mistakes, missing information, or attachments.
Click "Send": Once everything looks good, press the "Send" button to deliver your email.
What are the Types of Emails?
Onboarding Emails: These are sent to new users or customers to guide them on how to use a product or service. They often include welcome messages, setup instructions, or tips to get started.
Newsletters: Regular emails sent to subscribers to share updates, news, or valuable content. Examples include blogs, industry insights, and company announcements.
Promotional Emails: These emails are designed to advertise products, services, or special offers. They aim to attract customers with discounts, deals, or new launches.
Transactional Emails: These are triggered by a user’s actions, like confirming a purchase, resetting a password, or shipping notifications. They provide essential and specific information related to a transaction or activity.
Follow-Up Emails: These are sent after a specific interaction, like a meeting, event, or sales inquiry. They aim to maintain communication, provide additional details, or seek feedback.
Survey or Feedback Emails: These emails ask recipients to share their opinions or experiences. Companies use them to improve products, services, or overall customer satisfaction.
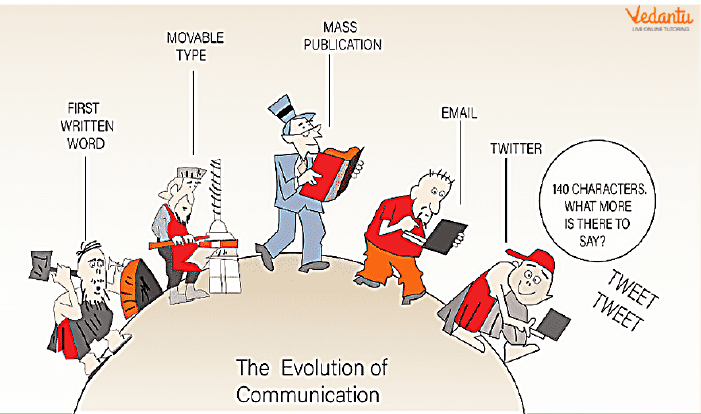
Evolution of Communication
Uses of Email?
The uses of electronic mail include communication, file sharing, professional use, record keeping, notification, and collaboration.
Communication: Email allows people to send and receive messages instantly across the world.
File Sharing: It makes it easy to share documents, images, and other files with others.
Professional Use: It is commonly used for business communication, sending resumes, and official correspondence.
Record Keeping: Emails act as a digital record of conversations and shared information.
Notifications: Companies and services use email to send updates, alerts, and reminders.
Collaboration: Teams can coordinate and share information effectively through email.
In short, email is a fast, reliable, and versatile way to connect and share information.
The Basic Components of an Email System
User Agent (UA): It is the software or application (like Gmail, or Outlook) that allows users to compose, read, and manage their emails. It provides a user-friendly interface to interact with the email system.
Message Transfer Agent (MTA): It is the system that transfers emails from the sender's server to the recipient's server. It ensures the email is routed correctly using protocols like SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol).
Mail Box: It is the storage space where incoming emails are stored on the server for a specific user. Each user has a unique mailbox to hold their emails until they access them.
Spool File: It is a temporary storage location where outgoing or undelivered emails are stored. The MTA processes emails in the spool file and sends them when the recipient’s server is available.
Advantages and Disadvantages of E-mail
Email Etiquette
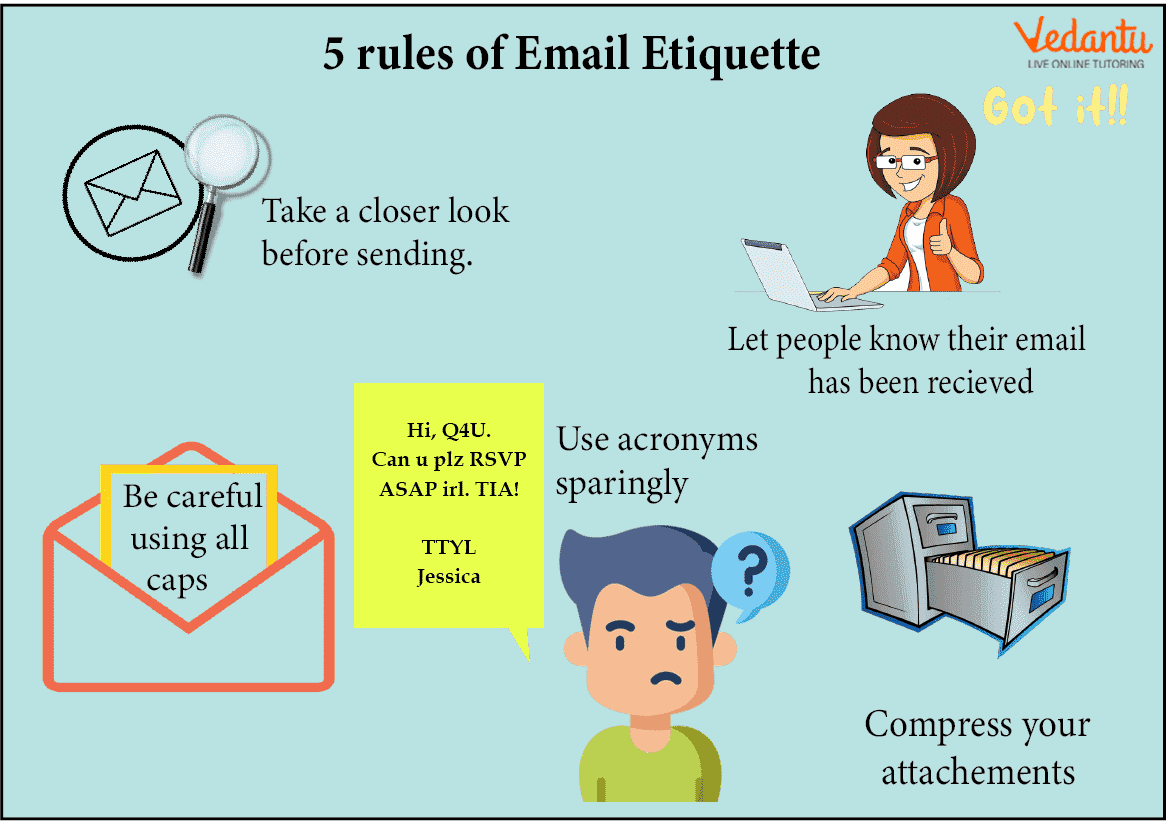
Email Etiquette
Interesting Facts
The first spam message was sent to the ARPANET in the year 1978.

Scariest Facts about Email
The first email message sent was “Hello, have a good day!”.
Summary
Email or Electronic mail is the most common form of communication either formally or informally. However, all the types of communication through email may sound similar but if we follow certain rules then the messages are conveyed easily, highlighting the advantages of electronic mail.
Learning by Doing
1. Solve the given puzzle.
Solve the Given Puzzle


FAQs on Understanding E-mail: Definition, History, and How to Send One
1. Write the difference between SMS and Email.
Even though SMS and email do the same job there are some differences between them,
SMS | |
Only short messages can be sent. | Can send longer messages. |
Can only send text messages. | Can send files, images, and videos, along with text messages. |
Usage of the internet is not required. | An Internet connection is required. |
2. What are the steps to be followed to create an email?
Email can be created by following simple steps,
Firstly add the email address of the receiver.
Keep the subject, it should be the summary of the overall email. For example, if you are sending an email inviting a person to a meeting then the subject should be the purpose of the meeting.
Next comes the body of the message, starting with a greeting formally. For example Hello or Good morning.
Add the message you want to send, including images or any files if required.
Conclude by adding a signature at the end.
3. Write an introduction mail.
To: ABC
CC/BCC:
Subject: My introduction
Dear students,
I am XYZ, I am your new Biology professor. I am from Bangalore, I am very much excited to meet you all in the class tomorrow.
Thanks and Regards
LMN
(Biology Professor)
4. What is electronic mail security?
Electronic mail security refers to measures taken to protect email communication from unauthorized access, fraud, and cyber threats.
5. What are CC and BCC in an email?
CC (Carbon Copy) sends a copy of the email to others, while BCC (Blind Carbon Copy) hides recipients' addresses from others.
6. What is a subject line in an email?
The subject line is a brief summary of the email’s purpose, shown before opening the message.
7. What is the difference between Inbox and Spam?
The Inbox stores valid emails, while the Spam folder holds unwanted or suspicious messages.
8. What is the importance of an email signature?
An email signature adds your name, title, contact details, or a professional touch at the end of your email.
9. What is an email draft?
A draft is an unsent email saved for future editing or sending.
10. What does "Reply All" mean in an email?
"Reply All" sends your response to the sender and all other recipients of the original email.