
Control and Coordination Class 10 Extra Questions and Answers Free PDF Download
The important questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 control and coordination will help the students to prepare for their examination in an ordered way. These control and coordination Class 10 important questions are written in a simple and easy-to-understand way by the subject matter experts at Vedantu. To enable the students to get a fair idea of the chapter, students can rely on Chapter 6 Science Class 10 important questions. Students can use these for their exam preparation as important questions are made according to the priority of topics in the examination. Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths and Science Students who are looking for better solutions can download Class 10 Maths NCERT Solutions and Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions to help you to revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science Control and Coordination - 2025-26



Study Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Control and Coordination
Very Short Answer Questions (1 Mark)
1. Junctions of two neurons are called.
Synapse
Synapsis
Joint
Junction
Ans: a) Synapse
2. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
Insulin
Thyroxin
Oestrogen
Cytokinin
Ans: d) Cytokinin
3. When a person is suffering from severe cold, he or she cannot –
Differentiate the taste of an apple from that of an ice – cream.
Differentiate red light from the green light.
Differentiate a hot object from a cold object.
Differentiate the smell of perfume from that of an agarbatti
Ans: (d) Differentiate the smell of perfume from that of an agarbatti.
4. What do you mean by geotropism?
Ans: The growth of a plant due to Gravitational force is called geotropism. Growth in the direction of the force (downward) is known as positive geotropism and the growth in the direction opposite to the force (upward) is known as negative geotropism.
5. Name the two sets of nerves that constitute the peripheral nervous system.
Ans: The two sets of nerves that constitute the peripheral nervous system are
Sympathetic nervous system
Parasympathetic nervous system.
6. The brain is lodged inside the cavity of the skull known as:
Piamater
Duramater
Cranium
Meninges
Ans: c) Cranium
7. The electrical impulse travels in a neuron from –
Dendrite $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end $\to $ Cell body
Cell body $\to $ Dendrite $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end
Dendrite $\to $ Cell body $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end
Axonal end $\to $ Axon $\to $ Cell body $\to $ Dendrite
Ans: Dendrite $\to $ Cell body $\to $ Axon $\to $ Axonal end
8. Which hormone brings about the development of the mammary gland?
Estrogen
Progesterone
Relaxin
Oxytocin
Ans: Estrogen
9. Name the hormone which promotes plant growth.
Ans: The hormone which promotes plant growth is auxin.
10. Which part of the brain maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body?
Ans: The part of the brain which maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body is the cerebellum.
11. Which one of the endocrine glands is known as the master gland?
Pituitary
Adrenal
Thyroid
Parathyroid
Ans: a) Pituitary
12. The growth of tendrils in pea plants is due to
effect of light
effect of gravity
rapid cell division in tendrillar cells in contact with the support
rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
Ans: d) rapid cell divisions in tendrillar cells that are away from the support
13. Dwarfism results by –
Excess secretion of thyroxin
Less secretion of growth hormone
less secretion of adrenaline
Excess secretion of growth hormone.
Ans: b) Less secretion of growth hormone.
14. Write the function of the hormone “thyroxine” produced in our body.
Ans: Thyroxine produced in our body controls the overall metabolic rate of the body, it plays a vital role in digestion, muscle function, brain development, heart, and maintenance of bones.
15. Name the hormones secreted by the pancreas.
Ans: The hormones secreted by the pancreas are:
Insulin
Glucagon
16. The neurons that carry nerve impulses from the spinal cord to effectors are called –
Sensory neurons
motor neurons
Interneurons
spinal neurons
Ans: Motor neurons.
17. Select the mismatched pair
Adrenaline – Pituitary gland
Testosterone – Testes
Estrogen – Ovary
Thyroxine – Thyroid gland.
Ans: Adrenaline – Pituitary gland.
18. Which one of the following is a nastic movement in plants?
Bending of plants towards light
Growing of roots towards gravity.
Dropping of touch – me – not leaflets on touch
Movement of pollen tubes towards chemicals.
Ans: Dropping of touch – me – not leaflets on touch
19. What is the function of the occipital lobe?
Ans: The function of the occipital lobe is visual perception. It includes:
Distance
Depth perception
Color determination
Object recognition
Movement, etc.
20. Which part of the brain links the endocrine system with the nervous system?
Ans: Hypothalamus is the part of the brain which links the endocrine system with the nervous system.
21. The visceral nervous system controls and integrates the function of –
Urinary bladder
Blood vessels
Heart
All of the above
Ans: d) All of the above
22. Which of the following statements are true about the brain?
The main thinking part of the brain is the hindbrain.
Centers of hearing, smell, memory, sight, etc are located in the forebrain.
Salivation, vomiting, and blood pressure is controlled by the medulla in the hindbrain.
The cerebellum does not control the posture and balance of the body.
(i) and (ii)
(ii) and (iii)
(i), (ii) and (iii)
(iii) and (iv)
Ans: b) (ii) and (iii)
23. The substance that results in the fall of mature leave and fruits from plants is due to:
Auxin
Gibberellins
ABA
Cytokinin
Ans: c) ABA
24. Name the structural and functional unit of the nervous system.
Ans: The structural and functional unit of the nervous system is the neuron (nerve cell).
25. Name one sex hormone.
Ans: An example of a sex hormone is testosterone.
26. Which part of the brain maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body?
Ans: The cerebellum is the part of the brain which maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body.
27. Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Ans: A plant hormone that promotes the growth of cells is auxin.
28. Which of the following is a plant hormone?
Insulin
Thyroxin
Oestrogen
Cytokinins
Ans: (d) Cytokinins
29. The gap between two neurons is called a
Dendrite
Synapse
Axon
Impulse
Ans: (b) synapse
30. The brain is responsible for
Thinking
Regulating the heartbeat.
Balancing the body
All of the above.
Ans: (d) all of the above.
31. What name is given to the microscopic gap between two adjacent neurons?
Ans: The microscopic gap between two adjacent neurons is known as the synapse.
32. If we step on something sharp accidentally, we move our foot away at once. What is this type of response known as?
Ans: This type of response is known as a reflex action.
33. Apart from the hindbrain, activities like walking, skating, riding a bicycle, and picking up a pencil are possible. Name this part of the hindbrain.
Ans: The cerebellum is the part of the brain which maintains the posture and equilibrium of the body.
34. Name the plant hormone:
a. Which inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves.
Ans: Abscisic acid inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves.
b. Which promotes cell division.
Ans: Cytokinin promotes cell division.
35. Who transmits nerve impulses across the synapse?
Ans: Neurotransmitters are responsible for transmitting nerve impulses across the synapse.
36. Give the reason why endocrine glands release theft secretions into the blood?
Ans: Endocrine glands are ductless glands and hence instead of pouring their hormones into ducts, they release theft secretions into the blood.
Short Answer Questions (2 Marks)
1. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans: Difference between reflex action and involuntary action is given below:
Involuntary Action | Reflex Action |
It is the set of muscle movement which do not require thinking. | It is rapid and spontaneous action in response to any stimulus. |
It is controlled by the brain. | It is controlled by the spinal cord. |
Example – breathing, digestion | Example- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand after touching something hot. |
2. Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Ans: Iodine is a trace element and a necessary substrate for thyroid gland hormone synthesis. It is required by the thyroid gland to make thyroxine hormone. The use of iodised salt is advisable because it provides iodine needed by the thyroid gland to make sufficient thyroxine for our body that helps prevent risk of goitre.
3. Name the centre of the brain that controls
Swallowing
Ans: Medulla oblongata in hind brain controls swallowing.
Hearing
Ans: Cerebrum in forebrain controls hearing.
4. Represent schematically the path of a reflex action.
Ans: The path of a reflex action is represented below:
5. Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Ans: Some patients of diabetes are treated by giving injections of insulin because insulin hormone regulates the levels of sugar in the blood. In diabetic patients, insulin hormone is not secreted by pancreas in the required amount and therefore blood sugar level rises.
6. Which signal will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Ans: Spinal cord controls the reflex actions. And hence, the effects of spinal cord injury are:
Disturbed involuntary actions.
Disturbed reflex actions.
Inability of the quick response required to safeguard the body.
7. How does a touch – me – not plant respond to touching? What is this movement called?
Ans: Touch – me – no plant responds to touching by folding its leaflets and this type of movement is called growth independent movement i.e., the movement of plants that do not result in their growth.
8. What are phytohormones? Name them.
Ans: Phytohormones are synthesized at sites away from where they act. They diffuse to the area of action and help to co – ordinate growth, development and responses to the environment. Phytohormones are –
Auxin
Gibberellins
Cytokinin
Abscisic acid
Ethylene.
9. What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Ans: A reflex action is a rapid and spontaneous action in response to any stimulus. It is controlled by the spinal cord. Example- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand after touching something hot. The reflex action is instant where thinking is not involved and hence the brain has no role. Although the information also goes on to the brain where the encounter remains the memory and makes us aware of our actions.
10. How is control and coordination between the environment and plants brought about?
Ans: Plants responses are of two types
Growth dependent – They are due to cell divisions.
Growth independent response – They are due to change in the amount of water.
Plants do not perform control & coordination like animals but they give responses to external stimuli like touch, light, and chemicals, etc.
11. Give two examples of functions in plants that are regulated by light.
Ans: The two functions in plants that are regulated by light are:
Seed germination - Breaking of dormancy
Photosynthesis – Respiration process
12. What is coordination? Give an example.
Ans: Coordination is a process through which two or more organs interact and complement the functions of one to adjust the vital activities of life. For example – under stressed conditions, the adrenal gland secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body.
13. How do endocrine glands help in maintaining feedback control?
Ans: The timing and amount of hormones released are regulated by the feedback mechanism. The endocrine system depends on the feedback system concerning hormones. There are two types of feedback systems –
Negative Feedback – This mechanism prevents deviation from the ideal mean value. For ex- less glucose levels in the blood do not induce the pancreatic cells to produce insulin so that less conversion of glucose to glycogen may occur.
Positive Feedback – These mechanisms promote deviation from the mean ideal value. For ex- High glucose level in the blood induces. The pancreatic cells produce insulin which converts glucose to glycogen.
14. Which types of glands in the human body secrete hormones? State any one location for them.
Ans: Three types of glands that secrete hormones in the human body are-
Exocrine gland – These types of glands have ducts that do not secrete their secretion into the blood. For example – the salivary gland.
Endocrine gland – These types of glands do not have ducts, they pour their secretion into blood. For example – The pituitary gland.
15. What is the result of hypothyroidism in children called?
Ans: The result of hypothyroidism in children is known as exophthalmic goiter. The exophthalmic goiter results in bulging of eyes, increased blood pressure, and heartbeat.
16. How is flowering affected in plants by various hormones?
Ans: Flowering is affected in plants by various hormones such as auxins and cytokinin promotes female flowers while gibberellins promote male flowers. Duration of light affects flowering in long-day plants and short-day plants.
17. Name the fluid-filled between the meninges of the brain. What are its functions?
Ans: The fluid-filled between the meninges of the brain is known as the cerebrospinal fluid. Its function is to protect the brain from mechanical shocks.
18. Name any two heterocrine glands and mention their function.
Ans: The two heterocrine glands are:
Pancreas – Its endocrine function is to produce insulin and glucagon. Its exocrine function is to produce digestive enzymes.
Ovaries – Its endocrine function is to produce estrogen and progesterone hormone. Its exocrine function is to produce female gametes.
19. What is the response of the stem towards light & gravity?
Ans: Plants' growth response to gravity is known as gravitropism and to light is phototropism. The stem shows a positive response toward the light i.e., it grows in the direction of the light and it shows a negative response toward gravity i.e., it grows in the opposite direction of gravity.
20. Name two activities that are regulated by plant pigments.
Ans: The two activities that are regulated by plant pigments are:
The response to the photoperiodic stimulus – due to some specialized pigments and phytochromes.
The control and coordination in plants with their environment.
21. How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Ans: Olfactory receptors help us detect the smell of an agarbatti. When you smell the scent of an incense stick, it first reaches your nose, where it is detected by the olfactory receptors. It is then sent to the forebrain in the form of electrical signals. The forebrain then interprets these electrical signals as the smell of an incense stick.
22. What are plant hormones?
Ans: Hormones are the chemicals that help to coordinate growth, and development. Plant hormones are the chemicals that help to coordinate growth, development, flowering and response to the environment in plants. For example – auxins, gibberellins, abscisic acid (ABA), cytokinin, etc.
23. How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Ans: In the movement of leaves of sensitive plants, growth is not involved and movement is away from the source. Whereas, in the movement of shot towards light, growth is involved and movement is towards the source.
24. How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Ans: The chemical coordination in animals is maintained by hormones which are secreted by endocrine glands.
25. Give one example of a plant part.
Which is positively hydrotropic as well as positively geotropic.
Ans: Roots are positively hydrotropic as well as positively geotropic.
Which is positively phototropic but negatively geotropic.
Ans: Stem is positively phototropic but negatively geotropic.
26. The neck of a person appears to be swollen.
Name the disease this person is suffering from.
Ans: The person is suffering from goitre.
Name the mineral whose deficiency in the diet causes this disease.
Ans: Deficiency of iodine in the diet causes this disease.
27. Taking the example of heart beat, justify the antagonistic action of the sympathetic and the parasympathetic nerves.
Ans: Antagonistic action of the sympathetic nerve – increases contraction and rhythm with respect to heart beat.
Antagonistic action of the parasympathetic nerve – decreases contraction and rhythm with respect to heart beat.
28. Why is abscisic acid known as stress hormone in plants?
Ans: Abscisic acid is known as a stress hormone in plants because unlike growth hormone, it inhibits growth and causes wilting of leaves.
29. Name the part of neuron
where information is acquired.
Ans: Dendrite is the part of the neuron where information is acquired.
through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
Ans: Axon is the part of the neuron through which information travels as an electrical impulse.
30. Why do leaves drop off seasonally?
Ans: The leaves drop off seasonally because of the cuts off supply of nutrients and water to leaves which happened due to stopped production of auxin.
31. A person suffered a head injury, due to which he faces breathing problems. No problem was detected with his respiratory system. What could be the cause of this problem?
Ans: A person suffered a head injury, faces breathing problems because he was injured in medulla oblongata. Medulla oblongata controls the respiratory system so he will be affected by breathing problems.
32. In a family of normal sized members, there are two exceptions, one member is dwarf and one is tall like “Khali”. What could be the cause of it?
Ans: Uneven heights in the family is caused due to malfunctioning of the growth hormone. In case of dwarfs, there is a deficiency of growth hormone whereas in case of giants there is an excess of growth hormone. Growth hormones are secreted from the pituitary gland.
33. Why do you blink your eyes as bright light is focused on you?
Ans: We blink our eyes as bright light is focused on us due to reflex action. It is done to protect the eye from bright light which otherwise would damage the retina. The amount of light that enters your eyes is controlled by the pupils. Hence, blinking the eyes cuts off the excessive light.
34. There is a polled plant in your drawing room, after a few days you notice that the plant has bent to one side. What could be the reason? How has this movement been coordinated?
Ans: The polled plant in your drawing room, after a few days bent to one side due to phototropic movement of the stem and it happens because of unequal growth of the stem on both sides which is initiated by the auxin hormone.
35. A leaf shaped gland is present above the intestine. The secretion of this gland regulates the metabolism of sugar in blood. Name the secretion and gland.
Ans: A leaf shaped gland that is present above the intestine and whose secretion regulates the metabolism of sugar in blood is the pancreas. The secretion is Insulin from special cells in it.
Short Answer Questions (3 Marks)
1. Mention three important functions of gibberellins.
Ans: Three important functions of Gibberellins are –
Stimulate stem elongation.
Help in breaking seed dormancy.
Promote production of male flowers.
2. What is the function of receptors in our body? What happens when receptors do not work properly?
Ans: The receptors detect information from the environment. If they do not work properly, the information will not be detected or will be detected late, due to which further process will be delayed and the signals will take time reaching the spinal cord or the brain. Hence, the response to the environmental stimulus will be delayed causing harm to the body.
3. What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Ans: Junctions of two neurons is called synapses. When a receptor detects a stimulus, chemicals is set off through the neurons. These electric signals travel from the dendrite of the presynaptic neuron to its cell body and then along its axon. At the end of axon of this neuron, the electrical impulse crosses the synapse and starts a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron.
4. What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Ans: The control and coordination in an organism is needed for the proper functioning of the body. It handles appropriate movement in response to any external stimulus.
Multicellular organisms have a complex body and hence it coordinates with various organs of the body of an organism working together in a proper manner to produce proper reaction to stimulus. For example – under stressed conditions, the adrenal gland secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body.
5. Pituitary is a master endocrine gland. Justify this statement.
Ans: Pituitary gland is a master gland because it regulates the secretion of other endocrine glands such as -
Growth hormones
Thyroid stimulating hormone
Adrenocorticotropic hormone
Follicle stimulating hormone
Luteinizing hormone
Prolactin
Pituitary gland is located at the base of the brain and is attached to the hypothalamus by nerve fibres and blood vessels. The pituitary gland consists of Anterior lobe and Posterior lobe.
6. Draw the structure of the neuron and explain its function.
Ans: The basic structure of a neuron has three components –
Cell body
Dendrites
Axon
Function:
Junctions of two neurons is called synapses. When a receptor detects a stimulus, chemicals is set off through the neurons. These electric signals travel from the dendrite of the presynaptic neuron to its cell body and then along its axon. At the end of axon of this neuron, the electrical impulse crosses the synapse and starts a similar electrical impulse in the dendrite of the next neuron.
7. How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Ans: Adrenaline is a hormone which is involved in regulating visceral functions. Adrenaline is normally produced both by the adrenal glands and by a small number of neurons in the medulla oblongata. Under stressed conditions, the adrenal gland secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body. The blood supply decreases from the skin and digestive system and increases to skeletal muscles.
8. Where are Pons and medulla oblongata located? Write their functions.
Ans: Pons and medulla Oblongata are located in hindbrain.
Function of Pons – it acts as a bridge between the brain and spinal cord.
Function of Medulla oblongata – it controls activities like salivation, swallowing, vomiting, breathing, coughing, sneezing, heartbeat, sleep, consciousness and activities of the cerebrum.
9. List the function of testosterone and estrogen. Where are they secreted?
Ans: Testosterone is secreted in male bodies.
Function of testosterone – It is responsible for development of male sex organs and secondary sex characteristics like moustache, beard & voice.
Estrogen is secreted in male bodies.
Function of estrogen – it is responsible for development of female sex organs and secondary sex characteristics like mammary gland and uterine growth.
10. Define ‘nerve impulse’. Which structure in a neuron helps to conduct a nerve impulse?
Towards the cell body?
Ans: Nerve Impulse is a wave of the passing of information through neurons in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Dendrite helps to conduct a nerve impulse towards the cell body.
Away from the cell body?
Ans: Nerve Impulse is a wave of the passing of information through neurons in the form of electrical and chemical signals. Axon helps to conduct a nerve impulse away from the cell body.
11. Differentiate between axon and dendrites?
Ans: Difference between axon and dendrites is:
Axon | Dendrons |
They are long. | They are small. |
It is only one. | They are numerous. |
They are unbranched. | They are branched. |
Terminal branches have swollen knobs. | Terminal swollen knobs are absent. |
Direction of the nerve impulse is away from the cyton. | Direction of nerve impulse is towards the cyton. |
12. Mention the structure of the human brain.
Ans: The structure of human brain is outlined below,
13. What are tropic movements? Name the types of tropic movements in plants.
Ans: Tropic movement is the bending or movement of a part of a plant in response to the external stimulus. The types of tropic movements in plants are:
Phototropism – response to light.
Geotropism – response to gravity
Chemotropism - response to chemicals.
Hydrotropism – response to water.
14. Name the different lobes of cerebrum.
Ans: There are four lobes of cerebrum –
a) Frontal lobe – The part of the brain associated with reasoning.
b) Parietal lobe – The part of the brain associated with perception of general sensation s like pressure, touch and pain.
c) Occipital lobe – The part of the brain associated with visual perception.
d) Temporal lobe – The part of the brain associated with formation of memory and interpretation of sound and the language.
15. How do auxins promote the growth of tendril around a support?
Ans: Auxin present in the plants is a growth hormone. When the tip of a tendril touches a support, auxins in its tip move away from the support. Hence, the side of the tendril away from the support grows faster and becomes longer than the side which is in contact with the support and makes the tendril curve towards the support.
16. Write different between exocrine and endocrine glands.
Ans: Difference between endocrine and exocrine gland is given below:
Endocrine Gland | Exocrine Gland |
They do not have ducts. | They have ducts. |
They secrete hormones. | They secrete enzymes. |
They pour their secretion into the ducts. | They pour their secretion into the blood. |
They are located away from the site of action. | They are located near the site of action. |
17. What are the different kinds of neurons?
Ans: There are three different kinds of neurons –
Sensory neurons – their work is to convey impulses from receptors to the main nervous system.
Motor neurons – their work is to carry impulses from the main nervous system to an effector.
Connecting (Relay) neurons – their work is to connect sensory and motor centres.
18. You have touched a hot object. Represent diagrammatically the path that leads to a response, i.e., quickly pulling back the hand.
Ans: The diagrammatic representation of the path that leads to a response when we touch a hot object is as below,
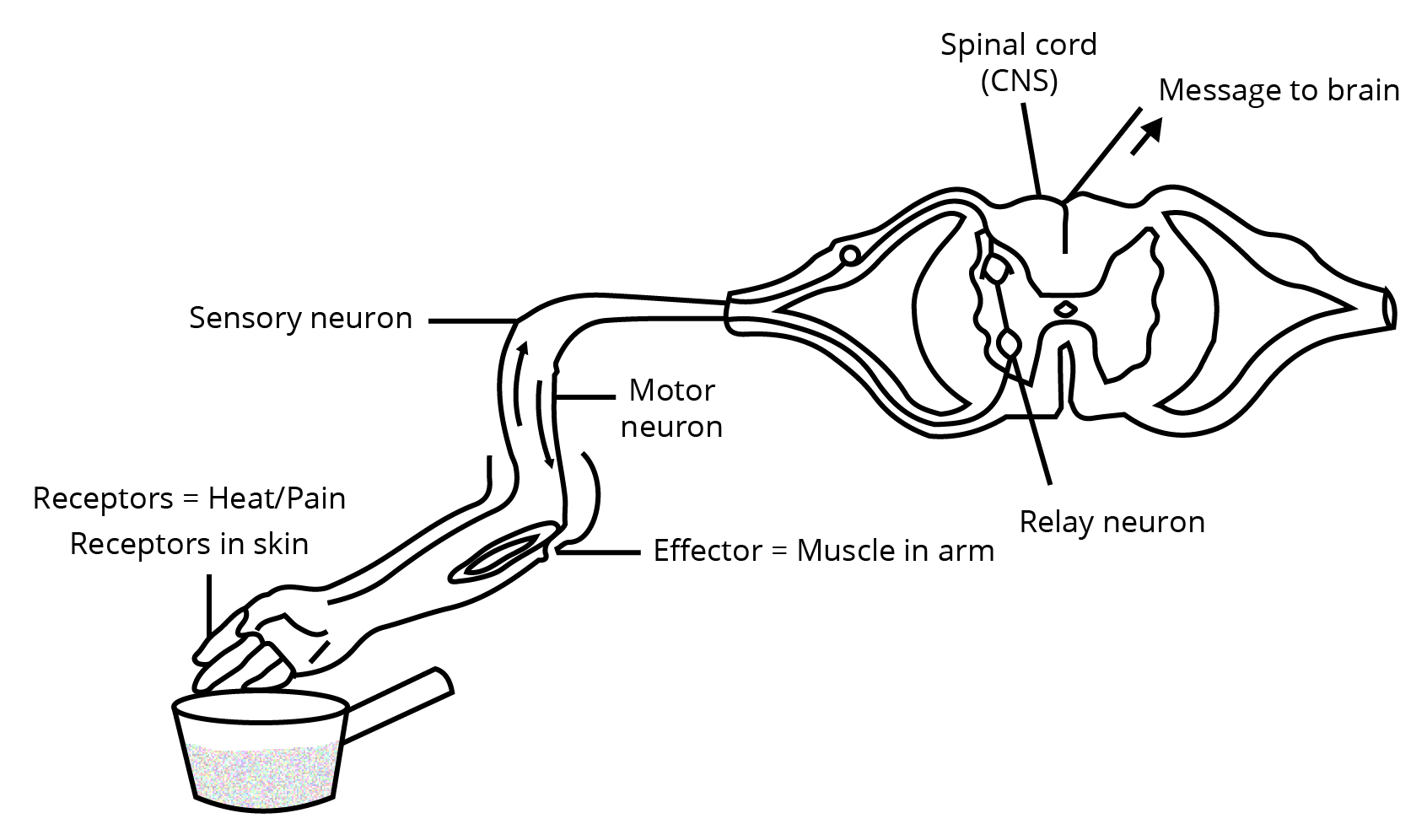
19. Nervous and hormonal system together performs the functions of control and coordination in human beings. Justify the statement.
Ans: Nervous and hormonal systems together perform the function of control and coordination in human beings. Under stressed conditions, the stimulus is being perceived by the Central Nervous System which stimulates the adrenal gland that secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body. The blood supply decreases from the skin and digestive system and increases to skeletal muscles.
20. What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Ans: Difference between reflex action and walking is given below:
Reflex Action | Walking |
It is controlled by the spinal cord. | It is controlled by the cerebellum. |
It is instant. | It involves thought process. |
It is an involuntary action. | It is a voluntary action. |
21. Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Ans: To demonstrate hydrotropism, take a tin box and make a hole its bottom. Fill the tin with moist saw dust and sow some gram seeds in it. In the next step, when the seed starts germinating, keep the tin box in a tilted position. After some time when you water the tin, you will observe that the radicle moves towards the wet saw dust which demonstrates positive hydrotropism.
22. How does phototropism occur in plants?
Ans: Movement of shoot towards light is called phototropism. This movement is caused due to more growth of cells towards the shaded side of the shoot as compared to the side of the shoot towards light. More growth of cells is due to secretion of auxin towards the shaded side.
23. How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Ans: Unlike animals, plants do not have a nervous system. Chemical coordination in plants is maintained by plant hormones also known as phytohormones. Some plant hormones are auxin, Gibberellins, Cytokinin etc. When sunlight falls on the side, the auxins hormone causes the shady side of the shoot to grow faster. Cytokinin is responsible for the cell division.
24. How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Ans: Difference between involuntary and reflex actions is given below:
Involuntary Action | Reflex Action |
It is the set of muscle movement which do not require thinking. | It is rapid and spontaneous action in response to any stimulus. |
It is controlled by the brain. | It is controlled by the spinal cord. |
Example – breathing, digestion | Example- Sudden jerky withdrawal of hand after touching something hot. |
25. Compare and contrast nervous system and hormonal control and coordination in animals.
Ans: Difference between nervous control and hormonal control is given below:
Nervous Control | Hormonal Control |
Work is done by the nervous system. | Work is done by hormones. |
Short lasting response | Long lasting response |
Not specific | Highly specific |
26. What is the difference between the manner in which movement takes place in a sensitive plant and movement in our legs?
Ans: Difference between movement in a sensitive plant and movement in our legs is given below:
Movement in a sensitive plant | Movement in our legs |
No specialized tissue | Specialized nervous tissue |
Change shape depending upon the amount of water in them. | Contract or relax by the movement. |
Do not have specialized proteins. | Have specialized proteins. |
27. On touching a hot plate, you suddenly withdraw your hand. Which category of neurons became active first and which one next?
Ans: Suddenly withdrawing the hand on touching a hot plate is an example of reflex action. Hence, first the sensory neurons are activated, which take the information to the spinal cord. After that, the motor neurons become active and bring the impulses from the brain to the muscles.
28. How does the plant shoot bends, when the plant is placed in a room having only one open window?
Ans: The shoot of the plant bends towards the direction of light when the plant is placed in such a room that has only one open window and this happens due to the auxin which is a plant growth hormone. Auxin diffuses towards the shady side of the shoot and stimulates the cells to live longer on the side of the shoot which is away from light.
29. Give a reason to explain why
adrenaline helps in dealing emergency situations?
Ans: Under stressed conditions, the stimulus is being perceived by the Central Nervous System which stimulates the adrenal gland that secretes the adrenaline hormone which prepares the body to face the emergency by increasing the breathing rate and heartbeat so that more oxygen can be supplied to the body. The blood supply decreases from the skin and digestive system and increases to skeletal muscles.
secretions of growth hormone should be specific in the human body?
Ans: Secretions of growth hormone should be specific in the human body because if growth hormones are secreted in excess quantity then it will lead to gigantism while the less secretion of this hormone causes dwarfism.
30. A man becomes unconscious due to head injury. A pin is pricked on his foot, he withdraws his foot. Why? Explain.
Ans: Withdrawal of the foot when a pin is pricked on the foot is an example of the reflex action and reflex actions are controlled by the spinal cord and not by the brain. Hence, although being injured on the head, the person will withdraw his foot.
Long Answer Questions (5 Marks)
1. Compare nervous and hormonal mechanism for control
Ans: Difference between nervous control and hormonal control is given below:
Nervous control | Hormonal control |
Work is done by the nervous system. | Work is done by hormones. |
Short lasting response | Long lasting response |
Not specific | Highly specific |
Made up of neurons | Made up of secretory cells |
Messages transferred in the form of electrical signals. | Messages transferred in the form of chemical signals. |
Transferred along nerve fibres | Transferred along blood stream |
Messages travel quickly | Messages travel slowly |
2. Mention one function for each of these hormones.
Thyroxine
Ans: Thyroxine controls the overall metabolic rate of the body.
Insulin
Ans: Insulin converts glucose to glycogen in liver and muscles and controls the blood sugar level.
Adrenaline
Ans: Adrenaline increases heartbeat and blood pressure.
Growth hormone
Ans: Growth hormones are responsible for body growth and development of bones.
Testosterone.
Ans: Testosterone is the male hormone and develops male sex organs and secondary sex characteristics like moustache, beard and voice.
3. Write the following:
What are hormones?
Ans: Hormones are chemical substances which help in growth, control and coordination of a living organism. They are secreted in very small amounts by endocrine glands.
list four characteristics of hormones
Ans: Four characteristics of hormones are –
They are required in very less amounts.
Hormones are specific in their function.
They act away from the site of production.
Deficiency or over secretions of hormones have negative effects in the body.
4. Describe Nervous systems in humans.
Ans: A flow chart of the human nervous system is given below:
Download Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 PDF
Control and Coordination Class 10 Important Questions - Summary
Control and coordination Class 10 important questions include the topic namely nervous system muscular tissue correlation. This chapter also explains human brain anatomy, tissue protection, and nervous tissue action. It also gives brief information about animals and plants chemical coordination. The human body is a complex machine, which performs a ton of functions and processes to maintain and sustain human life. Living organisms must use systems providing chemical control and coordination. Keeping the general principles of body organisation in multicellular organisms. Specialised tissues are used to provide control and coordination activities.
Topics covered in Chapter 6 Science Class 10 important questions are - animal nervous system, reflex action, the human brain, coordination in the plant, response to the stimuli, movement due to growth, and also hormones in animals.
Nervous System - In the nervous system, neurons are the structural and functional unit of the nervous system. There are three parts in the neurons: dendrites, cyton/stoma/cell body and axon. Dendrites receive impulses from other neurons, cyton/soma processes the impulse. Axon transmits the impulse, either to another neuron or to muscles/glands, etc and it may be myelinated or unmyelinated. Nervous systems covered in the chapter are - central nervous system, peripheral nervous system, somatic nervous system, and autonomic nervous system.
Reflex Action - It is a sudden and involuntary reaction of the body in response to the stimuli. A reflex arc is a path followed by the electrical impulse during reflex action. The impulse travels from the receptor organ to the brain or spinal cord.
Plant Hormones and Movement - Control and coordination in plants is carried out by different hormones. Some of the plant hormones are auxin, cytokinin, gibberellins, abscisic acid and ethylene. There are two types of movement in plants: growth independent movements and growth-dependent movements. Growth related movements are also known as tropic movements. Some of the tropic movements are Phototropic movement (light dependent), Geotropic movement (gravity-dependent), Chemotropic movement (chemical-dependent), Hydrotropic movement (water-dependent), and Thigmotropic movement (touch dependent).
Endocrine System - Endocrine system in human secrets wide range of hormones for different functions. It consists of different glands like exocrine glands, endocrine glands, pituitary glands, thyroid gland, pancreas, adrenal gland, and gonads.
Benefits of Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 - Control and Coordination
Given below are a few benefits that students will gain by referring to the Important Questions for Class 10 Science Chapter 6.
The questions and solutions have been framed in a simple and easy-to-follow language. This has been done to aid students of all intellectual capabilities to ensure that they can prepare the chapter more effectively and perform excellently in their final exams.
Reading the chapter and learning the concepts are just the tip of the iceberg. To ensure you are prepared to score high marks in your exam, you need to practice the important questions of the chapter. This would in turn facilitate a better understanding of the topics covered in the chapter.
The questions and answers have been provided by our subject experts keeping in mind the latest CBSE exam pattern and updated syllabus to give you a real-time experience of the exams.
An important part of doing well in any exam is being good at time management skills. Solving the important questions while timing yourself will give you a fair idea of how prepared you are to appear for your actual exam.
To be sure that you aren’t taken by surprise when you face the actual question paper, it is strongly advisable that you solve the important questions. These important questions will help boost your confidence and improve your chances of scoring better marks in the exams.
Conclusion
After going through all Class 10 Science Ch 6 important questions, which provides fully solved solutions to all the questions, it helps the student to save time in their exam preparation. Class 10 Control and coordination important questions answers are designed in such a way that improves the confidence of the student by solving them. Before going through the important questions, let's go through the NCERT solutions of Class 10 Chapter 6. If you refer to all the Class 10 Science Chapter 6 important questions, you can easily score five marks in the board examinations.
Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 6
S. No | Important Study Material Links for Class 10 Science Chapter 6 |
1 | Class 10 Science Chapter 6 Control and Coordination Solutions |
2 |
Important Questions Chapter-wise Links for Class 10 Science
S. No | CBSE Class 10 Science Important Questions Links |
1 | |
2 | |
3 | |
4 | |
5 | |
6 | |
7 | |
8 | |
9 | |
10 | |
11 | |
12 |
Related Study Material Links for Class 10 Science
S. No | Important Links for Science Class 10 |
1. | |
2. | |
3. | |
4. | |
5. |
FAQs on CBSE Important Questions for Class 10 Science Control and Coordination - 2025-26
1. Explain the nervous system according to Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science.
The nervous system is considered to be the most complex part of the body. The main function of the nervous system is to transmit signals to and from different parts of the body, the nervous system coordinates all the actions and sensory information. It is made up of the brain which acts as the control centre, the spinal cord which is the highway from the brain and all the nerves which carry the messages. The nervous system reacts to all the changes inside and outside the body.
2. What is control and coordination according to Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science?
In class 10 science, one of the most compelling chapters is Control and coordination. It is the seventh chapter of the class 10 science NCERT textbook. According to this chapter, control refers to the power of restraining and regulating a process. It even refers to the power of regulating pace in order to go fast, slow down, or stop completely. Whereas, Coordination refers to the process of different systems of an organism working together in order to create an appropriate stimuli reaction.
3. How can I ace Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science?
Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science is one of the most important chapters. It is one of the most scoring chapters for the CBSE Students. The simplest way of acing this chapter is by understanding the topics thoroughly. Using Vedantu’s Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science NCERT Solutions, students will gain more perspective and it will enrich their skills of learning. Using NCERT Solutions, students can solve practice papers which will give them more clarity on topics each individual student needs to concentrate on. This way a student can achieve the goal easily.
4. What do you mean by Reflex action according to Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science?
Reflex action is an important concept for class 10 Science. Reflex action is a fast, involuntary, spontaneous reaction to stimuli. It helps to reduce the damage to the body from any potentially harmful conditions. An example of a reflex action is touching something hot. As soon as you touch something hot, you spontaneously move it away from the hot object (this is reflex action). It is a very essential action for the survival of many organisms. A reflex action does not need any input or thought.
5. What are the important questions for Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science?
Chapter 6 of Class 10 Science is a very important chapter from the examination point of view. Using Vedantu’s Class 10 Chapter 6 Science important questions, students will have an upper hand in understanding the concepts and covering all the important aspects of each chapter. This will help all students wanting to score maximum marks, as all the important concepts and topics are organised. This will help students to prioritise the topics they need to concentrate on and perform better. The solutions or any study materials provided by Vedantu are absolutely free of cost.














 Watch Video
Watch Video
















