




An Overview of Class 10 Chemistry Types Of Reactions Experiment
Chemistry - Types of Reactions Experiment
One or more chemical compounds react to produce one or more products, the chemical reactions can be classified into: a) Combination reaction b) Decomposition reaction c) Displacement reaction d) Double Displacement reaction. The type of reaction is evident from the product of the chemical reaction.
Table of Content
Aim
Apparatus Required
Reactions between water and quicklime
Effect of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals
The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution
Procedure
Observations
Results
Aim
To experimentally verify the types of reaction by performing and observing:
The reactions between water and quicklime.
The effect of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals.
The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution.
Apparatus Required
Test Tube
Beaker
Glass rod
Measuring Cylinder
Conical Flask
Spatula
Sandpaper
Iron nails
Test tube holder
Test tube stand
Bunsen burner
Test tube holder diagram
Theory
1. The reactions between water and quicklime
Calcium oxide is the chemical formula for quick lime (CaO). It reacts with water to produce calcium hydroxide [Ca(OH)2], also known as slaked lime.
CaO + H2O→Ca(OH)2 + heat
A combination reaction occurs when two substances combine to form one product.
Because heat is produced during the reaction, it is referred to as an exothermic reaction.
The slaked lime solution is basic because it turns red litmus to blue.
Lime water is another name for freshly prepared slaked lime.
When carbon dioxide gas is passed through it, it turns milky.
2. Effect of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals
The colour of ferrous sulphate crystals is light green. The crystallisation of water causes the colour.
The following changes occur when ferrous sulphate crystals are heated.
2FeSO4.7H2O (s)→Fe2O3 (s) + SO2 (g) + SO3 (g)+14H2O
The colour changes to brown, and gases are released as new compounds form.
A decomposition reaction occurs when a single compound decomposes to form three new compounds.
SO2 and SO3 gas turn moist blue litmus paper red, indicating that it is acidic.
SO2 has the following reducing property: When SO2 gas passes through acidified potassium dichromate, it changes its orange colour to green.
The crystals release crystallisation water.
Because SO2 gas has a choking odour, avoid inhaling it and keep the test tube's mouth away from your face.
3. The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution
Both sodium sulphate solution and barium chloride solution are colourless.
When the two solutions are mixed, a white precipitate is formed due to the formation of barium sulphate.
The reaction is known as a double displacement reaction because it involves the exchange of ions.
As barium sulphate is insoluble in water, it precipitates.
BaCl2 (aq) + Na2SO4 (aq)→BaSO4 (s) + 2NaCl (s)
Procedure
1. Reactions between water and quicklime
Take a clean beaker.
Add a small piece of lime to it.
Add water drop by drop into the beaker.
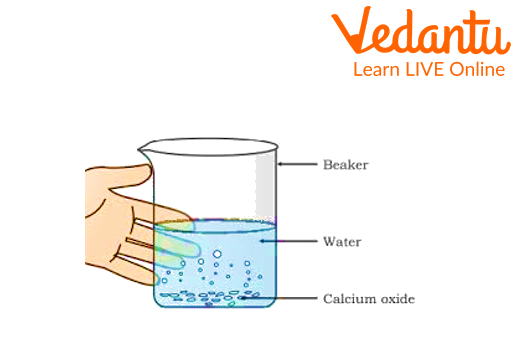
Reactions between water and quicklime
2. Effect of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals
a. Take a clean and dry test tube.
b. Add a few crystals of Ferrous Sulphate
c. Fix it on a test tube holder.
d. Heat the test tube on the burner, keeping the mouth of the test tube away from your face.
e. Waft the gas released to smell and test it with wet litmus paper.
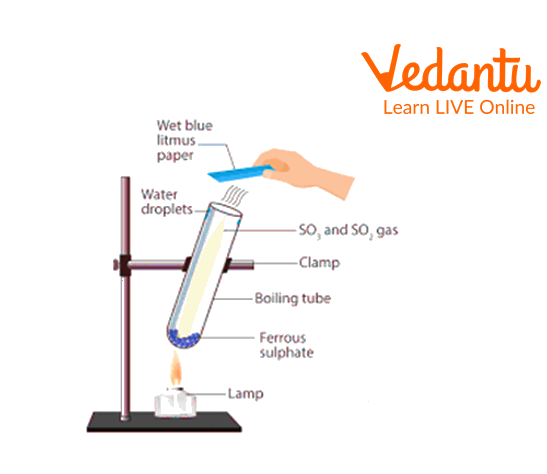
Effect of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals
3. The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution
a. In a clean test tube, take sodium sulphate solution, to this add barium chloride solution.
b. Shake the contents and observe.
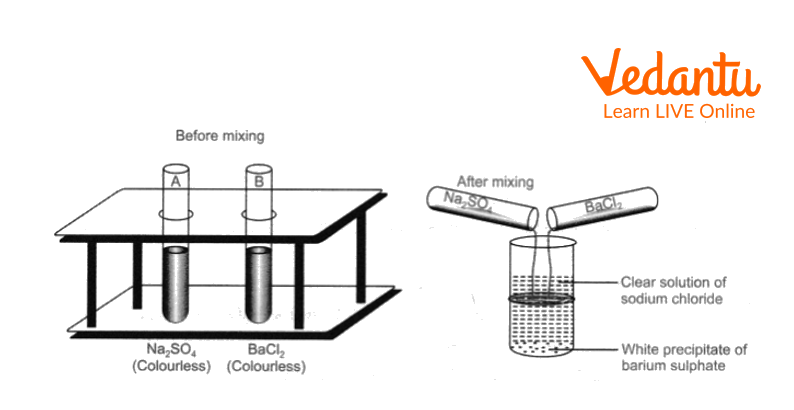
The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution
Observations
Result
Reactions between water and quicklime
Quick lime and water combine to form one product Calcium hydroxide, which is slaked lime along with the evolution of heat (exothermic reaction).
Hence, it's a combination reaction.
Effect of heat on ferrous sulphate crystals
Heating of ferrous sulphate crystals results in the decomposition of the compound into Fe2O3, SO2, and SO3.
As the decomposition is brought about by heating, it is called a thermal decomposition reaction.
The loss of water molecules from the ferrous sulphate crystals changes the colour from green to white.
The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution
A white precipitate of barium sulphate is formed upon mixing barium chloride and sodium sulphate, due to a double displacement reaction.
Precautions
Do not touch quicklime with your hands, use tongs.
Mixing quicklime and water releases a large amount of heat, so add water drop by drop and use a borosil beaker.
For heating, use hard glass tubes.
Never inhale any gas, just waft the gas.
Do not touch any chemicals with your hands.
Keep the mouth of the test tube away from your face while heating.
Lab Manual Questions
1. What is Quicklime?
Ans: Quick Lime is chemically known as Calcium Oxide (CaO)
2. What is the formula of ferrous sulphate crystals?
Ans: Chemical formula of ferrous sulphate - FeSO4.7H2O
3. What is the metal deposited on the iron nails when dipped in copper sulphate solution?
Ans: Copper metal deposits on the iron nails
4. What is the white precipitate formed when sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed?
Ans: Barium sulphate forms the white precipitate.
Viva Questions
1. How can you prepare lime water?
Ans: Mix calcium oxide and water
2. What is the product of mixing calcium oxide in water?
Ans: Calcium Hydroxide Ca(OH)2
3. What is a combination reaction?
Ans: The reaction where two compounds combine to give one product.
4. What are the products of the decomposition of ferrous sulphate?
Ans: On heating, ferrous sulphate crystals decompose into Ferric oxide (Fe2O3), Sulphur dioxide (SO2), and Sulphur trioxide (SO3)
5. What gases evolved during the decomposition of ferrous sulphate?
Ans: Sulphur dioxide (SO2) and Sulphur trioxide (SO3)
6. Name the reaction: heating of ferrous sulphate crystals?
Ans: Thermal decomposition reaction
7. What is the basic principle of the experiment of iron nails dipped in copper sulphate?
Ans: In this experiment, the highly reactive metal (Fe) displaces the lower reactive copper from copper sulphate to form ferrous sulphate.
8. Define double displacement reaction.
Ans: A reaction where two ionic compounds exchange their ions to form new insoluble compounds.
Practical Based Questions
Which of the following reactions does occur, as shown
Zn(s) + ZnSO4(aq) →
Fe(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) →
Cu(s) + ZnSO4 (aq) →
2Al(s) + 3ZnSO4(aq) →
Ans: The only reaction that occurs is 2Al(s) + 3ZnSO4(aq) → Al2(SO4)3 + 3Zn (s). As Aluminium is more reactive than zinc.
Identify the combination reactions in the following
NH3+HCl→NH4Cl
NaOH+KOH→NaOH+KCl
2CO+O2→2CO2
BaCl2+Na2SO4→BaSO4+2NaCl
Ans: The formation of ammonium chloride and carbon dioxide is a combination reaction.
What is Ferrous Sulphate?
Blue vitriol
Quick Lime
Green vitriol
Slaked Lime
Ans: Ferrous sulphate is known as green vitriol.
What is the colour of the deposition on iron nails?
Blue
Brown
Green
White
Ans: The deposition on the iron nail is brown.
What is the colour of the copper sulphate solution?
Blue
Brown
Green
White
Ans: Copper sulphate crystals are blue.
The reaction between Barium chloride and sodium sulphate is
Combination reaction
Double displacement reaction
Displacement reaction
Decomposition reaction
Ans: Double Displacement reaction
The white precipitate in the sodium sulphate and barium chloride reaction formed is
CaO
Ca(OH)2
Fe2O3
BaSO4
Ans: Sodium sulphate and Barium Chloride react to form a white precipitate of barium sulphate
Identify the combination reaction in the following equation
2C8H18+25O2→16CO2+18H2O
8Fe+S8→8FeS
MgO+CO2→MgCO3
3Pb(NO3)2+2AlCl3→3PbCl2+2Al(NO3)3
Ans. In a combination reaction, two or more reactants combine to form a single product. Only in the following reactions, two reactants combine to form one product.
8Fe+S8→8FeS
MgO+CO2→MgCO3
How many water molecules do ferrous sulphate crystals contain?
1
3
5
7
Ans: Ferrous sulphate crystals contain seven water of crystallisation.
Conclusion
The experiments demonstrated the different types of reactions:
The reactions between water and quicklime, demonstrated the combination reaction, as CaO and H2O combined to form calcium hydroxide
Ferrous sulphate crystals were heated to demonstrate the decomposition reaction, where FeSO4 decomposed into multiple compounds.
The effect on iron nails dipped in copper sulphate solution displayed colour change due to displacement reaction with iron displacing the copper from copper sulphate forming ferrous sulphate.
The reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride solution is an example of a double displacement reaction where ions are exchanged to form new compounds.
FAQs on Class 10 Chemistry Types Of Reactions Experiment
1. What are the main types of chemical reactions that are important for the CBSE Class 10 Board Exam 2025-26?
For the CBSE Class 10 Chemistry syllabus, the most important types of chemical reactions to focus on are:
- Combination Reaction: Where two or more reactants combine to form a single product.
- Decomposition Reaction: Where a single compound breaks down into two or more simpler substances. This includes thermal, electrolytic, and photolytic decomposition.
- Displacement Reaction: Where a more reactive element displaces a less reactive element from its compound.
- Double Displacement Reaction: Where there is an exchange of ions between two compounds. This often results in the formation of a precipitate.
- Oxidation-Reduction (Redox) Reaction: Reactions involving the simultaneous gain of oxygen (oxidation) and loss of oxygen (reduction).
2. A student heats green-coloured ferrous sulphate crystals in a boiling tube. What are the three key observations expected in this important experiment?
Heating ferrous sulphate (FeSO₄·7H₂O) is a crucial example of a thermal decomposition reaction. The three key observations are:
- Colour Change: The initial light green colour of the crystals first changes to white as they lose water of crystallisation. Upon further heating, the anhydrous ferrous sulphate decomposes to form a reddish-brown solid, which is ferric oxide (Fe₂O₃).
- Gas Evolution: A mixture of gases with a characteristic pungent smell, like burning sulphur, is evolved. These gases are sulphur dioxide (SO₂) and sulphur trioxide (SO₃).
- Chemical Test: The evolved gases (SO₂ and SO₃) are acidic in nature and will turn moist blue litmus paper red.
The balanced chemical equation is: 2FeSO₄(s) → Fe₂O₃(s) + SO₂(g) + SO₃(g)
3. Explain with a suitable example why a combination reaction can also be an exothermic reaction. This is a frequently asked 2-mark question.
A combination reaction is one where two or more substances combine to form a single product. An exothermic reaction is one that releases heat. Many combination reactions are exothermic because the formation of new, more stable bonds in the product releases more energy than is required to break the bonds in the reactants.
A classic example is the reaction of calcium oxide (quicklime) with water to form calcium hydroxide (slaked lime):
CaO(s) + H₂O(l) → Ca(OH)₂(aq) + Heat
Here, calcium oxide and water combine to form a single product, calcium hydroxide, making it a combination reaction. A significant amount of heat is evolved during this process, making it highly exothermic.
4. What happens when an iron nail is placed in a copper sulphate solution? Provide the balanced chemical equation and state the type of reaction.
When an iron nail is placed in a blue-coloured copper sulphate solution, a displacement reaction occurs because iron is more reactive than copper. The following changes are observed:
- The blue colour of the copper sulphate solution gradually fades and turns into light green as ferrous sulphate is formed.
- A reddish-brown coating of copper metal gets deposited on the surface of the iron nail.
Reaction Type: Displacement Reaction
Balanced Equation: Fe(s) + CuSO₄(aq) → FeSO₄(aq) + Cu(s)
5. Why is the reaction between sodium sulphate and barium chloride considered both a double displacement and a precipitation reaction?
This reaction is a prime example of two classifications because:
- Double Displacement Reaction: It involves the mutual exchange of ions between the two reacting compounds. The sodium ions (Na⁺) from sodium sulphate (Na₂SO₄) combine with the chloride ions (Cl⁻) from barium chloride (BaCl₂), while the barium ions (Ba²⁺) combine with the sulphate ions (SO₄²⁻).
- Precipitation Reaction: The reaction results in the formation of an insoluble solid product called a precipitate. In this case, barium sulphate (BaSO₄) is formed, which is a white, insoluble substance that settles down.
Equation: Na₂SO₄(aq) + BaCl₂(aq) → BaSO₄(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
6. From an exam perspective, what is a redox reaction? Identify the substance oxidised and the substance reduced in the following reaction: CuO + H₂ → Cu + H₂O.
A redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction that involves the simultaneous processes of oxidation and reduction. For Class 10, this is often defined in terms of oxygen gain or loss.
- Oxidation is the gain of oxygen or loss of hydrogen.
- Reduction is the loss of oxygen or gain of hydrogen.
In the reaction CuO + H₂ → Cu + H₂O:
- Copper Oxide (CuO) is losing oxygen to become Copper (Cu). Therefore, CuO is reduced.
- Hydrogen (H₂) is gaining oxygen to become Water (H₂O). Therefore, H₂ is oxidised.
7. How can a student differentiate between a displacement reaction and a double displacement reaction based solely on the nature of reactants?
The key difference lies in the reactants involved:
- A displacement reaction typically involves an element reacting with a compound. The more reactive element displaces the less reactive element from its compound. For example, Fe (element) + CuSO₄ (compound).
- A double displacement reaction involves two ionic compounds reacting together in an aqueous solution. The ions of these two compounds exchange places to form two new compounds. For example, Na₂SO₄ (compound) + BaCl₂ (compound).
Therefore, by observing whether the reactants are an element and a compound or two different compounds, you can predict the type of reaction.
8. All decomposition reactions require an input of energy. How does the source of this energy lead to different types of decomposition reactions? Explain with one example for each type.
Decomposition reactions are classified based on the form of energy used to break down the reactant. This is a crucial concept for board exams.
- Thermal Decomposition: The breakdown is caused by heat energy. Example: The decomposition of calcium carbonate (limestone) into calcium oxide and carbon dioxide upon heating.
CaCO₃(s) --(Heat)→ CaO(s) + CO₂(g) - Electrolytic Decomposition (Electrolysis): The breakdown is caused by electrical energy. Example: The decomposition of water into hydrogen and oxygen gas when an electric current is passed through it.
2H₂O(l) --(Electricity)→ 2H₂(g) + O₂(g) - Photolytic Decomposition (Photolysis): The breakdown is caused by light energy. Example: The decomposition of silver chloride into silver and chlorine when exposed to sunlight.
2AgCl(s) --(Sunlight)→ 2Ag(s) + Cl₂(g)
9. A student observes that an iron nail in copper sulphate solution causes a reaction, but a copper wire in an iron sulphate solution shows no change. What is the fundamental principle that explains this difference?
The fundamental principle governing this observation is the reactivity series of metals. A more reactive metal can displace a less reactive metal from its salt solution.
- Case 1 (Iron in Copper Sulphate): Iron (Fe) is placed higher in the reactivity series than copper (Cu). This means iron is more reactive. Therefore, it displaces copper from the copper sulphate solution, leading to the formation of iron sulphate and copper metal.
- Case 2 (Copper in Iron Sulphate): Copper (Cu) is placed lower in the reactivity series than iron (Fe). This means copper is less reactive. As a result, it is not strong enough to displace iron from the iron sulphate solution, and hence, no reaction occurs.






































