Difference Between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction with Examples
Sexual reproduction is a fundamental biological process that leads to the production of new organisms by combining genetic information from two individuals of different sexes. This process is widely found across animals, plants, and many other life forms. It involves the formation of special sex cells, called gametes, which carry chromosomes with genetic information. These gametes unite, resulting in a fertilized cell known as the zygote. The zygote then develops into a new individual with unique genetic traits.
Understanding Sexual Reproduction
The essence of sexual reproduction lies in the union of two gametes—typically a male gamete (sperm) and a female gamete (egg/ovum). Each gamete carries half the number of chromosomes of a typical body cell. When these gametes fuse, the resulting zygote contains a complete set of chromosomes. This exchange and combination underpin genetic diversity in offspring.
| Term | Definition |
|---|---|
| Gamete | A specialized sex cell (sperm or egg) carrying genetic material from one parent. |
| Zygote | The first cell formed after gamete fusion, developing into a new organism. |
| Chromosome | Thread-like structure carrying hereditary information in cells. |
Key Steps in Sexual Reproduction
-
Formation of gametes: Specialized cells develop in the reproductive organs of each sex. In animals, male gametes are called sperm and female gametes are called eggs or ova.
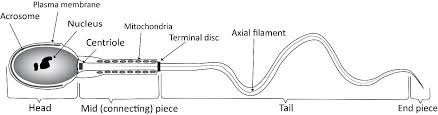
-
Fusion of gametes (fertilization): Typically, a male and a female gamete unite. This event restores the full chromosome complement and launches the development of a new individual.
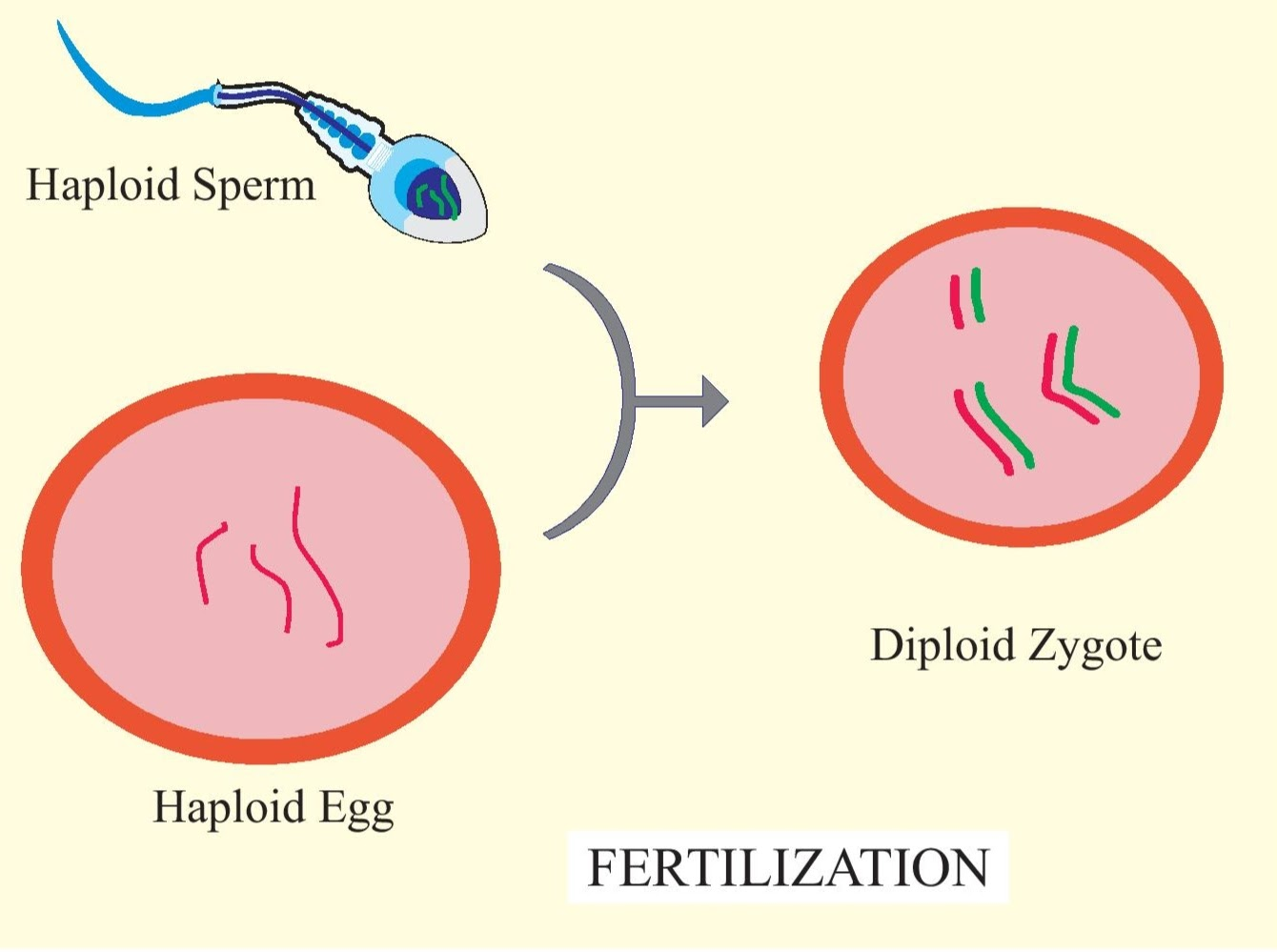
-
Zygote and development: The zygote divides repeatedly and undergoes changes, eventually forming a multicellular organism. This developmental process ensures traits from both parents are inherited.
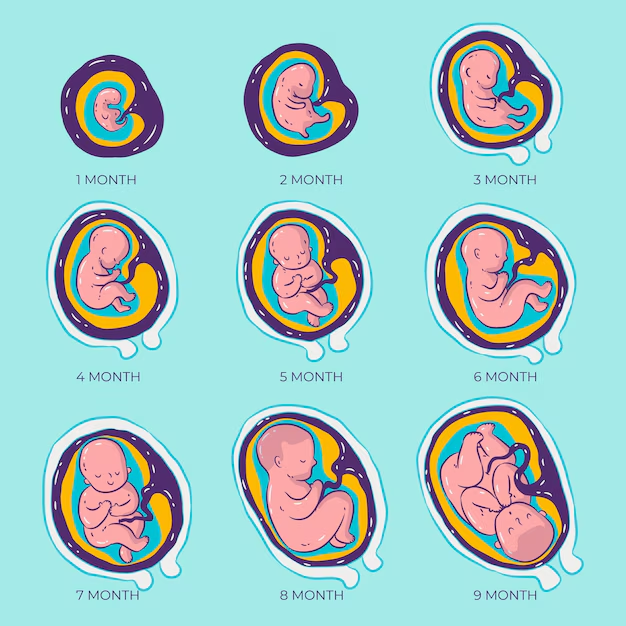
Biological Significance and Examples
The main significance of sexual reproduction is genetic variation. As offspring inherit mixed genetic material from two individuals, they often display unique traits. This diversity allows populations to survive changes in their environment and adapt over generations.
Examples of sexual reproduction include the union of pollen and ovule in flowering plants, and the fertilization of an egg by a sperm in animals such as humans and birds.
| Organism | How Sexual Reproduction Occurs |
|---|---|
| Plants | Combination of pollen (male) and ovule (female) cells forms a seed, which develops into a new plant. See more at Sexual Reproduction in Plants. |
| Animals | Fusion of sperm and egg leads to a zygote. For details, visit Human Reproductive System. |
Process Breakdown: From Gametes to New Life
- Gametes, each carrying half the parent's genetic material, are formed in specialized organs.
- The male and female gametes meet, usually after being carried or moved by various biological mechanisms.
- Fertilization unites the chromosomes within the two gametes, restoring the full chromosome count.
- The resulting zygote undergoes multiple divisions, differentiates, and grows into a mature organism.
Comparison: Sexual vs. Asexual Reproduction
| Feature | Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Number of parents | Two | One |
| Genetic variation | High, due to mixing of genes | Low, offspring identical to parent |
| Role of gametes | Present | Absent |
| Examples | Humans, plants, most animals | Bacteria, some plants, budding organisms |
Explore more: Difference between Sexual and Asexual Reproduction
Why is Sexual Reproduction Important?
Sexual reproduction creates variation in populations, vital for natural selection and the long-term survival of a species. This process supports evolution, adaptation, and the emergence of beneficial traits.
Practice & Next Steps
- Define gamete and zygote. Why are they crucial in sexual reproduction?
- Compare how sexual reproduction takes place in plants versus animals.
- Learn more about fertilization: Fertilization
- Explore related topics such as Gamete.
For further study, visit related concepts including Sexual Reproduction and Reproductive Systems and Reproductive System in Animals. These resources provide more examples, diagrams, and explanations to support your understanding of sexual reproduction.


FAQs on Sexual Reproduction – Concepts, Steps, and Importance
1. What is sexual reproduction?
Sexual reproduction is the process where two parent organisms combine their genetic material through the fusion of male and female gametes to produce offspring with genetic variation. This process results in increased genetic diversity and helps in adaptation and evolution of species.
2. What are the main steps of sexual reproduction?
The main steps of sexual reproduction are:
• Gametogenesis – Formation of haploid gametes (sperms/eggs) by meiosis
• Gamete Transfer – Bringing together male and female gametes (e.g., pollination, insemination)
• Fertilization (Syngamy) – Fusion of gametes to form a zygote
• Embryogenesis – Zygote divides to form an embryo
• Development – Embryo matures into a new organism
3. What is the main difference between sexual and asexual reproduction?
The main difference is that sexual reproduction involves two parents and leads to genetically varied offspring, while asexual reproduction involves only one parent and produces genetically identical offspring (clones).
4. Why is variation important in sexual reproduction?
Variation is important because it:
• Enables adaptation to changing environments
• Increases survival chances of offspring
• Drives evolution and development of new species
5. What is fertilization and why is it important?
Fertilization is the fusion of male and female gametes (e.g., sperm and egg) to form a diploid zygote. It restores the normal chromosome number, combines traits from both parents, and initiates development of a new organism.
6. What are the advantages and disadvantages of sexual reproduction?
Advantages:
• Produces genetic variation
• Increases adaptability
• Promotes removal of harmful mutations
Disadvantages:
• Slower process
• Requires energy and two parents
• Fewer offspring compared to asexual reproduction
7. Give examples of organisms that reproduce sexually.
Examples of sexually reproducing organisms include:
• Humans and other mammals
• Flowering plants (angiosperms)
• Fungi like yeast and algae like Spirogyra
• Birds, reptiles, amphibians, most animals
8. What is gametogenesis?
Gametogenesis is the biological process by which haploid male (sperm/pollen) and female (egg/ovule) gametes are produced through meiosis. It ensures genetic diversity in sexually reproducing organisms.
9. What is pollination and how does it relate to sexual reproduction in plants?
Pollination is the transfer of pollen (male gamete) from anther to stigma of a flower, allowing fertilization in flowering plants. This step is essential for sexual reproduction and seed formation in plants.
10. How does sexual reproduction promote evolution?
Sexual reproduction promotes evolution by generating genetic variation among offspring, which increases the likelihood that some individuals will possess traits suited to survive environmental changes, thus driving natural selection.
11. What role does meiosis play in sexual reproduction?
Meiosis is a special type of cell division that reduces chromosome number by half, producing genetically unique gametes. It is essential for maintaining chromosome number across generations and introducing variation.
12. Can you compare sexual and asexual reproduction in a table format?
Yes. Here is a comparison table:
| Feature | Sexual Reproduction | Asexual Reproduction |
|---|---|---|
| Number of Parents | Two | One |
| Variation in Offspring | Yes (Genetic diversity) | No (Clones) |
| Cell Division Involved | Meiosis and Mitosis | Mitosis only |
| Evolutionary Significance | High | Low |
| Examples | Humans, Plants, Animals | Amoeba, Hydra, Bacteria |










