Key Examples of Natural Resources in Everyday Life
Earth is unique among the planets in our solar system because it offers everything we need to survive, such as water, air, and food. But what are the resources of Earth? They include a wide range of elements like minerals, fossil fuels, forests, and sources of energy that help us live comfortably. They can be broadly divided into those obtained directly from nature (like water and sunlight) and those that require human intervention (like refined petroleum products).
In simple terms, resources on Earth support life in every possible way. Our existence depends on how wisely we use these resources so that future generations can also benefit from them.
What are Natural Resources?
Natural resources are substances and materials that exist in nature without human effort. Examples include water, sunlight, wind, soil, plants, and animals. These resources form the basis of life on Earth because they help fulfil our fundamental needs – for instance, soil helps grow food, and water is vital for drinking and irrigation.
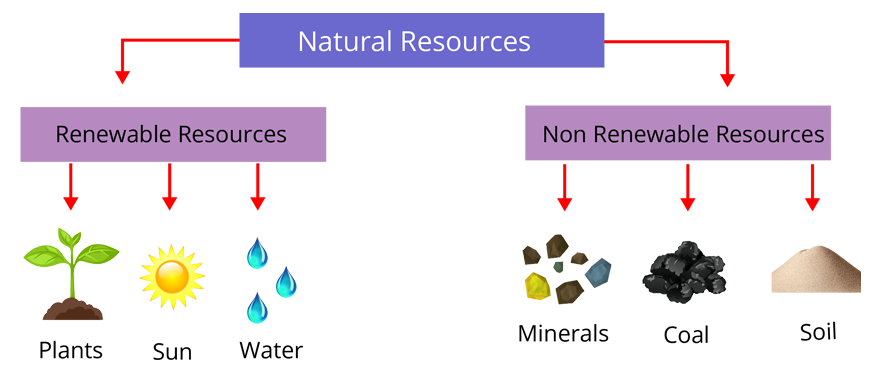
Types of Natural Resources
Have you ever wondered what are the 4 types of natural resources? While we often classify them into just two categories—renewable and non-renewable—some experts group them into four broader types:
Actual Resources: Those that are surveyed, quantified, and currently in use (e.g., active coal mines or operating oil wells).
Potential Resources: Those that exist but are not yet fully used or explored (e.g., tidal energy in certain coastal areas).
Renewable Resources: Resources that can be replenished relatively quickly by natural processes.
Non-renewable Resources: Resources available in limited quantities that cannot be replaced easily once they are exhausted.
Renewable Resources
These are resources that nature can restore or replenish over time. Examples include sunlight, wind, fresh water (through the water cycle), and biomass (like wood from forests). Because they can be regenerated, they are considered more sustainable for long-term use.
Non-renewable Resources
These resources either take millions of years to form or exist in fixed amounts. Fossil fuels (coal, petroleum, and natural gas) and minerals (iron, gold, and diamonds) fall into this category. Once used, it is extremely difficult or impossible to replace them within a human lifespan.
What are 20 Natural Resources?
Water
Air
Sunlight
Wind
Soil
Coal
Petroleum (Crude Oil)
Natural Gas
Forests (Timber)
Wildlife (Fauna)
Agricultural Crops
Marine Life (Fish)
Salt
Iron Ore
Copper Ore
Gold
Silver
Sand
Clay
Geothermal Energy
All these examples are found naturally on our planet, though some require human effort to make them usable.
What are the 10 Important Natural Resources?
Freshwater (Drinking and Irrigation)
Clean Air (Respiration and Health)
Soil (Agriculture and Habitat)
Forests (Timber, Habitat, Oxygen Production)
Fossil Fuels (Energy Production)
Sunlight (Solar Energy)
Wind (Wind Energy)
Minerals (Construction and Manufacturing)
Marine Resources (Food and Trade Routes)
Biodiversity (Genetic Variety and Ecosystem Balance)
Each of these resources plays a pivotal role in supporting life and various economic activities worldwide.
Importance of Natural Resources
Natural resources are crucial for several reasons:
Sustaining Life: They supply essential elements like oxygen (through plants), water, and nutrients for plants and animals.
Economic Development: Many industries—such as construction, agriculture, and manufacturing—depend on raw materials derived from natural resources.
Energy Generation: Resources like coal, petroleum, natural gas, sunlight, and wind are used to produce energy.
Environmental Balance: Forests and other ecosystems maintain oxygen and carbon dioxide levels, support biodiversity, and regulate climate.
Future Security: Wise use of resources ensures that future generations can also meet their own needs.
Depletion of Resources on Earth
Sadly, human activities are leading to the rapid depletion of Earth’s resources. The major causes include:
Overpopulation: With more people, there is a higher demand for food, water, energy, and land.
Over-exploitation: Excessive harvesting of resources like fisheries, forests, and minerals depletes them quickly.
Deforestation: Clearing forests for agriculture and urban development disrupts ecosystems.
Loss of Biodiversity: Pollution and habitat loss lead to the extinction of various species.
Industrialisation: The rapid growth of industries consumes large amounts of fossil fuels and minerals.
Pollution: Land, water, and air pollution make resources unusable.
Erosion: Loss of fertile soil reduces agricultural productivity.
Tips to Conserve Resources
Use Renewable Energy: Switch to solar, wind, or hydro energy whenever possible.
Recycle and Reuse: Decrease the need to extract new raw materials by recycling paper, metals, and plastics.
Responsible Consumption: Limit waste, especially food and water.
Reforestation: Plant trees to combat deforestation and maintain ecological balance.
Sustainable Farming: Adopt eco-friendly agricultural methods to keep the soil fertile.
Public Awareness: Educate others about natural resources examples and why conservation matters.
Also refer:
These topics will further deepen your understanding of resource management and ecological balance.


FAQs on Earth Resources: Types, Uses, and How to Conserve Them
1. What are the main types of natural resources on Earth?
Natural resources on Earth are broadly classified into two main categories:
- Renewable Resources: These are resources that can be replenished by natural processes in a relatively short period. Examples include sunlight, wind, water (through the water cycle), and forests.
- Non-renewable Resources: These are resources that exist in finite quantities and take millions of years to form, making them irreplaceable once depleted. Examples include fossil fuels like coal and petroleum, and minerals like iron ore and gold.
2. What is the primary difference between renewable and non-renewable resources, with examples?
The primary difference lies in their rate of regeneration. Renewable resources, like solar energy and wind, can be replenished naturally at a pace equal to or faster than our consumption. In contrast, non-renewable resources, such as coal, petroleum, and natural gas, are finite. They were formed over millions of years, and once we use them up, they are effectively gone forever within a human timescale.
3. Why is the conservation of natural resources essential for both humans and the environment?
Conservation of natural resources is essential for several critical reasons:
- Ensuring Future Availability: It ensures that future generations will have access to the resources needed for their survival and well-being.
- Maintaining Ecosystem Balance: Resources like forests and wetlands support biodiversity and regulate climate. Conserving them prevents ecological collapse.
- Sustaining Economic Activity: Many industries depend on raw materials from nature. Conservation supports long-term economic stability.
- Preventing Pollution: Wise resource use, such as shifting to renewable energy, reduces land, air, and water pollution.
4. What makes soil an indispensable natural resource?
Soil is an indispensable resource because it forms the foundation of most terrestrial life. Its importance includes:
- Agriculture: Fertile soil is necessary to grow crops that feed the global population.
- Habitat: It provides a home for countless organisms, from microbes to burrowing animals, which are crucial for ecosystem health.
- Water Filtration: Soil acts as a natural filter, purifying groundwater.
- Nutrient Cycling: It plays a vital role in cycling essential nutrients like carbon and nitrogen.
5. What are some practical methods for conserving Earth's resources in our daily lives?
We can all contribute to resource conservation through simple daily actions:
- Reduce, Reuse, Recycle: Minimise waste by reducing consumption, reusing items, and recycling materials like paper, plastic, and metal.
- Conserve Water: Fix leaky taps, take shorter showers, and avoid wasting water.
- Save Energy: Switch to energy-efficient appliances, turn off lights when not in use, and use renewable energy sources like solar power where possible.
- Support Reforestation: Plant trees and support initiatives that restore forests.
- Practice Sustainable Consumption: Choose products that are made sustainably and have minimal environmental impact.
6. How do natural resources like forests and oceans participate in Earth's vital biogeochemical cycles?
Forests and oceans are active participants in Earth's essential cycles. Forests play a key role in the carbon cycle by absorbing carbon dioxide through photosynthesis and storing carbon in their biomass. They are also crucial to the water cycle through transpiration. Oceans are the largest carbon sink on the planet and drive the water cycle through evaporation. The delicate balance of these resources is critical for regulating global climate and atmosphere composition.
7. What is the key difference between an 'actual resource' and a 'potential resource'? Can you provide an example?
The key difference is their current state of use and technological accessibility. An actual resource is one that has been surveyed, its quantity and quality determined, and is currently being exploited. For example, the coal mines operating in Jharkhand are an actual resource. A potential resource is one that exists in a region but has not been utilised yet, often due to a lack of technology or economic viability. For instance, tidal energy along India's coastline is a potential resource that is not yet being used on a large scale.
8. How can pollution render a natural resource unusable, even if it is not fully depleted?
Pollution can degrade a resource to the point where it becomes unusable or harmful, effectively depleting its value. For example:
- Water Pollution: Industrial waste or sewage can contaminate a river or lake, making its water unsafe for drinking or irrigation, even if the water volume remains high.
- Soil Pollution: The overuse of chemical fertilisers and pesticides can strip the soil of its natural fertility and contaminate the food grown in it.
- Air Pollution: Acid rain, caused by air pollutants, can damage forests and acidify water bodies, harming the life within them without physically removing the trees or water.
9. Beyond environmental protection, why is conserving resources crucial for economic stability?
Conserving natural resources is fundamental to economic stability because modern economies are built upon them. Resource depletion can lead to scarcity of raw materials, which increases production costs for industries like manufacturing, construction, and energy. This can cause inflation, job losses, and economic slowdown. Furthermore, a healthy environment with resources like clean water and fertile land supports sectors like agriculture and tourism. Therefore, sustainable resource management is not just an environmental issue but a long-term economic imperative.










