What Are the Main Structural Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells?
Understanding the Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell is crucial for biology students. These differences explain why plants and animals behave and adapt differently at a cellular level. The study of these cells highlights distinct features, such as the presence of a cell wall and chloroplasts in plants, making this topic essential for classes like Class 12 and beyond.
What are Plant Cells and Animal Cells?
Plant cells and animal cells are the basic building blocks of life for plants and animals, respectively. Both are eukaryotic, which means they have a well-defined nucleus. However, each type of cell has unique structures and functions that reflect their role in nature. Understanding their structure helps explain diverse biological processes.
Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell Definition
Plant cells are cells that make up plants. They feature a rigid cell wall, chloroplasts, and a large central vacuole. Animal cells form the tissues of animals and lack a cell wall and chloroplasts, but they have centrosomes and lysosomes. These definitions lay the foundation for further exploration of their differences.
Key Differences Between Plant and Animal Cells
Let's look at the main points that distinguish plant cells from animal cells. The following table summarizes the major differences in a concise format, which is useful for both theory exams and practical applications like preparing a difference between plant cell and animal cell diagram and answering MCQs.
Comparison Table: Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present (provides rigidity and support) | Absent (only plasma membrane) |
| Chloroplasts | Present (for photosynthesis) | Absent |
| Vacuoles | Large central vacuole | Small or absent |
| Shape | Usually regular, rectangular | Usually round or irregular |
| Lysosomes | Rare | Present |
| Centrosome | Absent | Present (with centrioles) |
| Energy Storage | Starch | Glycogen |
| Cilia | Usually absent | Present in many cells |
This side-by-side table helps students visualize each feature. Notice the unique presence of cell wall and chloroplasts in plant cells, while lysosomes and centrosomes are unique to animal cells.
Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell Diagram
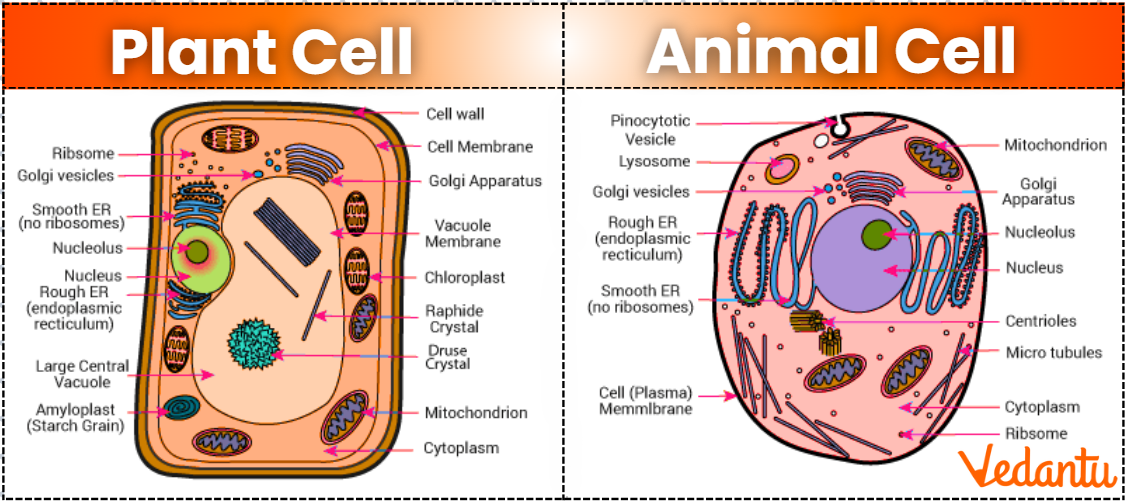
This diagram clearly marks the main organelles within both a plant cell and an animal cell. It is a helpful visual for comparing structural differences, and is often used in textbooks, biology classes, and competitive exams. For more diagrams relevant to biology, visit important diagrams for CBSE.
Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell Explanation
The primary differences are linked to function and adaptation. The cell wall in plants provides structural strength, which is vital for standing upright and growth. Chloroplasts enable photosynthesis, making plants autotrophic. In contrast, animal cells lack these features but have structures like lysosomes and centrioles for digestion and cell division. These adaptations perfectly suit the roles of plants and animals in nature and ecosystems.
Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell Examples
Common examples of plant cells include cells in leaves (containing chloroplasts for photosynthesis), and xylem cells in roots. Animal cell examples include nerve cells, blood cells, and muscle cells. These examples demonstrate the practical differences in structure and function between the two cell types.
- Plant Cell Example: Cells in a mango leaf (with chloroplasts and a cell wall).
- Animal Cell Example: Human muscle cell (no chloroplasts, flexible membrane).
Real-World Application and Importance
Understanding the difference between plant cell and animal cell is crucial in fields like food science, agriculture, and medicine. For example, knowledge of plant cells supports advancements in crop breeding and genetic engineering. Animal cell research is vital in medical studies, drug testing, and understanding diseases. Exploring life science topics further broadens our knowledge of cellular functions and their impact on the environment.
Sample Questions and MCQs
Students frequently encounter questions on the difference between plant cell and animal cell in their exams. Here are some examples of difference between plant cell and animal cell questions you may encounter:
- Which structure is unique to plant cells but absent in animal cells?
- Identify the storage product of energy in animal cells.
- Explain how a plant cell maintains its shape.
For more MCQs, visit the Vedantu MCQ section.
Summary of Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell
The difference between plant cell and animal cell is vital to biology. It highlights unique features such as the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuole in plant cells, and lysosomes and centrosomes in animal cells. Knowing these differences deepens your grasp of how life functions on Earth, driving scientific discoveries in agriculture, medicine, and the environment.


FAQs on Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell: Key Features and Comparison
1. What is the main difference between plant cell and animal cell?
Plant cells and animal cells have several major differences, mainly in structure and organelles.
- Plant cells have a cell wall and chloroplasts, while animal cells do not.
- Plant cells contain a large central vacuole; in animal cells, vacuoles are small or absent.
- Centrioles are present in animal cells but usually absent in higher plant cells.
2. What are the similarities between plant and animal cells?
Plant cells and animal cells share several fundamental features.
- Both have a cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, and mitochondria.
- Both carry out essential life processes like respiration and cell division.
- Each cell type contains Golgi apparatus, endoplasmic reticulum, and ribosomes.
3. What are three differences between plant cell and animal cell?
The three main differences between plant cells and animal cells are:
- Cell wall: Present in plants, absent in animals.
- Chloroplasts: Present in plants for photosynthesis, absent in animals.
- Vacuole: Large and central in plant cells, small or absent in animal cells.
4. What is a plant cell?
A plant cell is a basic structural and functional unit found in all plants and contains specific organelles.
- It has a cell wall made of cellulose for support.
- It possesses chloroplasts for photosynthesis.
- A large vacuole helps maintain cell shape and stores nutrients.
5. Why do plant cells have a cell wall and animal cells do not?
Plant cells need a cell wall for support and protection because they cannot move; animal cells are more flexible and do not need one.
- Cell wall provides rigidity and prevents bursting in hypotonic solutions.
- Animal cells rely on their cytoskeleton for shape and support.
6. What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts in plant cells are responsible for photosynthesis.
- They contain chlorophyll, allowing plants to capture sunlight.
- Convert solar energy, carbon dioxide, and water into glucose and oxygen.
7. Do animal cells have plastids?
No, animal cells do not have plastids.
- Plastids (like chloroplasts, chromoplasts, leucoplasts) are unique to plant cells.
- These are essential for photosynthesis and food storage in plants.
8. What roles do vacuoles play in plant and animal cells?
Vacuoles serve storage and support functions, more prominent in plant cells.
- In plant cells, the large central vacuole maintains turgor pressure and stores water, ions, and nutrients.
- In animal cells, vacuoles are smaller and mainly involved in storage and waste disposal.
9. What is the function of mitochondria in both plant and animal cells?
Mitochondria are the "powerhouse" of both plant and animal cells.
- They produce energy (ATP) through cellular respiration.
- Essential for all energy-requiring processes in living organisms.
10. How do plant and animal cells differ in terms of energy production?
Plant cells produce energy both by photosynthesis and respiration, while animal cells rely only on respiration.
- Plant cells use chloroplasts for photosynthesis and mitochondria for respiration.
- Animal cells use only mitochondria for respiration as they lack chloroplasts.










