What is the structure and function of a plant cell?
The plant cell is a fundamental building block of all plants, playing vital roles in growth, development, and survival. Unlike animal cells, plant cells have specific structures such as cell walls and chloroplasts that help them thrive. Understanding plant cells is essential for learning about photosynthesis, plant adaptations, and applications in agriculture and biotechnology.
What is a Plant Cell?
A plant cell is a basic unit of life found in the tissues of all plants. It is a eukaryotic cell, meaning it has a true nucleus and various specialized organelles. Unique features like the plant cell wall, chloroplasts, and large vacuole set it apart from animal cells. These structures enable plants to produce food, store energy, and maintain rigidity.
Plant Cell Structure
The plant cell structure is distinct due to certain key components. Here are the major parts found in a typical plant cell model:
- Cell Wall: A rigid outer layer made of cellulose that protects and gives shape to the cell.
- Plasma Membrane: The thin, flexible boundary inside the cell wall, controlling entry and exit of substances.
- Nucleus: Contains DNA and controls cellular activities.
- Chloroplasts: Organelles that perform photosynthesis using sunlight, water, and carbon dioxide.
- Vacuole: A large, fluid-filled sac that stores water, nutrients, and waste products.
- Cytoplasm: The jelly-like fluid where organelles are suspended.
- Mitochondria: Powerhouse of the cell, generating energy for cellular processes.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Network helping in protein and lipid synthesis.
- Golgi Apparatus: Packages and transports proteins within the cell.
- Plasmodesmata: Channels between plant cells that allow transport and communication.
These organelles work together, enabling plants to perform vital functions such as growth, energy conversion, and nutrient storage.
Plant Cell Diagram
A well-labelled plant cell diagram helps in visualizing the locations and relationships of different organelles. Diagrams are commonly used in textbooks and exams to test understanding of the plant cell model.
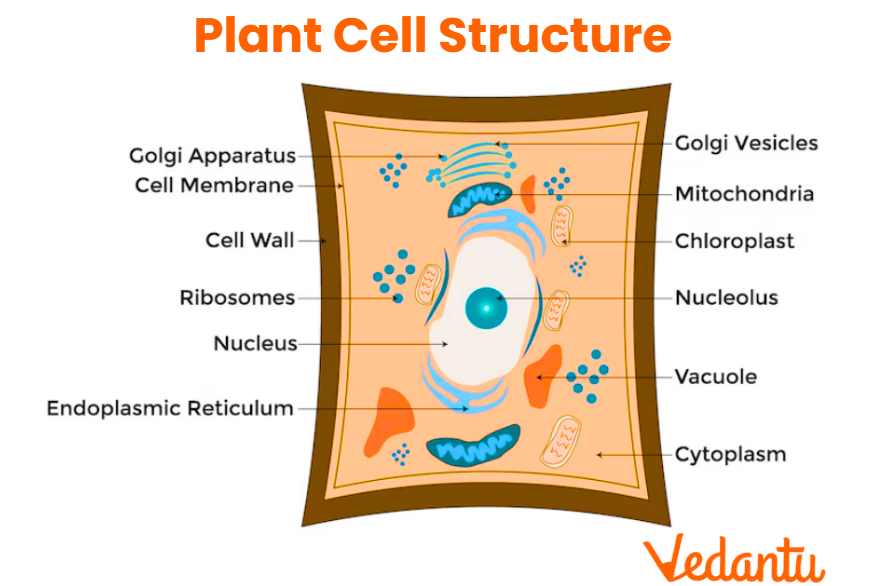
Unique Features of Plant Cells
Plant cells possess certain unique structures that are not present in animal cells:
- Plant Cell Wall: Provides mechanical strength and protection; made from cellulose.
- Chloroplasts: Enable photosynthesis—conversion of sunlight into chemical energy (glucose).
- Large Central Vacuole: Maintains cell turgidity and stores vital substances.
- Plasmodesmata: Tiny channels that facilitate direct communication between adjacent plant cells.
These features help plants carry out functions essential for survival, growth, and adaptation to their environment. To explore how these unique adaptations affect plants in different conditions, read about adaptations in plants.
Comparison: Plant Cell vs. Animal Cell
| Feature | Plant Cell | Animal Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Cell Wall | Present (cellulose) | Absent |
| Chloroplasts | Present | Absent |
| Central Vacuole | Large and single | Small and multiple |
| Shape | Usually rectangular or square | Usually round or irregular |
This table highlights the main differences between plant and animal cells. To learn more, visit difference between plant cell and animal cell.
Functions of Key Plant Cell Organelles
Each plant cell organelle has a specific function:
- Cell Wall: Prevents bursting in hypotonic solutions and provides support.
- Chloroplasts: Capture sunlight and carry out photosynthesis.
- Vacuole: Maintains turgor pressure and stores nutrients.
- Nucleus: Contains genetic material and controls cell division.
- Mitochondria: Break down glucose to release energy via cellular respiration.
These organelles coordinate to ensure the plant cell survives and functions efficiently in its natural environment.
Plant Cell Model: Types and Uses
A plant cell model can be physical (3D), digital, or drawn for educational purposes. These models are used in classrooms, research, and biotechnology labs to:
- Demonstrate detailed plant cell structure and organelle arrangement.
- Support interactive learning for students through hands-on projects.
- Assist in plant biology research and genetic studies.
Building a plant cell model helps visualize organelle functions and their spatial relationships.
Plant Cell Wall: Composition and Importance
The plant cell wall, composed mainly of cellulose, is vital for:
- Maintaining cell shape and preventing collapse.
- Protecting against pathogens and mechanical injury.
- Facilitating communication between cells via plasmodesmata.
Plant cell walls also enable plants to stand upright and grow tall. To explore cell wall structure in depth, check structure of the cell wall.
Processes Involving Plant Cells
Plant cells are involved in various vital biological processes. Here’s how photosynthesis works in plant cells:
- Chloroplasts capture sunlight energy.
- This energy splits water molecules (photolysis) and produces oxygen.
- Carbon dioxide combines with hydrogen to form glucose.
- Glucose is used for energy and growth; oxygen is released as a byproduct.
This process not only sustains plant life, but also produces oxygen for humans and animals to breathe. Learn about the photosynthesis process for a deeper understanding.
Applications and Relevance of Plant Cells
Plant cells have wide-ranging importance in biology, agriculture, and medicine:
- Basis of plant tissue culture and genetic modification.
- Understanding plant diseases and immunity, as seen in studies on Tobacco Mosaic Virus.
- Research into crop improvement and sustainable agriculture.
- Significance in life processes, food production, and the environment.
For further reading about how plant biology connects to health and nutrition, see food and health on Vedantu.
Page Summary
Plant cells are the core of plant structure and function, characterized by specialized features like the cell wall, chloroplasts, and vacuole. Their study is essential for understanding plant life, agriculture, and environmental science. Mastering plant cell concepts opens doors to advanced topics in biotechnology, genetics, and sustainable crop management.


FAQs on Understanding the Plant Cell
1. What is a plant cell?
A plant cell is the basic structural and functional unit found in plants.
Key features of plant cells include:
- Cell wall made of cellulose
- Chloroplasts for photosynthesis
- A large central vacuole for storage
- Nucleus containing genetic material
2. What are the main differences between plant cells and animal cells?
The main differences between plant cells and animal cells are:
- Plant cells have a rigid cell wall; animal cells do not.
- Chloroplasts are present in plant cells for photosynthesis; absent in animal cells.
- Plant cells have a large central vacuole; animal cells have smaller vacuoles.
- Animal cells have centrioles; most plant cells do not.
3. What is the function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
Chloroplasts in plant cells are responsible for photosynthesis.
Functions of chloroplasts:
- Capture sunlight using chlorophyll
- Convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose and oxygen
- Provide energy for plant growth and development
4. What is the role of the cell wall in a plant cell?
The cell wall in a plant cell provides structural support and protection.
Main roles include:
- Maintaining the shape of the cell
- Protecting against mechanical stress
- Allowing the passage of water and nutrients
- Composed mainly of cellulose
5. What does the central vacuole do in plant cells?
The central vacuole is a large, membrane-bound organelle that stores water and nutrients in plant cells.
Its functions include:
- Maintaining turgor pressure (cell rigidity)
- Storing nutrients, wastes, pigments, and ions
- Helping in plant growth by expanding and providing internal support
6. Explain the structure of a plant cell with a labeled diagram.
A plant cell has distinct organelles arranged within a membrane.
Typical plant cell structure includes:
- Cell wall – outermost layer
- Cell membrane – just inside the cell wall
- Cytoplasm – gel-like substance containing organelles
- Nucleus – controls cell activities
- Chloroplasts – site of photosynthesis
- Central vacuole – storage
- Mitochondria – energy production
7. What are the functions of different organelles in a plant cell?
Each organelle in a plant cell performs a specific function:
- Nucleus – controls cell activities and stores DNA
- Chloroplast – photosynthesis
- Cell wall – provides shape and protection
- Central vacuole – storage and support
- Mitochondria – produces energy
- Endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus – transport and processing
8. Why is the plant cell wall made of cellulose?
The plant cell wall is made of cellulose because cellulose provides strength and rigidity.
Main points:
- Cellulose is a strong, fibrous carbohydrate (polysaccharide)
- Gives the cell wall its structural integrity
- Protects against osmotic stress and mechanical damage
9. Are all plant cells the same? Explain.
Not all plant cells are the same; they are specialized for different functions.
Types of plant cells:
- Parenchyma – storage and photosynthesis
- Collenchyma – support
- Sclerenchyma – strength
- Xylem and phloem – transport of water and nutrients
10. Draw a neat labelled diagram of a plant cell.
A labelled diagram of a plant cell should include:
- Cell wall
- Cell membrane
- Cytoplasm
- Nucleus
- Chloroplasts
- Central vacuole
- Mitochondria
- Other organelles (as required by syllabus)
11. Which organelle is called the 'powerhouse' of the plant cell?
The mitochondria are called the 'powerhouse' of the plant cell.
Main points:
- They convert glucose into ATP (energy) through respiration
- Present in both plant and animal cells
- Support cellular activities with required energy
12. What is cytoplasm and what is its role in plant cells?
The cytoplasm is a jelly-like fluid inside the cell that holds all organelles in place.
Roles include:
- Supporting organelles and enabling their movement
- Providing space for biochemical reactions
- Maintaining cell shape










