What Are the Main Parts of Plants and How Do They Help Plants Grow?
Plants are fascinating organisms made up of several unique structures, each carrying out vital roles for survival and growth. Understanding the parts of plants is fundamental in biology, as it helps us learn how plants get food, grow, and reproduce. Let’s explore each part’s name, structure, and essential function with clear explanations and diagrams.
What Are the Parts of Plants?
The parts of plants include six main structures: roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. Each part works in harmony to help the plant grow, adapt, and continue its life cycle. For kids and beginners, these parts are often introduced first to build a foundation in biology.
Understanding the Main Parts of Plants
Main parts of a plant are:
- Root – Underground part absorbing water and anchoring the plant.
- Stem – Supports and transports nutrients and water.
- Leaf – Primary site for making food by photosynthesis.
- Flower – Reproductive organ; often colorful and attractive.
- Fruit – Protects the seed; aids in seed dispersal.
- Seed – Contains the embryo; grows into a new plant.
The aerial parts of plants refer to all the structures above the ground such as the stem, leaves, flowers, and fruits.
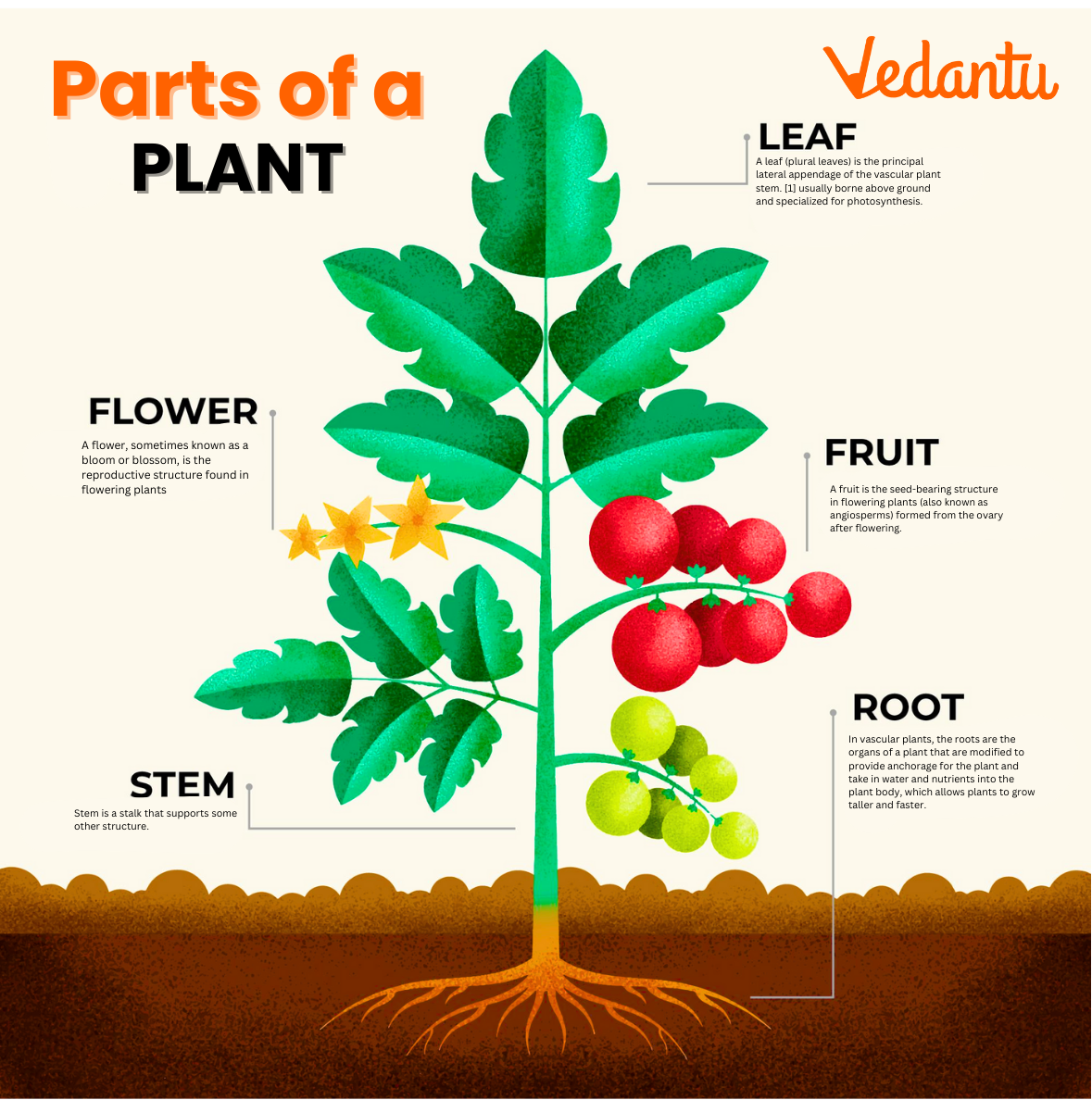
Parts of Plants Name and Their Functions
Every plant part has a particular job. Here’s a chart to show each key part and its function, providing a clear overview for students and educators.
| Parts of Plants Name | Main Function |
|---|---|
| Root | Anchors the plant, absorbs water & minerals from the soil |
| Stem | Supports the aerial parts; transports food, water & minerals |
| Leaf | Performs photosynthesis and creates food |
| Flower | Reproduction through pollination and seed formation |
| Fruit | Protects seeds and assists with their dispersal |
| Seed | Germinates to form a new plant (embryo inside) |
This parts of plants chart makes it easy to match each plant part with its unique job, reinforcing exam and workbook learning.
Parts of Plants Diagram: Visualizing Plant Structure
A labeled parts of plants diagram is essential for learning and revising. It shows each structure’s position and helps students remember the difference between roots, stem, leaves, and flowers. If you wish to deepen your diagram practice, check out important plant diagrams provided by Vedantu.
Parts of Plants for Kids: Simple Explanations
Parts of plants for kids focuses on simple definitions and fun activities:
- Root: The "anchor" holding the plant in place under the soil.
- Stem: The "straw" that lets water travel up to the leaves and flowers.
- Leaves: The "kitchen" where food is created from sunlight.
- Flower: The "show" or "party" that attracts insects and helps the plant make seeds.
- Fruit & Seed: The "package" that protects baby plants (seeds) inside.
Try drawing each part at home or in class to boost your memory of plant structure!
Worked Example: Exploring Plant Structure Step by Step
- Observe a local plant. Identify the root and stem.
- Notice where leaves are attached to the stem.
- Examine the flower if present—look for petals, stamens, and pistil.
- Find the fruit or seed if possible, such as a bean or apple.
Practice drawing and labelling a diagram. You’ll quickly master recognizing different plant parts for all biology classes!
Different Parts of Plants We Eat: Edible Parts and Real-Life Examples
Many foods come from various edible parts of plants. Recognizing which part we eat is both educational and fun! Here’s an edible parts of plants chart with examples:
- Roots: Carrot, beetroot, radish
- Stems: Potato, sugarcane, ginger
- Leaves: Spinach, lettuce, cabbage
- Flowers: Cauliflower, broccoli
- Fruits: Apple, mango, tomato
- Seeds: Rice, wheat, beans
Explore more with this food science overview by Vedantu!
Functions of Aerial and Underground Parts of Plants
The aerial parts of plants above ground—such as stems, leaves, and flowers—are important for photosynthesis, nutrient transport, and reproduction. Underground parts, mainly roots, secure the plant and help take up water and minerals. This division supports efficient growth and survival in different environments.
Parts of Plants and Their Functions – Quick Reference
- Root: Absorbs water, anchors the plant, stores some food.
- Stem: Carries nutrients, provides support, stores food in certain plants (like potato).
- Leaf: Makes food using sunlight (photosynthesis).
- Flower: Helps in reproduction, attracts pollinators (insects, birds).
- Fruit: Protects seeds, helps in dispersal.
- Seed: Starts a new plant through germination.
Real-World Applications and Significance
Learning about the different parts of a plants is useful in daily life. Farmers study plant parts to grow healthy crops. Scientists find medicines in roots and leaves. Environmentalists track how leaves and roots help clean the air and soil. Understanding the functions supports concepts like effect of climate change on crops and growth and development. This knowledge makes biology practical for both exams and life.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Plant Parts Questions
- Not labeling roots and stem correctly in diagrams.
- Thinking flowers are only for decoration (they do reproduction too!).
- Confusing seeds with fruits (seeds are inside the fruit).
With practice and careful revision, these errors will become easy to spot and correct.
Explore More Plant Biology Topics
- Study parts of a seed in depth and learn how seeds grow.
- Dive into plant cell structure and learn how cells make up all plant parts.
- Discover the process of photosynthesis in leaves.
- Understand plant growth with plant tissues and morphology of flowering plants.
- Explore reproduction in plants and nature’s diverse methods.
Page Summary
The main parts of plants—roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds—work together to help plants survive, grow, and reproduce. From food to medicines, every part plays an important role in our lives. Understanding these parts builds biology knowledge for children and supports exam success. Keep exploring with Vedantu for deeper science insights!


FAQs on Parts of Plants and Their Functions
1. What are the main parts of a plant?
A plant has several basic parts, each with specific functions. The main parts of a plant are:
- Roots – anchor the plant and absorb water and nutrients
- Stem – supports the plant and transports nutrients
- Leaves – make food through photosynthesis
- Flowers – help in reproduction
- Fruits – protect seeds and help in their dispersal
- Seeds – grow into new plants
2. What is the function of roots in a plant?
Roots anchor the plant in soil and absorb water and minerals.
- Anchorage – hold the plant firmly
- Absorption – take in water and minerals from soil
- Storage – store food and nutrients
3. What are the functions of the stem?
The stem supports the plant and acts like a transport system.
- Support – holds leaves, flowers, and fruits upright
- Transport – moves water, minerals, and food between roots and leaves
- Storage – stores food in some plants (e.g., potato)
4. What is the role of leaves in plants?
Leaves are mostly responsible for preparing food for the plant through photosynthesis.
- Photosynthesis – making food using sunlight
- Transpiration – releasing excess water vapor
- Gas Exchange – taking in carbon dioxide and releasing oxygen
5. What is the function of flowers in a plant?
Flowers are the reproductive parts of plants.
- Reproduction – help plants produce seeds through pollination
- Attract Pollinators – colorful petals attract insects and birds
6. What are the uses of fruits for plants?
Fruits protect and help disperse seeds.
- Protection – cover seeds to keep them safe
- Dispersal – assist in spreading seeds so new plants can grow elsewhere
7. What are the different types of roots?
Roots are usually of two main types:
- Tap Root – a single, thick main root (e.g., carrot)
- Fibrous Root – many thin roots growing from the base (e.g., grass)
8. What is the difference between tap root and fibrous root?
Tap roots have one main root, while fibrous roots have many thin roots.
- Tap Root: Thick, single root with smaller branches (e.g., mango)
- Fibrous Root: Cluster of roots of equal size, spread out (e.g., wheat)
9. What do seeds need to grow into a new plant?
Seeds need the right conditions to germinate and grow.
- Water
- Oxygen
- Warmth
- Soil
10. Which part of the plant makes food?
Leaves make food for the plant through the process of photosynthesis.
- They use sunlight, chlorophyll, water, and carbon dioxide
- Their green color is due to chlorophyll
11. Why is the leaf called the kitchen of the plant?
Leaves are called the kitchen of the plant because they make food.
- Leaves use sunlight, water, and air to prepare food by photosynthesis
- This food is then sent to other parts of the plant
12. How do plants reproduce?
Plants reproduce mainly through their flowers by producing seeds.
- Pollination: Pollen from one flower reaches another flower
- Fertilization: Egg and pollen combine to form seeds
- Seed Dispersal: Seeds grow into new plants










