What Are the Main Parts of a Plant and Their Roles?
Understanding the parts of a plant is crucial in biology as it helps explain plant growth, food production, and reproduction. Each part plays a unique role, and learning about these structures builds a strong foundation for plant science, exams, agriculture, and everyday observations. Let’s explore the names, functions, and diagrams of plant parts for school and real-world learning.
What Are the Parts of a Plant?
The main parts of a plant are the structures that support its growth, prepare food, and ensure reproduction. The basic parts include the root, stem, leaf, flower, fruit, and seed. These different parts of a plant have distinct roles that keep the plant healthy and enable it to complete its life cycle.
Diagram: Parts of a Plant
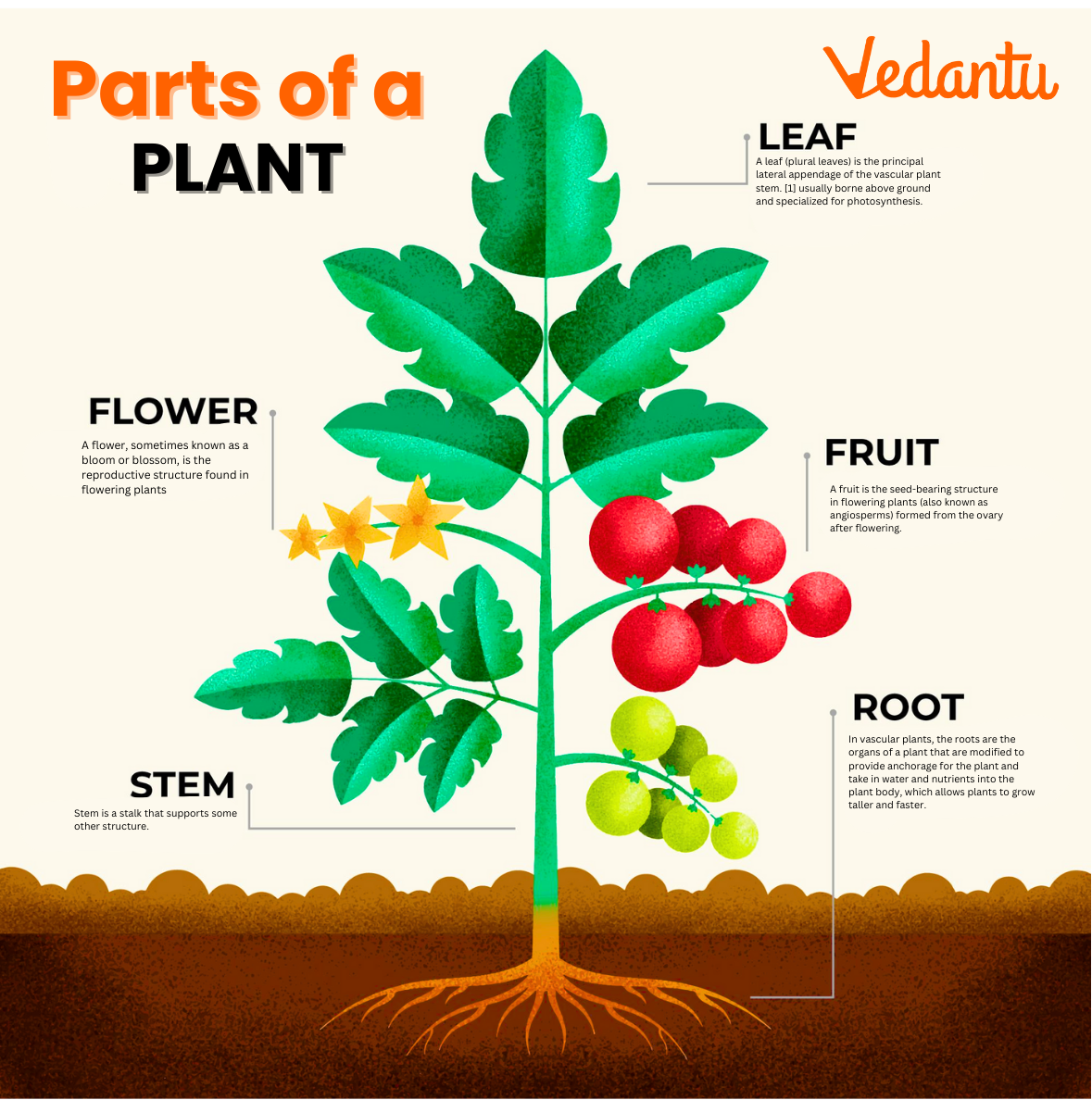
A labelled diagram of a plant helps students identify and learn to draw and label the parts of a plant such as the roots, stem, leaves, flower, fruit, and seed. This is a useful tool for visual learners and for practice with diagram labelling in school projects and exams.
Main Parts of a Plant and Their Functions
Each part of a plant has a specific function. The following table summarizes the parts of a plant and their key roles. Memorizing these functions is essential for understanding topics like photosynthesis, reproduction, and plant adaptations.
| Plant Part | Name | Main Function |
|---|---|---|
| Root | Vegetative | Anchors the plant; absorbs water and minerals from soil |
| Stem | Vegetative | Supports the plant; transports water, food, and nutrients |
| Leaf | Vegetative | Makes food for the plant using photosynthesis |
| Flower | Reproductive | Reproduction; attracts pollinators for pollination |
| Fruit | Reproductive | Protects seeds; aids in seed dispersal |
| Seed | Reproductive | Grows into a new plant; stores food for early growth |
Knowing the 6 parts of a plant and their functions helps students write clear answers and complete worksheets or science projects.
Detailed Explanation of Each Part
1. Root: Found below ground, roots anchor the plant in the soil and absorb water and minerals. In carrots and beetroots, roots also store food.
2. Stem: The stem grows above ground and supports leaves and flowers. It acts as a transport channel for water, minerals, and food. Modified stems, like potatoes, store food.
3. Leaf: Leaves are flat, green parts responsible for making food through photosynthesis. They exchange gases and may store food in lettuce or spinach.

The leaf’s structure includes the blade (lamina), petiole, and veins. These parts help maximize sunlight capture and efficient transport within the leaf.
4. Flower: Flowers are the reproductive parts of a plant. They contain male parts (stamens) and female parts (pistil/carpel), and are essential for pollination and seed formation.
5. Fruit: After fertilization, the flower changes into a fruit. The fruit protects the seeds and is sometimes eaten by animals, which helps spread the seeds.
6. Seed: Seeds develop inside the fruit. They have a tough covering and contain the embryo of a new plant, along with stored food to start growth.
How Different Parts Help Plants Grow and Survive
The combined functions of various plant parts enable the plant to grow, make food, and reproduce. For example, the root system absorbs essential water, while the stem transports it upward. Leaves perform photosynthesis, and the flower produces seeds. This teamwork is vital for a plant’s life cycle, as seen in lessons on photosynthesis and reproduction in plants.
Parts of a Plant Diagram: Exam Tips and Practice
To do well in biology exams, practice a parts of a plant drawing. Follow these steps:
- Draw the main outline, showing roots below, stem above, and branches if needed.
- Add leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds as appropriate.
- Label each part clearly. Use a ruler for neat lines.
Use parts of a plant worksheet or clipart for extra practice. You can create a 3D model for a school project or work on a parts of a plant outline for revision.
Examples: Edible Plant Parts in Daily Life
Many everyday foods are specific plant parts:
- Roots (carrot, radish, beetroot)
- Stems (potato, ginger, sugarcane)
- Leaves (spinach, lettuce, cabbage)
- Flowers (cauliflower, broccoli)
- Fruits (tomato, apple, mango)
- Seeds (beans, peas, rice, wheat)
Understanding which of the following parts of a plant we eat helps us appreciate food science and nutrition. Learn more about this in food science and plant nutrition topics.
Vegetative and Reproductive Parts
Vegetative parts of a plant are roots, stems, and leaves. They help with growth, support, and food production. Reproductive parts include flowers, fruits, and seeds. They are needed for reproduction and species survival. This distinction is important in plant classification and crop breeding.
Real-Life Applications of Plant Parts Knowledge
Knowledge of plant parts is useful in agriculture, horticulture, and medicine:
- Farmers choose crop varieties using root and stem features.
- Doctors use plant seeds, leaves, and roots in herbal medications.
- Environmentalists study plant adaptations to understand the impact of climate change.
- Biologists research these parts in topics like plant tissues and plant cell structure.
All these fields rely on understanding the basic as well as advanced features of the parts of a flowering plant.
Common Mistakes in Parts of a Plant Diagrams
Students often make these errors:
- Confusing the stem and the root (especially in diagrams of underground stems like ginger).
- Mixing up the fruit and seed (remember, seeds are inside the fruit).
- Forgetting that flowers are for reproduction, not only decoration.
Carefully label the parts of a plant to avoid losing marks in exams or worksheets.
Practice Questions for Students
- Name the different parts of a plant and mention one function of each.
- Draw a neat parts of a plant diagram and label roots, stem, leaves, and flower.
- Which plant part is involved in food preparation? Describe the process.
- List two plant parts we commonly eat as food.
- Describe the functions of various parts of a plant in your own words.
Related Biology Topics to Explore
- Photosynthesis in Leaves – How plants make food.
- Plant Tissues – Learn about tissues forming each part.
- Plant Cells – Cellular basis of plant parts.
- Parts of a Seed – Structure and importance.
- Reproduction in Plants – Explore plant life cycles.
- Getting to Know Plants – Morphology of flowering plants.
Studying the parts of a plant gives students a foundation for all plant-based biology, linking to nutrition, environmental science, and agriculture. For more practice and expert resources, explore biology topics with Vedantu’s online learning platform.
The parts of a plant, including roots, stems, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds, each have a unique function essential for plant health, growth, and reproduction. Learning to identify, draw, and label the parts of a plant helps build scientific understanding and supports school success in plant biology.


FAQs on Parts Of A Plant: Names, Structure and Key Functions
1. What are the main parts of a plant?
The main parts of a plant include the root, stem, leaves, flowers, fruits, and seeds. These parts work together for growth and reproduction:
- Roots: Anchor the plant and absorb water/nutrients from soil.
- Stems: Support the plant and transport food and water.
- Leaves: Make food by photosynthesis.
- Flowers: Help in reproduction.
- Fruits: Protect seeds.
- Seeds: Grow into new plants.
2. What is the function of roots in a plant?
Roots anchor the plant and absorb water and minerals for growth. The key functions of roots are:
- Anchoring the plant firmly in the soil
- Absorbing water and essential nutrients
- Storing food in some plants (e.g., carrot, beetroot)
- Preventing soil erosion by holding soil particles together
3. What is the role of the stem in plants?
The stem supports the plant and transports water, minerals, and food between roots and leaves. Additional functions of the stem include:
- Holding leaves, flowers, and fruits upright
- Storing food in some plants (e.g., potato, ginger)
- Helping in vegetative propagation in some cases
4. Why are leaves important for a plant?
Leaves are essential because they prepare food for the plant through photosynthesis. Their major roles include:
- Absorbing sunlight for photosynthesis
- Exchanging gases (oxygen and carbon dioxide) through stomata
- Losing water by transpiration to cool the plant
5. What are the functions of flowers in a plant?
Flowers help plants in reproduction by producing seeds. Main functions of flowers are:
- Attracting pollinators for pollination
- Producing pollen and ova
- Developing into fruits that contain seeds
6. How do seeds and fruits form in plants?
Seeds and fruits form from flowers after pollination and fertilization. The process involves:
- Ovules in flowers develop into seeds after fertilization
- The ovary transforms into a fruit to protect the seeds
- Fruits help in dispersal so new plants can grow in different places
7. What are difference between tap root and fibrous root?
Tap roots have one main long root, while fibrous roots have many thin roots. Key differences:
- Tap root: One main root (e.g., carrot, radish)
- Fibrous root: Many similar-sized roots (e.g., wheat, rice)
8. Name two plants that store food in their roots.
Carrot and beetroot are examples of plants that store food in their roots. These root vegetables store nutrients underground, making them edible and nutritious for humans.
9. How does the stem help in the transportation of food and water?
The stem contains tubes called xylem and phloem that transport water, minerals, and food. The function includes:
- Xylem: Carries water and minerals from roots to leaves
- Phloem: Distributes food made in leaves to all parts of the plant
10. What do you mean by photosynthesis?
Photosynthesis is the process by which green plants make their own food using sunlight, carbon dioxide, and water. In photosynthesis:
- Leaves use chlorophyll to absorb sunlight
- Carbon dioxide from air and water from soil are used to prepare food (glucose)
- Oxygen is released as a byproduct
11. Which part of the plant absorbs water and minerals from the soil?
Roots are responsible for absorbing water and minerals from the soil. They have tiny extensions called root hairs that increase their surface area for better absorption.
12. What is the function of fruit in a plant?
The main function of the fruit is to protect the seeds and help in their dispersal. Fruits come in different shapes and sizes and may attract animals to help spread the seeds to new places.
13. Why do plants need leaves?
Plants need leaves to make food and exchange gases with the environment. Leaves carry out photosynthesis and have stomata for gas exchange and transpiration.
14. What are the two main types of roots found in plants?
The two main types of roots are tap roots and fibrous roots. Tap roots have one main thick root, while fibrous roots have many thin, similar roots sprouting from the base of the stem.










