What Is the Structure and Function of Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are essential cell organelles found in eukaryotic cells, often referred to as the cell’s “waste disposal system.” These membrane-bound structures contain powerful digestive enzymes that break down unwanted materials, old cell parts, and even invading microbes. Understanding lysosomes helps us explore vital biological concepts and their effects on health, disease, and everyday life.
What are Lysosomes?
Lysosomes are small, round vesicles found in the cytoplasm of animal cells and some plant cells. They are filled with hydrolytic enzymes capable of digesting various biological molecules. These enzymes work best in an acidic environment, maintained inside the lysosome. Lysosomes play a crucial role in maintaining cellular health by removing waste, recycling cell materials, and defending against pathogens. Their discovery revolutionized our understanding of cell biology and disease mechanisms.
Lysosomes Definition
Lysosomes definition: Lysosomes are membrane-bound cell organelles containing digestive enzymes that break down macromolecules, cellular debris, and foreign invaders within eukaryotic cells.
Structure and Diagram of Lysosomes
A typical lysosome is a spherical sac surrounded by a single membrane. This membrane protects the rest of the cell from the digestive enzymes stored inside. Lysosomal enzymes can break down proteins, nucleic acids, lipids, and complex sugars. The slightly acidic pH inside lysosomes is key for enzyme activity.
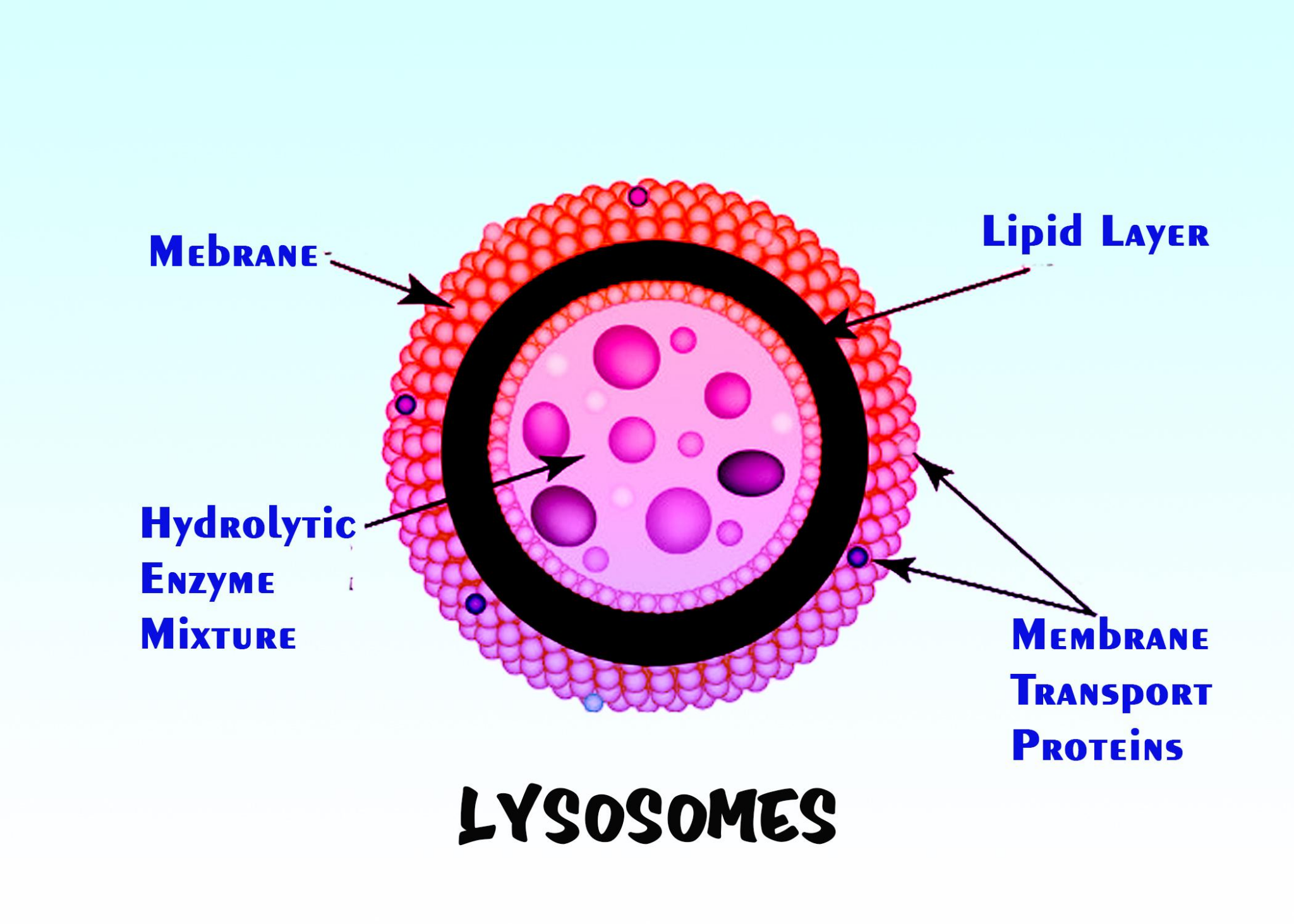
Formation and Types of Lysosomes
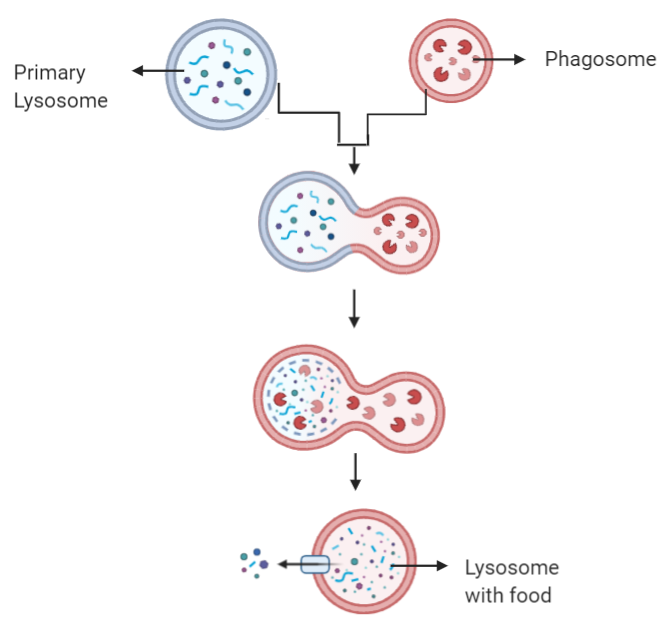
Lysosomes originate from the Golgi apparatus. As primary lysosomes bud off, they carry newly synthesized enzymes. When these fuse with material-containing vesicles in the cytoplasm, they form secondary lysosomes that digest cellular components.
- Primary lysosomes: Newly formed, enzyme-filled vesicles yet to digest any material.
- Secondary lysosomes: Formed after primary lysosomes fuse with materials to be degraded. (Also known as phagolysosomes or autolysosomes.)
The ability to break down diverse substances allows lysosomes to support various cell functions, including autophagy and apoptosis. You can explore related topics, such as apoptosis and cell theory, to understand their interconnected roles.
Functions of Lysosomes
Lysosomes perform vital activities in the cell. They contribute to digestion, recycling, and defense by processing unwanted, damaged, or harmful material.
- Intracellular digestion: Breaking down worn-out organelles, cell debris, or engulfed food particles.
- Autophagy: Recycling damaged or unnecessary cell parts to maintain health and energy balance.
- Defense: Destroying harmful microorganisms that invade the cell, linking to immune responses (see immunity).
- Cell death: Initiating programmed cell death (apoptosis) when necessary.
These versatile functions make lysosomes essential for the survival and proper functioning of cells and organisms.
Lysosomes Examples in Everyday Biology
The importance of lysosomes is seen throughout nature and medicine:
- White blood cells: Use lysosomes to digest bacteria and viruses during infections.
- Tadpoles: Lysosomal enzymes help digest tail tissue as they develop into frogs.
- Liver cells: Clear toxins and recycle cellular waste via lysosomal activity.
- Inherited disorders: Diseases like Tay-Sachs are caused by abnormal lysosomal enzymes (see genetic disorders for more).
Lysosomes Short Notes & Key Features
For quick revision, here are the main features of lysosomes notes useful for Class 12 or exam prep:
- Membrane-bound organelle present in animal and some plant cells.
- Contains hydrolytic (digestive) enzymes active at acidic pH.
- Formed from Golgi apparatus vesicles and aid in cellular recycling.
- Involved in defense, autophagy, cell death, and breaking down foreign material.
- Malfunction can lead to lysosomal storage disorders.
Lysosomes Diagram
Understanding the structure of lysosomes through diagrams is helpful, especially for Class 12 board exams or NEET preparation. For other cell organelles, view animal cell diagrams and plant cell diagrams.
Lysosomes Questions and Practice MCQs
Testing your knowledge with MCQs improves understanding of lysosome concepts and helps in competitive exams. Practice more at Lysosomes MCQs or try related sets like cell biology MCQs.
Applications & Importance of Lysosomes
Lysosomes are not just textbook concepts—they matter in medicine, agriculture, and even environmental science. These organelles are targeted in studying disease treatments, improving understanding of immunity, and are a key focus in genetic research. Malfunctioning lysosomes can lead to illnesses that impact real lives, highlighting the need for scientific discovery.
To deepen your biology knowledge, check out areas like biomolecules, life science, and how traits are inherited on Vedantu.
Difference Between Lysosomes and Related Organelles
| Feature | Lysosomes | Peroxisomes |
|---|---|---|
| Main Function | Digestion of cellular debris and pathogens | Breakdown of fatty acids and detoxification |
| Main Enzymes | Hydrolytic enzymes | Oxidative enzymes |
| pH Requirement | Acidic pH | Neutral to slightly alkaline |
This table highlights that, while lysosomes and peroxisomes both act as clean-up crews in the cell, their enzymes and functions differ significantly.
Lysosomes Explanation: In Simple Words
To sum up, lysosomes are like the recycling and cleaning centers of eukaryotic cells. They maintain a cell’s health by digesting old parts, helping fight infection, and supporting natural cell death. Their breakdown of diverse wastes is essential for growth, immunity, and survival.
Download Lysosomes Notes & PowerPoint
Want to learn more? You can access detailed lysosomes notes for revision or create a lysosomes ppt for school projects by using resources on Vedantu’s biology platform. Use these for exams, assignments, or conceptual clarity.
In conclusion, lysosomes are vital organelles known for their waste-cleaning and recycling role in cells. Their functions support cell survival, health, and immunity, while their dysfunction can cause severe diseases. Learning about lysosomes deepens your understanding of how life works at the microscopic level and empowers you for exams and real-world applications.


FAQs on Understanding Lysosomes and Their Role in Animal (Eukaryotic) Cells
1. What are lysosomes and what is their main function?
Lysosomes are membrane-bound organelles found in eukaryotic cells that act as the cell's digestive system. They break down waste materials, cellular debris, and foreign substances using powerful digestive enzymes.
Key points include:
- Contain hydrolytic enzymes (like proteases, lipases, nucleases).
- Destroy worn-out organelles and pathogens.
- Help maintain cellular health by recycling materials (cellular autophagy).
2. Why are lysosomes called the 'suicide bags' of the cell?
Lysosomes are called the ‘suicide bags’ of the cell because they can self-destruct a cell by releasing their digestive enzymes.
They are important for:
- Autolysis (self-destruction) during cell damage or death.
- Removal of harmful/infected cells from the body.
- Maintaining tissue health and development.
3. What enzymes are present in lysosomes?
Lysosomes contain over 40 different types of hydrolytic enzymes that work best in acidic pH.
Common enzymes include:
- Proteases (break down proteins)
- Lipases (break down fats/lipids)
- Nucleases (degrade nucleic acids)
- Glycosidases (degrade carbohydrates)
4. Where are lysosomes found in the cell?
In eukaryotic cells, lysosomes are scattered in the cytoplasm and are especially abundant in animal cells.
Main points:
- Absent in most plant cells (plants use vacuoles for similar functions).
- Numerous in phagocytic cells (e.g., white blood cells).
- Visible as small, single-membrane organelles under a microscope.
5. What would happen if lysosomes in a cell burst?
If lysosomes burst, their enzymes can digest the entire cell, leading to cell death.
Consequences include:
- Cellular autolysis (self-destruction).
- Release of hydrolytic enzymes into the cytoplasm.
- Useful during programmed cell death (apoptosis) or severe cell damage.
6. What is the structure of a lysosome?
Lysosomes are small, spherical, single-membrane organelles filled with digestive enzymes.
Structural features:
- Size: 0.1 – 1.2 μm in diameter
- Enclosed by a lipid bilayer (membrane)
- Interior has acidic pH (optimum for enzyme activity)
7. What are the main functions of lysosomes in the cell?
Lysosomes are essential for cell maintenance and survival by digesting different materials.
Main functions:
- Digestion and removal of cellular waste
- Destruction of invading bacteria/viruses (cell defence)
- Recycling old cell components (autophagy)
- Aid in apoptosis (programmed cell death)
8. How do lysosomes maintain an acidic environment?
The interior of lysosomes remains highly acidic (pH ~5) due to proton pumps in their membrane that transport hydrogen ions inside.
The acidic environment:
- Activates digestive enzymes
- Prevents enzyme functioning outside the lysosome (protects the cell)
- Ensures efficient breakdown of materials
9. Who discovered lysosomes and when?
Lysosomes were discovered by Christian de Duve in 1955.
Key facts:
- He used cell fractionation techniques to identify them.
- Won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1974 for this discovery.
10. What diseases are caused by malfunctioning lysosomes?
Malfunctioning lysosomes can cause several genetic disorders known as lysosomal storage diseases.
Examples include:
- Tay-Sachs disease
- Gaucher’s disease
- Pompe disease
11. Do plant cells have lysosomes?
Most plant cells do not have typical lysosomes, but they have vacuoles that perform similar digestive and storage functions.
Points to note:
- Vacuoles contain hydrolytic enzymes in plants.
- Lysosomes are mainly found in animal cells.
12. How are lysosomes formed inside the cell?
Lysosomes are formed by the Golgi apparatus in eukaryotic cells.
The process involves:
- Synthesis of hydrolytic enzymes in the rough endoplasmic reticulum (ER).
- Packaging and modification in the Golgi body.
- Budding off of vesicles, which mature into functional lysosomes.










