What Are the Steps and Significance of Double Circulation in Humans?
The process known as double circulation is vital for efficient oxygen and nutrient transport in humans and other mammals. This unique system ensures blood flows through the heart twice in each complete cycle — once for oxygenation and once for delivery to the rest of the body. Understanding double circulation helps explain how our body maintains oxygen supply for energetic activities and supports overall health.
Double Circulation Definition
Double circulation refers to the mechanism where blood passes through the heart twice during one full round in the body. The first circuit sends deoxygenated blood to the lungs for oxygenation (pulmonary circulation), and the second circuit delivers oxygen-rich blood to body tissues (systemic circulation). This system, present in birds and mammals, maintains high efficiency and a clear separation between oxygenated and deoxygenated blood.
Double Circulation Diagram
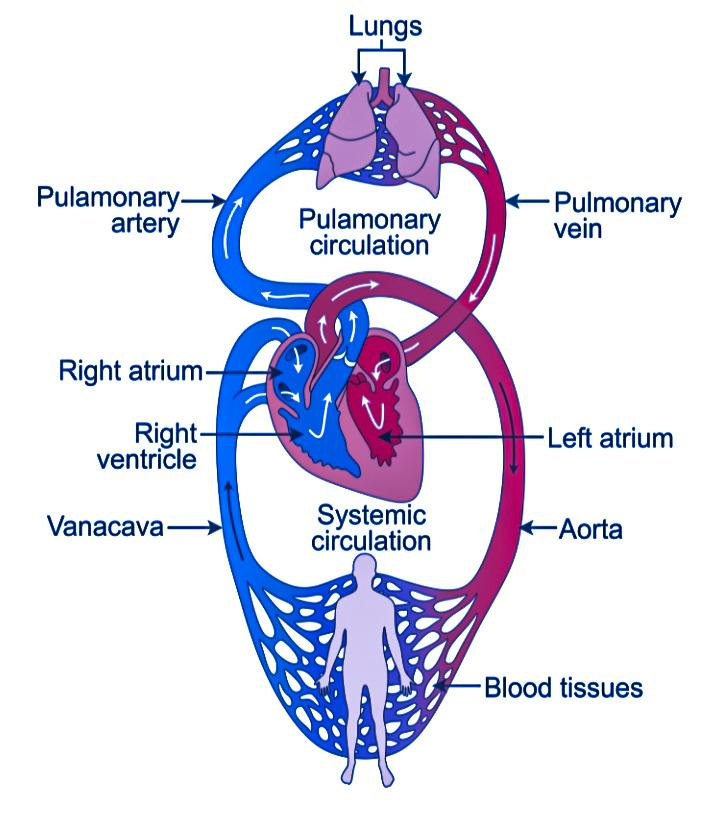
The diagram above illustrates double circulation in the human heart. The blue arrows show the flow of deoxygenated blood, while the red arrows represent oxygenated blood. This clear separation allows for efficient gas exchange and is a feature of advanced vertebrate circulatory systems.
Phases of Double Circulation
Double circulation operates through two main circuits. These work together in a precise sequence to ensure continuous and effective blood transport throughout the body. Here’s how the process unfolds:
- Deoxygenated Blood Enters the Heart: Blood that has delivered oxygen to the body and picked up carbon dioxide returns to the right atrium.
- Pulmonary Circulation: The right ventricle pumps this deoxygenated blood to the lungs through the pulmonary artery.
- Gas Exchange in the Lungs: In the alveoli, blood releases carbon dioxide and absorbs fresh oxygen.
- Oxygenated Blood Returns: Oxygen-rich blood then flows into the left atrium of the heart via pulmonary veins.
- Systemic Circulation: The left ventricle pumps this oxygenated blood to all parts of the body through the aorta.
- Cycle Repeats: After oxygen delivery, blood becomes deoxygenated and returns to the heart, restarting the cycle.
This dual-pathway system allows for a complete separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood, increasing the efficiency of the circulatory process in humans and other mammals.
Comparison: Double Circulation vs Single Circulation
| Feature | Double Circulation | Single Circulation |
|---|---|---|
| Number of heart passages per cycle | Blood passes twice | Blood passes once |
| Separation of oxygenated/deoxygenated blood | Complete separation | No separation |
| Main organisms | Mammals, birds | Fish |
| Circulatory pressure | High efficiency, high pressure | Lower pressure |
Double circulation allows mammals and birds to maintain high metabolic rates and active lifestyles, unlike the simpler single circulation in fish.
Key Features of Double Circulation
- Separation of blood types: Oxygenated and deoxygenated blood never mix.
- Two distinct circuits: Pulmonary (heart-lungs-heart) and systemic (heart-body-heart).
- Ensures high-pressure delivery: Oxygen-rich blood reaches tissues efficiently and rapidly.
- Aids temperature regulation: Particularly essential for mammals and birds.
- Supports extensive exercise and activity: Essential for humans and many animals.
This arrangement enables a higher metabolic rate, needed for warmth, growth, and complex organ functions. High-pressure systemic circulation ensures all body parts get sufficient oxygen and nutrients. Double circulation also supports mammals living in diverse climates and active environments.
Double Circulation Explanation with Examples
An easy way to understand double circulation is by comparing how blood flows in humans and many other mammals. Take the example of a person running — their muscles need more oxygen. The heart pumps vigorously, sending oxygen-rich blood through the systemic circuit. Deoxygenated blood returns to the heart, goes to the lungs for fresh oxygen, then re-circulates again. Animals such as cows, dogs, and birds also use double circulation to support their active lifestyles.
- Humans and mammals (e.g., cats, elephants)
- Birds (e.g., pigeons, eagles)
In contrast, organisms like fish exhibit only single circulation. For more on differences, see arteries and veins or other circulatory system topics on Vedantu.
Significance and Benefits
The primary benefit of double circulation is the separation of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood. This maximizes oxygen supply to body organs, supports efficient energy use, and enables a fast response during increased activity. It also helps with removing waste products like carbon dioxide rapidly from tissues. Thus, double circulation is a fundamental advantage in vertebrate evolution and essential for complex life.
Double Circulation in Human Health and Medicine
Understanding double circulation is crucial in medicine for diagnosing heart and lung conditions. For example, defects that allow mixing of the two blood types can lead to health issues. Physicians use this knowledge to interpret heart murmurs and congenital heart diseases. Concepts like the alveoli for gas exchange and heart structure are also linked to double circulation.
Double Circulation Questions & Practice MCQs
Regular practice of objective questions helps consolidate learning about double circulation, especially for double circulation class 12 or entrance exams. Use these sample MCQs:
- Which chamber receives deoxygenated blood in humans?
- What is the main advantage of double circulation?
- Name one animal that shows double circulation.
- List the two primary circuits in double circulation.
For further exploration and quizzes, Vedantu offers plenty of body fluids and circulation resources.
Real-World Relevance and Related Topics
Double circulation is not only a biological concept but also relevant in real-world contexts like environmental adaptation and survival. For instance, temperature regulation via efficient circulation supports life in various climates. To understand more about life processes such as photosynthesis, climate effects, or life processes, explore related lessons on Vedantu:
- Nutrient roles in the body
- Effects of climate change on living beings
- Acquired and inherited traits
- Vertebrate and invertebrate differences
The study of double circulation connects to broader scientific topics like health, environment, and evolution.
Page Summary
Double circulation describes the efficient system through which blood passes twice through the heart — enabling constant oxygen delivery to tissues and robust waste removal. This page highlighted its definition, process, advantages, examples, and its role in health. To master related biological systems, learner-friendly resources are available on Vedantu for deeper understanding.


FAQs on Understanding Double Circulation
1. What is double circulation in humans?
Double circulation in humans refers to a unique blood flow system where blood passes through the heart twice during each complete cycle. This ensures efficient oxygenation and separation of oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood.
Main features:
- Systemic circulation: Carries oxygenated blood from the left side of the heart to the body tissues.
- Pulmonary circulation: Transports deoxygenated blood from the right side of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation.
2. Why is double circulation important in humans?
Double circulation is crucial because it keeps oxygen-rich and oxygen-poor blood separate, ensuring efficient oxygen delivery to all cells and supporting higher metabolic rates.
Key points:
- Prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
- Ensures tissues receive fully oxygenated blood
- Supports faster, more efficient removal of carbon dioxide
3. What are the two types of circulation in the human body?
The two types of circulation in the human body under double circulation are systemic circulation and pulmonary circulation.
Systemic circulation:
- Transports oxygenated blood from the left ventricle to the body
- Carries deoxygenated blood from the right ventricle to the lungs
4. Explain the pathway of blood in double circulation.
In double circulation, blood travels through the heart twice in one complete cycle.
Pathway:
- Deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium → right ventricle → pumped to the lungs (pulmonary circulation)
- Oxygenated blood returns from lungs → left atrium → left ventricle → pumped to the entire body (systemic circulation)
5. How is double circulation different from single circulation?
The main difference between double circulation and single circulation is that in double circulation, blood flows through the heart twice during each cycle, while in single circulation it passes only once.
Differences:
- Double circulation: Found in mammals and birds; separates oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
- Single circulation: Seen in fishes; blood passes through the heart just once per cycle and mixes freely
6. What advantages does double circulation provide to mammals and birds?
Double circulation provides several advantages to mammals and birds:
- Efficient delivery of oxygen and nutrients
- Better regulation of body temperature (endothermy)
- Supports higher metabolic rates and active lifestyles
- Prevents mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood
7. Draw and label a diagram of double circulation in humans.
To illustrate double circulation, draw two circuits showing:
- Heart chambers (right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, left ventricle)
- Arrows showing deoxygenated blood to lungs (pulmonary circuit)
- Arrows showing oxygenated blood to body (systemic circuit)
8. What happens if there is mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood in humans?
If oxygenated and deoxygenated blood mix in humans, tissues receive less oxygen, leading to shortness of breath and reduced efficiency.
- Mixing decreases oxygen supply to organs
- Can result in bluish skin (cyanosis) and fatigue
- Common in heart defects like septal defects
9. How does the heart maintain double circulation?
The heart maintains double circulation with its four chambers: right atrium, right ventricle, left atrium, and left ventricle.
- Right side pumps deoxygenated blood to lungs
- Left side pumps oxygenated blood to the body
- Valves prevent backflow and maintain direction
10. What is pulmonary circulation and what is systemic circulation?
Pulmonary circulation is the blood flow from the heart to the lungs and back, while systemic circulation is the flow from the heart to the rest of the body.
Pulmonary circulation:
- Right ventricle → lungs → left atrium
- Left ventricle → body tissues → right atrium










