Steps and Applications of DNA Fingerprinting Explained for Students
DNA fingerprinting is a powerful technique used to identify individuals based on their unique DNA patterns. Widely used in forensic science, medicine, and paternity cases, DNA fingerprinting class 12 students learn its steps and applications as part of their curriculum. This topic explains what is DNA fingerprinting, its process, significance, and its impact on society.
What is DNA Fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting is a technique that analyses specific regions in DNA to create a unique genetic profile for an individual. Because no two people (except identical twins) have the same DNA pattern, this method is highly reliable for identification. Developed by Alec Jeffreys in 1984, DNA fingerprinting revolutionized genetics and forensic science.
Principle of DNA Fingerprinting
The principle of DNA fingerprinting is based on the presence of variable number tandem repeats (VNTRs) in the non-coding regions of human DNA. These are sequences that differ greatly among individuals, making them ideal for identification. Restriction enzymes, PCR, and gel electrophoresis are commonly used in the DNA fingerprinting technique to analyze these regions.
History and Discovery
DNA fingerprinting was discovered by British geneticist Alec Jeffreys at Leicester University in 1984. During an experiment on myoglobin genes, he noticed unique patterns in DNA. The first practical use was in an immigration case, soon followed by its application in criminal investigations. This method became an essential tool in modern biology and forensic science.
Steps of DNA Fingerprinting (Process Diagram)
The steps involved in DNA fingerprinting are systematic and precise. Here is a simplified outline of the DNA fingerprinting process for class 12 and above, along with a schematic DNA fingerprinting diagram.
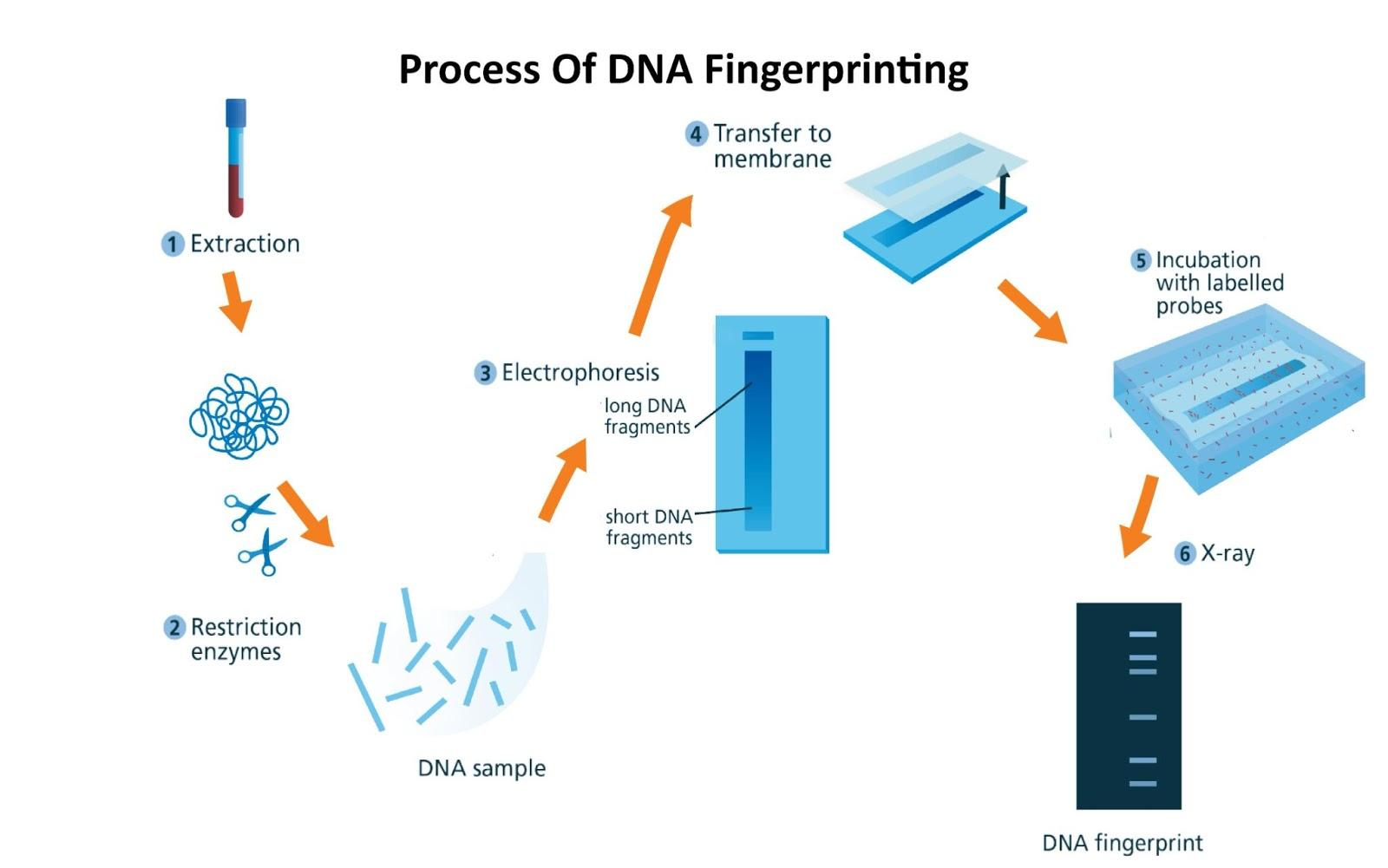
- Sample Collection: Obtain DNA from sources like blood, hair, or saliva.
- DNA Extraction: Isolate DNA by breaking open cells and purifying genetic material.
- Digestion with Restriction Enzymes: Cut DNA into fragments at specific sites using restriction endonucleases.
- Gel Electrophoresis: Separate DNA fragments by size using an electric field.
- Transfer (Blotting): Move DNA from gel onto a nylon or nitrocellulose membrane (Southern blotting).
- Hybridization with Probes: Use radioactive or fluorescent DNA probes to bind to complementary sequences.
- Visualization: Detect unique banding patterns (DNA fingerprints) using X-ray film or special scanners.
These steps of DNA fingerprinting make each person’s DNA band pattern distinctive, allowing for precise comparison.
Applications of DNA Fingerprinting
The application of DNA fingerprinting has a wide range of benefits in science, law, and society. It plays a key role in criminal justice, medical diagnostics, and environmental research.
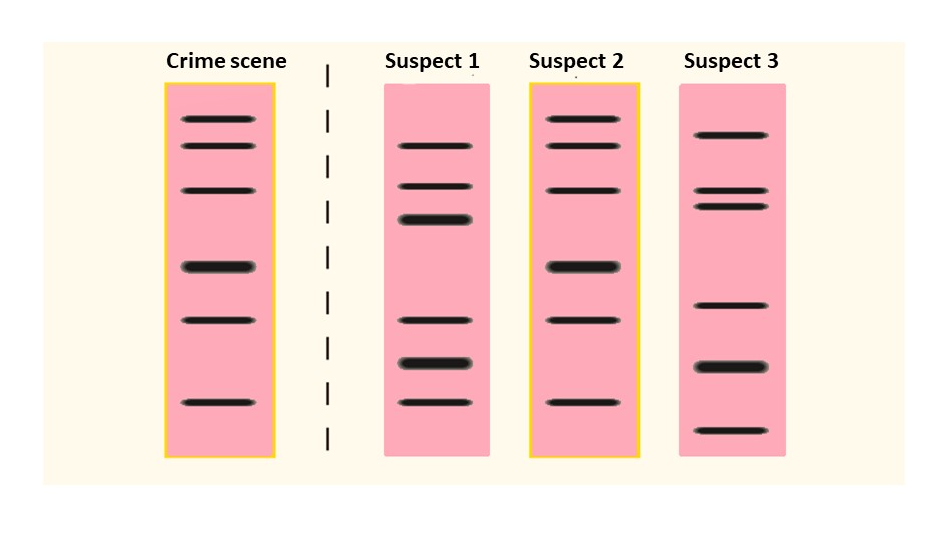
- Forensic Science: Identifying suspects and victims in crime investigations.
- Paternity and Maternity Testing: Resolving disputes by confirming family relationships.
- Detection of Inherited Disorders: Screening for genetic diseases in newborns or before birth.
- Wildlife and Conservation: Tracking poached animals or endangered species for conservation efforts.
- Immigration and Identification: Establishing identities in complex legal and social cases.
DNA fingerprinting applications are also useful in agriculture for plant and animal breeding and in epidemiology to track disease outbreaks. The Centre for DNA Fingerprinting and Diagnostics in India is a leading institution in this field.
Advantages and Limitations
There are many advantages of DNA fingerprinting. It is accurate, highly sensitive, and can analyze even old or degraded samples. However, limitations include contamination risks, high cost, and the need for skilled experts. Accuracy depends on the quality of handling and laboratory procedures.
Real-World Examples
DNA fingerprinting has helped solve major criminal cases, such as the identification of serial offenders and missing persons. In medicine, it aids bone marrow transplants and diagnosis of hereditary diseases. In environmental studies, it helps identify illegally traded animals or plants, supporting conservation biology and sustainable ecosystems. You can explore more about genetic inheritance here.
Practice: DNA Fingerprinting Class 12 Project Ideas
Students working on a DNA fingerprinting class 12 project can:
- Model the DNA fingerprinting steps using paper bands to represent DNA fragments.
- Discuss how gel electrophoresis separates DNA fragments.
- Research a famous DNA fingerprinting case and explain its impact on law and science.
- Create a presentation or PPT about the applications of DNA fingerprinting in modern biology.
DNA Fingerprinting in Hindi
DNA फिंगरप्रिंटिंग kya hai? यह एक जैव-प्रौद्योगिकी तकनीक है जो डीएनए की विशिष्टता के आधार पर किसी व्यक्ति की पहचान करती है। भारत में भी इसका उपयोग अपराध की जांच, पितृत्व परीक्षण, और आनुवंशिक रोगों का पता लगाने के लिए होता है।
Express Your Opinion about the Use of DNA Fingerprinting
DNA fingerprinting has transformed how we ensure justice and solve biological mysteries. It protects the innocent and provides scientific evidence. However, proper regulation is necessary to safeguard privacy and prevent misuse. Integrating ethics with science is key to harnessing the full potential of DNA fingerprinting in society and medicine.
Related Topics at Vedantu
To explore more biology topics, visit:
- Difference between Acquired and Inherited Traits
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- DNA Structure
- Recombinant DNA Technology
- Genetic Engineering
For comprehensive notes, diagrams, and projects related to life science, biomolecules, and cell theory, explore Vedantu's Biology resources.
DNA fingerprinting combines advances in genetics, biotechnology, and forensic science, impacting law, healthcare, environment, and agriculture. It is an indispensable scientific tool, taught in class 12 and applied worldwide. Understanding its principles, steps, and applications empowers students and professionals to make informed decisions and contribute to society.


FAQs on What is DNA fingerprinting and how does it work?
1. What is DNA fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting is a scientific method used to identify individuals based on their unique patterns of DNA sequences.
Key points include:
- It analyzes specific regions of DNA that vary greatly among people.
- It is highly accurate for personal identification and relationship testing.
- This technique is commonly called DNA profiling or DNA typing.
2. Who developed the technique of DNA fingerprinting?
The technique of DNA fingerprinting was developed in 1984 by Sir Alec Jeffreys, a British geneticist at the University of Leicester.
Important details:
- His discovery revolutionized forensic science and paternity testing.
- First used in criminal investigations and immigration disputes.
- Considered a landmark in genetics and biotechnology.
3. What are the steps involved in DNA fingerprinting?
The process of DNA fingerprinting consists of several key steps:
- Sample Collection: Obtaining DNA from blood, hair, saliva, or other tissues.
- DNA Extraction: Isolating pure DNA from the cells.
- Restriction Enzyme Digestion: Cutting DNA into fragments using enzymes.
- Gel Electrophoresis: Separating DNA fragments by size using an electric field.
- Southern Blotting: Transferring DNA fragments onto a membrane.
- Hybridization with DNA probes: Detecting specific DNA sequences using labeled probes.
- Autoradiography: Visualizing the unique pattern to produce the DNA fingerprint.
4. What are the applications of DNA fingerprinting?
DNA fingerprinting is widely used for identification and relationship analysis in various fields:
- Forensic science: Identifying criminals and solving crimes.
- Paternity and maternity testing: Establishing biological relationships.
- Personal identification: Recognizing unidentified individuals.
- Wildlife and biodiversity studies: Tracking genetic diversity and species conservation.
- Disaster victim identification: Recognizing victims in accidents or calamities.
5. What are Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) in DNA fingerprinting?
Variable Number Tandem Repeats (VNTRs) are short, repetitive DNA sequences that vary in number among individuals.
Key concepts:
- VNTRs are used as genetic markers in DNA fingerprinting.
- They provide the uniqueness in every individual’s DNA profile.
- VNTR analysis helps distinguish one person’s DNA from another.
6. How does DNA fingerprinting help in solving criminal cases?
DNA fingerprinting aids in forensic investigations by matching DNA found at crime scenes with suspects.
It is used to:
- Identify the actual perpetrator by comparing crime scene DNA to suspect samples.
- Exonerate innocent individuals wrongly accused or suspected.
- Link multiple crimes to the same offender using biological evidence.
7. What are the advantages of DNA fingerprinting?
The major advantages of DNA fingerprinting are:
- Extremely high accuracy for individual identification.
- Wide applicability in forensics, kinship analysis, and conservation.
- Small biological samples can be used for analysis.
- Results are reliable, reproducible, and withstand legal scrutiny.
8. What is the significance of DNA fingerprinting in paternity testing?
DNA fingerprinting conclusively determines biological relationships.
- Matches DNA profiles of parents and children with near-perfect accuracy.
- Resolves disputes in legal, inheritance, and family scenarios.
- Used for establishing both paternity and maternity.
9. What are the limitations or drawbacks of DNA fingerprinting?
Despite its power, DNA fingerprinting has some limitations:
- Contamination or improper handling of samples can affect results.
- Expensive and requires sophisticated laboratory equipment.
- Ethical and privacy concerns about storing genetic information.
10. What are the ethical issues associated with DNA fingerprinting?
Ethical concerns with DNA fingerprinting arise from misuse and data privacy, including:
- Potential misuse of genetic data for unauthorized surveillance or discrimination.
- Loss of privacy if DNA databases are not properly secured.
- Need for strict legal and ethical guidelines to protect individual rights.










