What Are the Main Structural and Functional Differences Between Xylem and Phloem?
Understanding the Difference Between Xylem And Phloem is crucial for students studying plant biology, especially for class 12 and competitive exams. Both these tissues play an essential role in the transport of substances within plants, but their mechanisms, structure, and functions differ greatly. This topic page provides clear explanations, diagrams, notes, and examples to help you grasp these key concepts easily.
Difference Between Xylem and Phloem: Definition
Xylem and Phloem are the two main types of vascular tissues found in higher plants. Xylem transports water and soluble mineral nutrients from the roots throughout the plant. Phloem transports organic compounds, especially sugars, from the leaves to other parts of the plant. Understanding the difference between xylem and phloem definition builds a foundation for further topics in life science.
Structure and Components
Both xylem and phloem are classified as complex tissues because they consist of more than one type of cell. Let’s look at their cell composition:
- Xylem is composed of tracheids, vessel elements, xylem fibres, and xylem parenchyma.
- Phloem is made of sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma.
These structural differences allow each tissue to perform specialized functions, supporting the plant’s growth and survival.
Xylem and Phloem Diagram
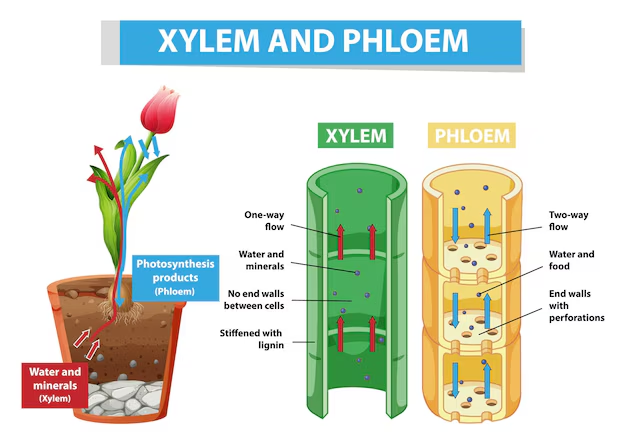
The above diagram shows the arrangement of xylem and phloem tissues in a plant stem. Xylem typically occupies an inner position, while phloem is found towards the outer layer. Observing such diagrams helps answer difference between xylem and phloem diagram-based questions in exams.
Tabular Comparison: Difference Between Xylem And Phloem
| Feature | Xylem | Phloem |
|---|---|---|
| Function | Transports water and minerals | Transports food and organic nutrients |
| Direction of Flow | Unidirectional (root to leaves) | Bidirectional (source to sink) |
| Location in stem | Inner side (towards pith) | Outer side (towards cortex) |
| Main Cell Types | Tracheids, vessels, fibres, parenchyma | Sieve tubes, companion cells, fibres, parenchyma |
| Living/Dead at maturity | Mostly dead (except parenchyma) | Mostly living (except fibres) |
| Thickness of cell walls | Thick-walled | Thin-walled |
The above table clearly highlights the difference between xylem and phloem in terms of their structure, function, and position within plant tissues. Such tabular notes are extremely useful for revision and quick reference, especially before exams.
Explanation: How Do Xylem and Phloem Work?
Xylem works like a one-way pipeline, conducting water from roots to the leaves using physical forces like capillary action, root pressure, and transpiration pull. In contrast, phloem carries food (mainly sucrose) in both directions—either from leaves to the rest of the plant or from storage organs back to growing tissues. This process is called translocation, and it requires metabolic energy.
Difference Between Xylem and Phloem: Key Examples
Let’s look at some real-world examples to clarify the difference between xylem and phloem:
- When you water a plant, the water travels upward via the xylem to reach the leaves.
- When glucose formed during photosynthesis in leaves moves to roots for storage or to flowers for growth, this transport happens through the phloem.
Studying these examples helps students answer application-based questions and MCQs on this topic.
Short Notes: Points to Remember
- Xylem transports water; phloem carries food.
- Xylem flow is unidirectional; phloem flow is bidirectional.
- Xylem cells are mostly dead at maturity; phloem cells are largely living.
- Xylem is found inside the vascular bundle; phloem occupies the outer part.
For revision, create difference between xylem and phloem short notes and use these points for class 12 board exams or quick recaps.
Application in Agriculture, Environment, and Human Life
These vascular tissues are vital in agriculture, as healthy xylem ensures crops get enough water and minerals, while efficient phloem enables proper food distribution. Problems in xylem can cause wilting, while phloem diseases can reduce yields. Understanding these differences supports key topics like adaptations in plants and reproduction in plants.
Related Topics for Deeper Understanding
To explore plant tissues further or deepen your biology concepts, check out these important resources on Vedantu:
- Classification of Tissues
- Difference Between Simple and Complex Tissues
- Difference Between Monocot and Dicot Stem
- Plant Tissues
- Transportation in Plants
Exploring these topics will help strengthen your biology foundation and score higher in exams.
Difference Between Xylem And Phloem: Sample Questions
- Define xylem and phloem. How are they different?
- Draw a well-labelled diagram showing xylem and phloem in a dicot stem.
- State two points of difference between xylem and phloem.
- Give one example that illustrates xylem function and one that illustrates phloem function.
- Solve MCQs based on the features of xylem and phloem for practice.
Practice these questions and review the difference between xylem and phloem notes or PPTs for revision.
Downloadable Resources
Vedantu offers curated difference between xylem and phloem notes, diagrams, and MCQ questions to help you prepare efficiently. These resources are helpful for quick revision and include class 12-level explanations, making your preparation complete.
In summary, the Difference Between Xylem And Phloem forms the backbone of plant physiology topics taught in biology. Grasping their structure, function, and unique features helps students build a strong base for more advanced concepts in plant science, agriculture, and environmental studies, as covered in various Vedantu resources.


FAQs on Difference Between Xylem And Phloem Explained
1. What is the difference between xylem and phloem?
Xylem and phloem are two distinct types of vascular tissues in plants that serve different functions.
- Xylem primarily transports water and minerals from roots to leaves.
- Phloem transports food (sugars) produced in leaves to other parts of the plant.
- Xylem cells are mostly dead and provide mechanical support.
- Phloem cells are living and help distribute nutrients.
- Xylem movement is generally upward only; phloem moves substances in both directions as needed.
2. What is xylem?
Xylem is a plant vascular tissue responsible for transporting water and dissolved minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant.
- It consists mainly of vessel elements, tracheids, xylem fibers, and xylem parenchyma.
- Most xylem cells are non-living at maturity, except for parenchyma cells.
- It provides structural support to plants.
3. What is phloem?
Phloem is the vascular tissue in plants that transports organic nutrients, especially sucrose, from leaves to all parts of the plant.
- Phloem consists of sieve tube elements, companion cells, phloem fibers, and phloem parenchyma.
- Most phloem cells are living at maturity, except for fibers.
- It allows bidirectional movement of food substances.
4. What are the main functions of xylem and phloem?
Xylem and phloem are responsible for the transportation of water, minerals, and food in plants.
- Xylem: Conducts water and minerals upwards from roots.
- Phloem: Distributes food like glucose from leaves to the entire plant.
5. List two differences between xylem and phloem.
Xylem and phloem differ in structure and function.
- Xylem transports water and minerals; phloem transports organic food.
- Xylem cells are mainly dead; phloem cells are mainly living.
6. What are the components of xylem and phloem?
Xylem and phloem are complex tissues, each made of several specialized cells.
- Xylem: Vessel elements, tracheids, fibers, and parenchyma.
- Phloem: Sieve tubes, companion cells, fibers, and parenchyma.
7. Why is xylem considered a dead tissue and phloem a living tissue?
Xylem is considered mostly dead because most of its conducting cells (vessels and tracheids) lack cytoplasm when mature, while phloem is living as it primarily consists of living cells (except fibers).
- Xylem's dead cells help support water movement by forming hollow tubes.
- Phloem's living cells are actively involved in translocation of food.
8. How does the direction of transport differ in xylem and phloem?
The direction of movement in xylem is unidirectional—always upwards from roots to shoots—while in phloem it is bidirectional, depending on the plant's needs.
- Xylem: Upwards only.
- Phloem: Upwards and downwards.
9. Can you explain the role of xylem and phloem in plant survival?
Both xylem and phloem are essential for the survival and growth of vascular plants as they enable efficient transport of materials.
- Xylem supplies water and minerals necessary for photosynthesis and structure.
- Phloem distributes synthesized food to all parts, supporting growth and metabolism.
10. What would happen if phloem in a plant is damaged?
If the phloem is damaged, the plant cannot transport food from leaves to other parts, causing tissues to die due to starvation.
- Root and non-photosynthetic parts will not receive necessary nutrients.
- This leads to plant wilting, poor growth, and eventually death of affected parts.










