Batch vs Continuous Fermentation: Definitions, Process, and Benefits
The fermentation process usually occurs in microbes and this process is used to form various products. For this, large tanks are used known as bioreactors in which all the components such as nutrition, and microbes are mixed and products allowed to be formed in controlled conditions. To learn more about fermentation, batch and continuous fermentation and the difference between them, continue reading through the following article.
What is Fermentation?
Fermentation is the process of oxidation of organic material in absence of oxygen. It is a metabolic process that occurs in microbes.
Types of Industrial Fermentation
There are mainly three types of fermentation:
Batch fermentation
Fed-Batch fermentation
Continuous fermentation
Batch Fermentation
In batch fermentation, all the components are mixed at once then the reaction undergoes without any further intake from outside. During the whole process, no extra nutrients are added. It is a closed system because all the components are added at once and no other components are added in between the process of fermentation.
There are three phases in the batch fermentation process - lag phase, exponential phase, and stationary phase.
In the lag phase, microbes adapt to the environment of the culture and
In the exponential phase, the microbial cells grow rapidly and consume most of the nutrients and the last phase is
The stationary phase is when the growth of microbes stops due to the consumption of all nutrients. It is the simplest type of all industrial fermentation.
The batch fermentation diagram is given below.
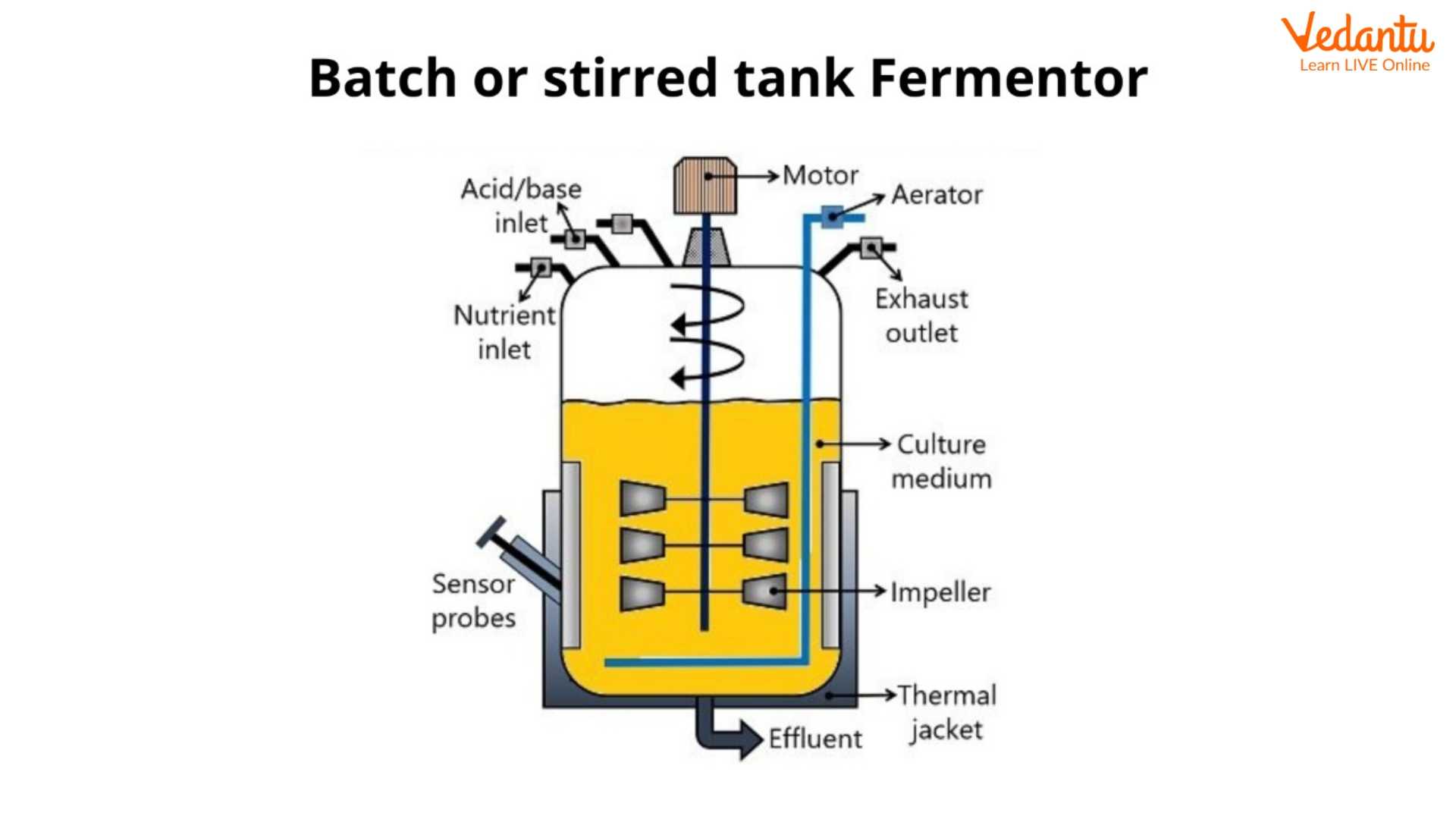
Batch Fermenter
Fed-Batch Fermentation
It is a modification of batch fermentation.
In this nutrition is added aseptically and the amount of liquid culture in the bioreactor increases as the culture is added systematically.
It is a type of semi-open system.
It yields a better result than batch fermentation.
After consumption of early substrate continuous and constant nutrition is added.
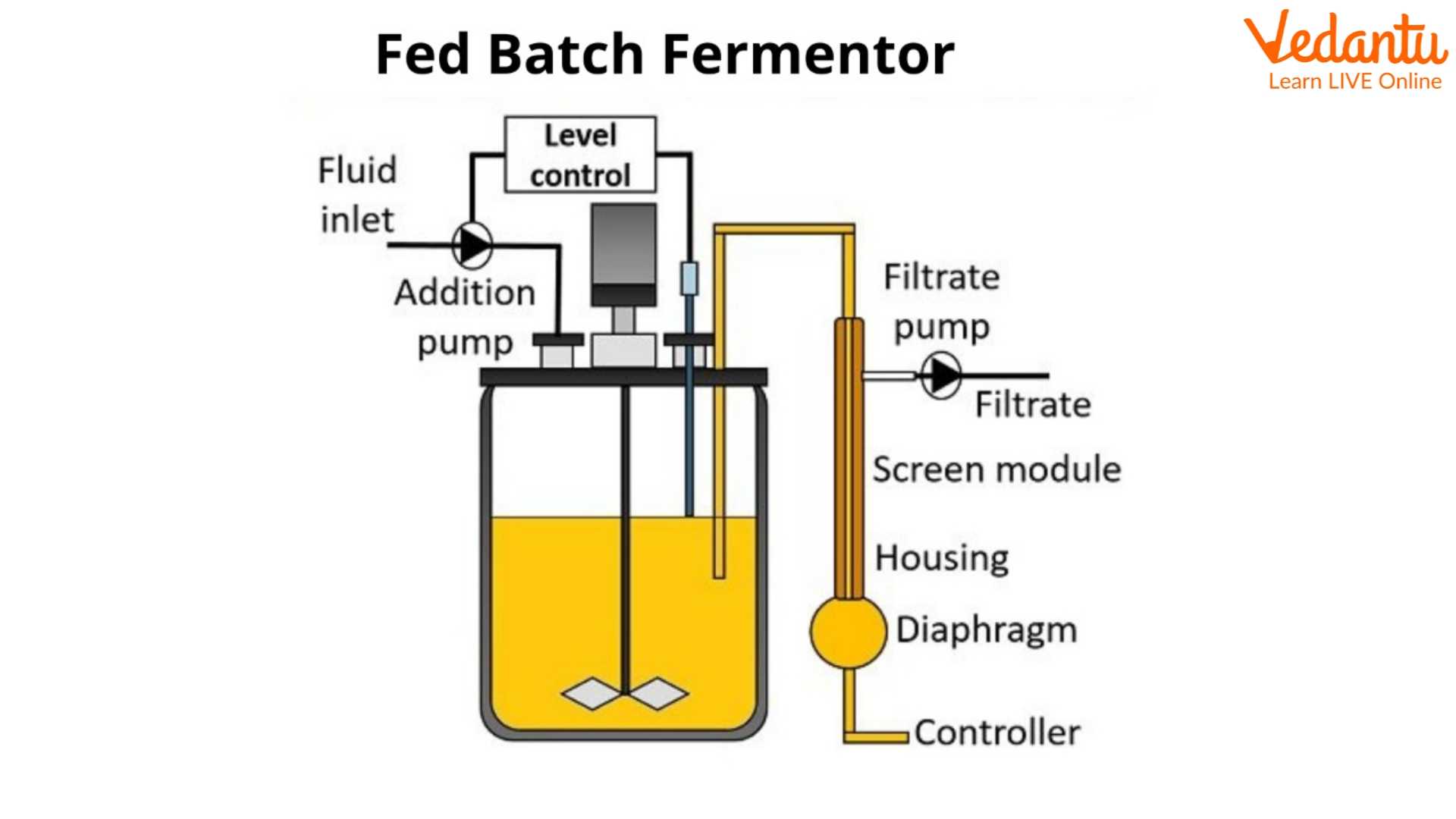
Fed-batch Fermenter
Continuous Fermentation
It is a type of fermentation in which constant addition and flow of solution occur.
Microorganisms and sterile nutrients are added continuously and the nutrient solutions and microbes are transformed simultaneously.
It is a type of open fermentation system in which comments can be added and removed in between the process.
There are many methods of continuous fermentation.
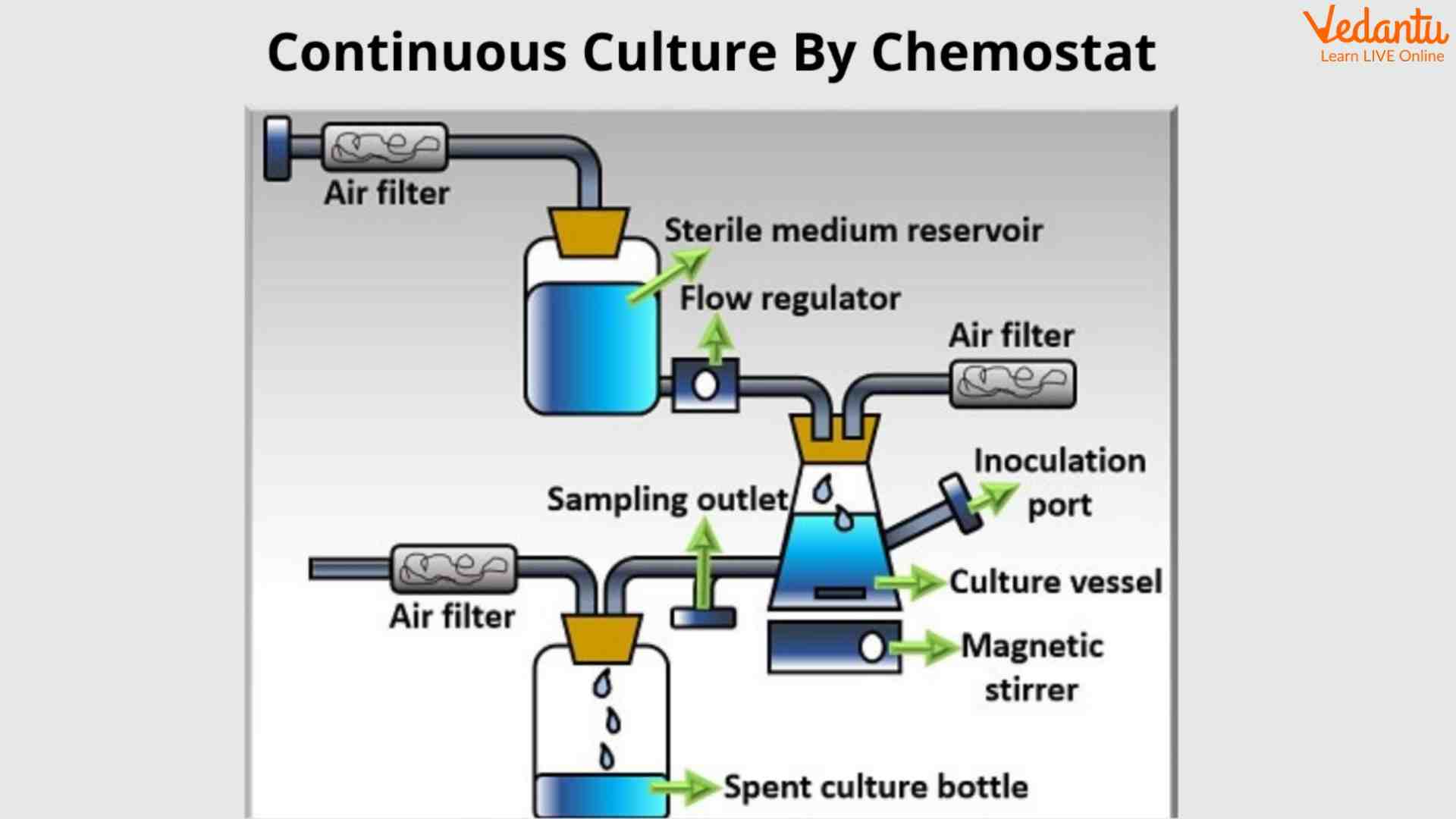
Continuous Fermenter
Similarity between Batch Fermentation and Continuous Fermentation
There are many similarities between batch and continuous fermentation. In both batch fermentation and continuous fermentation, development conditions are provided from the outside. In both, temperatures, pH and aeration are maintained. In both types of fermentation useful products are formed.
Difference between Batch and Continuous Fermentation
There are many differences between batch and continuous fermentation.
Important Questions
1. Which phase is longer in continuous fermentation?
Ans: Exponential phase is of longer duration in continuous fermentation as nutrients are continuously being added to the solution. This phase shows the maximum growth rate. This phase is also known as the log phase.
2. What are the limitations of fermentation?
Ans: Fermentation is a slow and continuous process and it requires more energy. and resources.
3. Which microorganism is responsible for fermentation?
Ans: Mostly lactic acid bacteria of several genera, including lactobacillus, streptococcus, yeast, and another fungus also used for the fermentation process.
Fun Facts about Fermentation
The fermentation process is one of the important processes as it enhances the nutritional value of food.
Various types of expensive dishes are made by the fermentation process.
Wine or alcohol is also made by the fermentation process.
Fermentation is also a method of preserving food items.
Practice Questions
Does fermentation require oxygen?
Why is temperature important in the fermentation process?
What factors speed up the fermentation process?
What is batch culture used for?
What are the advantages of batch culture?
Key Features
The fermentation process is used to make various products.
There are three types of industrial fermentation.
Batch fermentation is the simplest type of fermentation and batch-fed is a modification of batch fermentation.
In this article, we have also studied batch culture and continuous culture.
There are differences between continuous fermentation and fed-batch fermentation like fed-batch is a closed system whereas continuous fermentation is an open system.


FAQs on Difference Between Batch and Continuous Fermentation
1. What is the main difference between batch and continuous fermentation?
The main difference lies in how the process is managed. In batch fermentation, all ingredients are added at the start into a closed system, and the process runs until completion, after which the product is harvested. In continuous fermentation, it's an open system where fresh nutrients are continuously added while the fermented broth and products are simultaneously removed.
2. How do the growth phases of microorganisms differ in batch and continuous systems?
The microbial growth curve is very different in each system.
- In batch fermentation, microorganisms go through all four growth phases: lag, log (exponential), stationary, and decline.
- In continuous fermentation, the environment is controlled to keep the microorganisms in a constant state of exponential (log) growth, leading to higher productivity over time.
3. Why is continuous fermentation often called an 'open system'?
It is called an 'open system' because there is a constant exchange with the outside environment. A fresh medium containing nutrients is continuously fed into the fermenter, and an equal volume of used medium and product is removed. This maintains a steady state inside, unlike a 'closed' batch system where nothing is added or removed after the start.
4. For producing something like ethanol on a large industrial scale, which method is more efficient?
For large-scale industrial production of products like ethanol, continuous fermentation is generally more efficient. This is because it offers higher productivity, consistent product quality, and reduced downtime between batches. The process can run for long periods, making it more cost-effective for high-volume products.
5. What is fed-batch fermentation and how is it different from the other two methods?
Fed-batch fermentation is a hybrid method. It starts like a batch process, but nutrients are added incrementally (in 'feeds') throughout the fermentation. Unlike continuous fermentation, the product is usually not removed until the end. This method helps to:
- Control the concentration of substrate to avoid toxicity.
- Achieve very high cell density and product yield.
- Extend the productive phase of the culture.
6. Are there situations where batch fermentation is better than continuous fermentation?
Yes, batch fermentation is preferred in several scenarios. It is ideal for producing secondary metabolites like many antibiotics, which are typically formed during the stationary phase of microbial growth. It is also simpler to operate, requires less complex control systems, and poses a lower risk of contamination over long run times, making it suitable for smaller-scale or high-value products.
7. What key environmental factors must be controlled in any fermentation process?
Several factors are critical for successful fermentation. The most important ones to monitor and control are:
- Temperature: Each microorganism has an optimal temperature for growth and production.
- pH: The acidity or alkalinity of the medium affects enzyme activity and microbial health.
- Oxygen Level: Depending on whether the process is aerobic or anaerobic, the oxygen supply must be regulated.
- Substrate Concentration: The amount of nutrient available directly impacts the growth rate and product formation.










