Key Types of Cell Organelles and Their Roles in Cells
Imagine a bustling city where each building has a specific role, ensuring the city runs smoothly. Similarly, within every cell, various organelles work in harmony to maintain life. From generating energy to storing genetic information, cell organelles are the unsung heroes of biology. But what exactly are cell organelles, and how do they contribute to a cell’s functionality? Let’s delve into the fascinating world of cell organelles and uncover their vital roles.
Understanding Cell Organelles
What are Cell Organelles?
Cell organelles are specialised structures within a cell that perform distinct functions necessary for the cell's survival and proper operation. These organelles can be classified based on whether they are membrane-bound or non-membrane-bound, and they exist in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Each organelle plays a crucial role, from providing structure and support to facilitating complex biochemical processes.
Also, read Difference Between Organs and Organelles
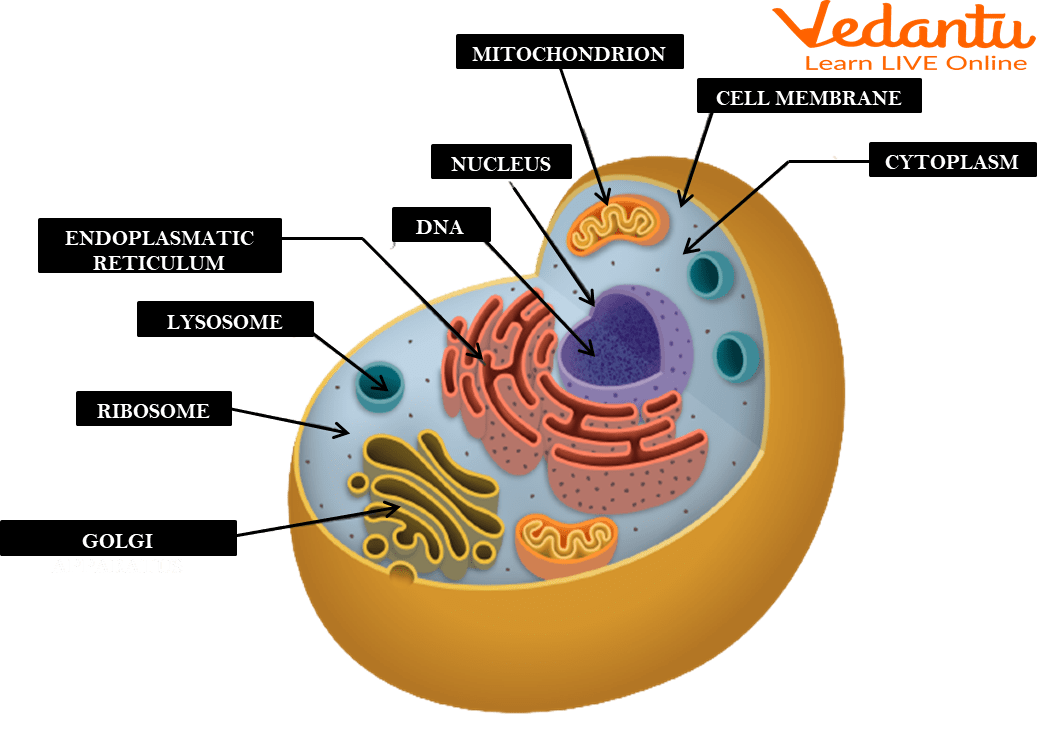
Types of Cell Organelles
Cell organelles are broadly categorised into three groups:
Non-Membrane-Bound Organelles:
Cytoskeleton: Provides structural support and facilitates cell movement.
Ribosomes: Synthesise proteins necessary for various cellular functions.
Centrosomes and Centrioles: Organise microtubules and are essential during cell division.
Single Membrane-Bound Organelles:
Vacuoles: Store nutrients, and waste products, and help maintain cellular homeostasis.
Lysosomes: Contain enzymes for digesting macromolecules.
Golgi Apparatus: Modifies, sorts, and packages proteins and lipids for transport.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough and Smooth): Involved in protein and lipid synthesis.
Double Membrane-Bound Organelles:
Nucleus: Houses genetic material and controls cellular activities.
Mitochondria: Produce energy through ATP synthesis.
Chloroplasts (in plant cells): Conduct photosynthesis to produce glucose.
A Brief Summary of Cell Organelles
Detailed Functions of Key Cell Organelles
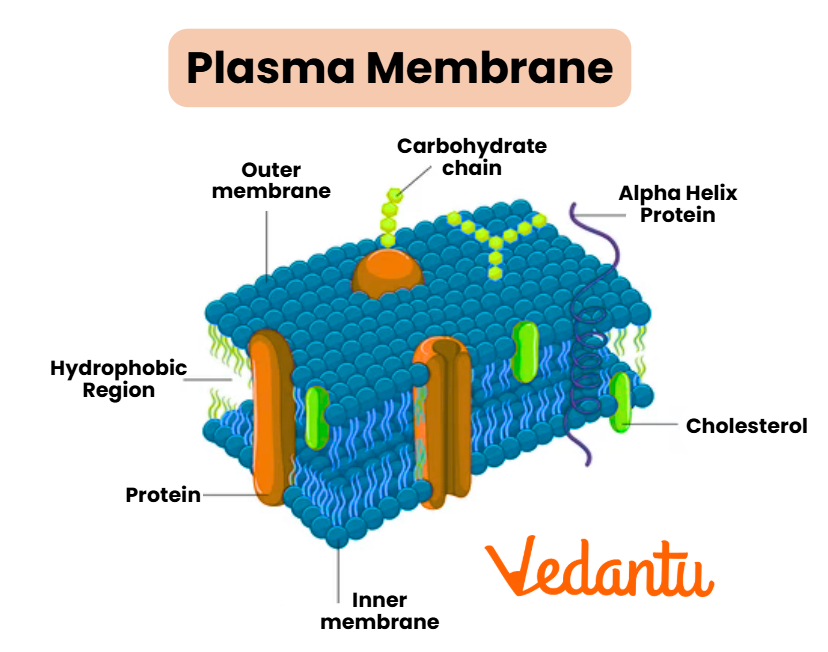
Plasma Membrane
The plasma membrane, also known as the cell membrane, is a selectively permeable barrier that regulates the movement of substances in and out of the cell. Composed of a lipid bilayer with embedded proteins, it maintains the cell’s integrity and facilitates communication with the external environment.
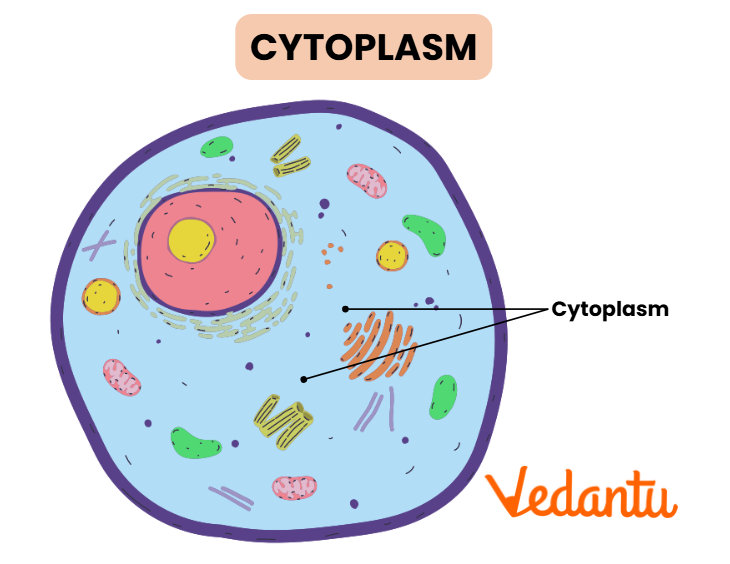
Cytoplasm
Cytoplasm is the jelly-like substance within the cell, excluding the nucleus. It contains all the cell organelles and is the site for most of the cell's metabolic activities, including protein synthesis and energy production.
Nucleus
The nucleus is the cell's command centre, containing DNA that dictates cellular functions and heredity. It is surrounded by a double membrane called the nuclear envelope, which houses the nucleolus, where ribosomal RNA is synthesised.

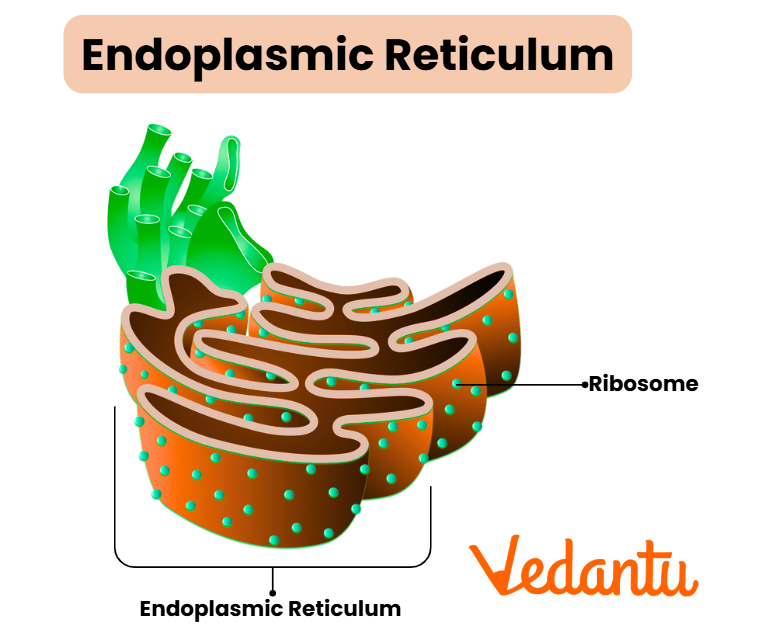
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Rough ER: Studded with ribosomes, it is involved in protein synthesis and modification.
Smooth ER: Lacks ribosomes and is responsible for lipid synthesis, detoxification, and calcium storage.
Also, Read the Endoplasmic Reticulum(ER)
Mitochondria
Mitochondria is also known as the powerhouse of the cell, mitochondria generate ATP through cellular respiration. They have their own DNA and are involved in regulating the cell's energy supply and apoptosis.

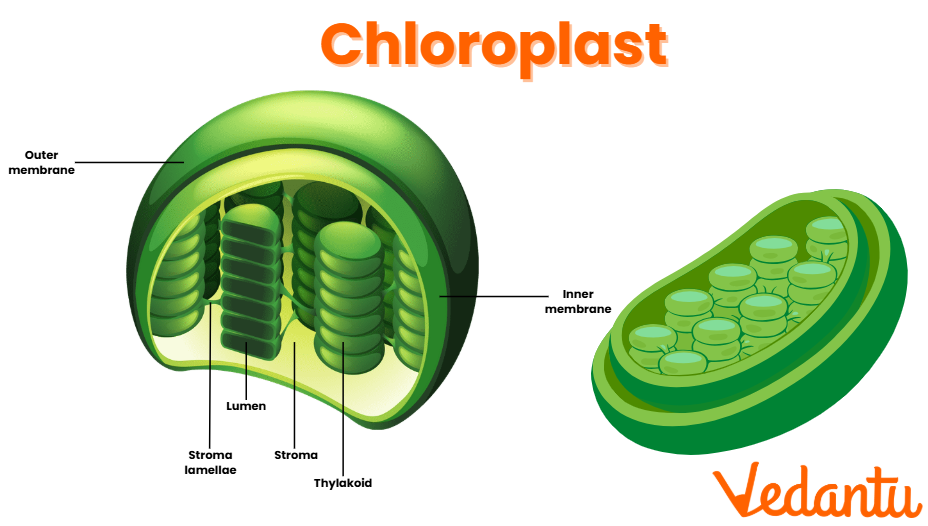
Plastids
Plastids are found in plant cells and include chloroplasts, chromoplasts, and leucoplasts.
Chloroplasts: Perform photosynthesis, converting light energy into chemical energy.
Chromoplasts: Store pigments that give plants their vibrant colours.
Leucoplasts: Store starches, oils, and proteins.
Ribosomes
Ribosomes are the sites of protein synthesis, translating genetic information from mRNA to build proteins essential for various cellular functions. They can be free-floating or attached to the rough ER.
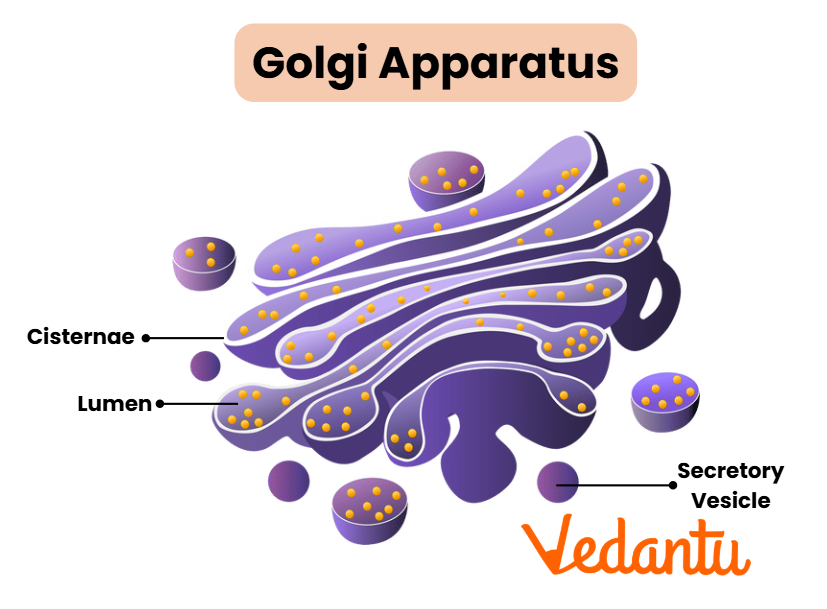
Golgi Apparatus
The Golgi apparatus modifies proteins and lipids received from the ER and packages them into vesicles for transport to their destination, whether inside or outside the cell.
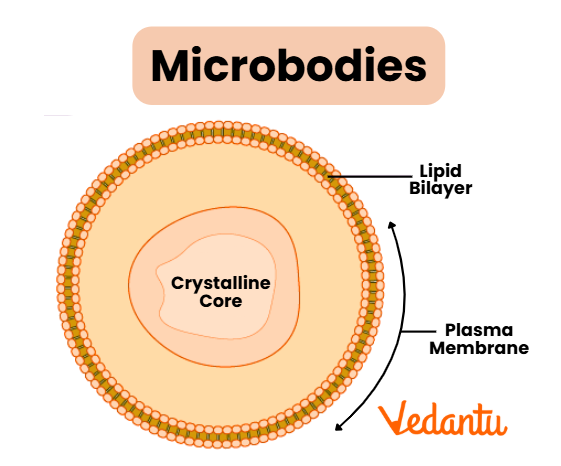
Microbodies
Microbodies, including peroxisomes, contain enzymes that oxidise fatty acids and detoxify harmful substances, contributing to cellular metabolism and protection.
Cytoskeleton
The cytoskeleton is a network of protein fibres that maintain the cell’s shape, secure organelles in specific positions, and allow for cellular movement.
Cilia and Flagella
These hair-like structures protrude from the cell surface and facilitate movement. Cilia move fluid over the cell’s surface, while flagella propel the entire cell.
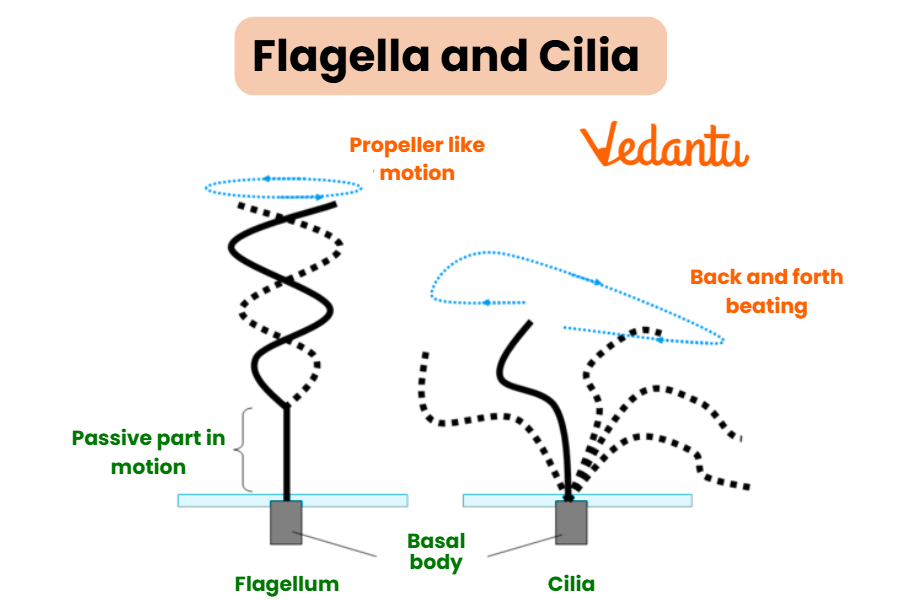
Also, read the Difference between Cilia and Flagella
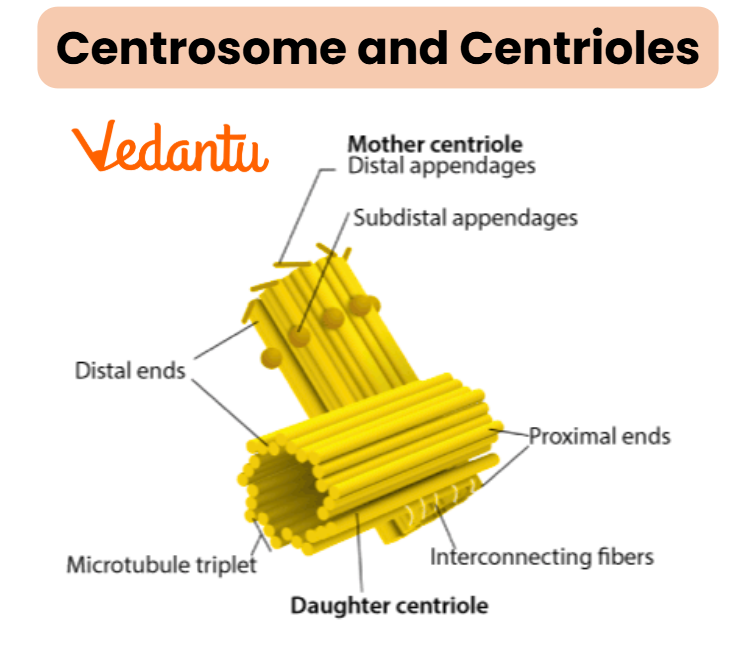
Centrosome and Centrioles
Centrosomes organise the microtubules of the cytoskeleton and play a key role during cell division by forming the spindle fibres that separate chromosomes.
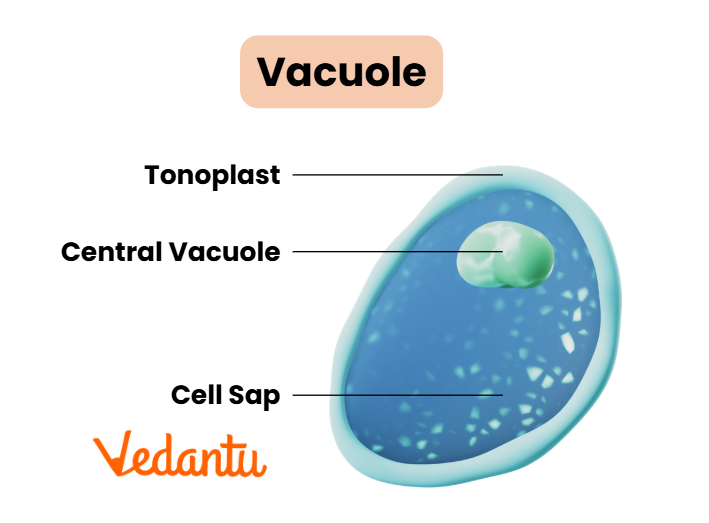
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are storage organelles that hold nutrients, waste products, and other substances. In plant cells, a large central vacuole maintains turgor pressure.
Interactive Quiz: Test Your Knowledge on Cell Organelles
Question: Which organelle is known as the powerhouse of the cell?
A) Nucleus
B) Ribosome
C) Mitochondria
D) Golgi Apparatus
Question: What is the primary function of the Golgi apparatus?
A) Protein synthesis
B) Energy production
C) Modifying and packaging proteins
D) DNA storage
Question: Which organelle is responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells?
A) Chloroplast
B) Lysosome
C) Endoplasmic Reticulum
D) Vacuole
Check your answers below:
C) Mitochondria
C) Modifying and packaging proteins
A) Chloroplast
Fun Task:
Draw and label a cell organelles diagram. Identify each organelle and write a brief description of its function. Share your diagram with classmates or friends to test their knowledge!
Fun Facts about Cell Organelles
Mitochondrial DNA: Unlike most of our DNA, mitochondrial DNA is inherited only from the mother.
Chloroplast Independence: Chloroplasts have their own DNA and can reproduce independently of the cell.
Ribosome Abundance: A single cell can contain millions of ribosomes, highlighting their importance in protein synthesis.
Real-World Applications
Understanding cell organelles is crucial in various fields such as medicine, genetics, and biotechnology. For example, targeting mitochondria can help treat diseases related to energy production, while manipulating chloroplasts can enhance crop yields through improved photosynthesis. Additionally, knowledge of ribosomes is essential in developing antibiotics that inhibit bacterial protein synthesis without affecting human cells.


FAQs on Cell Organelles: Functions, Structure, and Importance
1. What exactly are cell organelles?
Cell organelles are specialised, often membrane-bound structures found inside a eukaryotic cell. Think of them as a cell's 'mini-organs'. Each one performs a specific job, such as producing energy, building proteins, or getting rid of waste, all of which are essential for the cell to function and survive.
2. Which organelle is known as the 'powerhouse of the cell' and why?
The mitochondrion (plural: mitochondria) is famously called the 'powerhouse of the cell'. This is because it is the main site of cellular respiration, the process that converts nutrients like sugar into ATP (adenosine triphosphate), which is the main energy currency that fuels almost all cellular activities.
3. What is the main function of the nucleus in a cell?
The nucleus acts as the cell's command centre. Its primary functions are to:
- Store the cell's genetic blueprint in the form of DNA.
- Control all of the cell's activities, including growth, metabolism, and division, by regulating gene expression.
4. What is the difference between the rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum (ER)?
The main difference is their structure and function. The rough ER is covered with ribosomes, giving it a 'rough' look, and its job is to synthesise and modify proteins. In contrast, the smooth ER has no ribosomes and is responsible for making lipids, breaking down toxins, and storing calcium ions.
5. How do the organelles in a plant cell differ from those in an animal cell?
While both cell types share many organelles like the nucleus and mitochondria, plant cells have three distinct structures that animal cells do not:
- A rigid cell wall made of cellulose that provides structural support.
- Chloroplasts, the sites where photosynthesis occurs.
- A large central vacuole that stores water and helps maintain cell rigidity.
6. Why are lysosomes often called the 'suicide bags' of the cell?
Lysosomes earn this nickname because they contain powerful digestive enzymes capable of breaking down cellular components. If a cell becomes severely damaged or old, the lysosome can rupture and release these enzymes, leading to the self-digestion of the cell. This process, called autolysis, is a form of programmed cell death.
7. How do organelles like the Golgi apparatus and endoplasmic reticulum work together?
These organelles function like a factory's production and shipping line. The endoplasmic reticulum synthesises proteins and lipids. These products are then sent to the Golgi apparatus, which acts as a 'post office'. It modifies, sorts, and packages these molecules into vesicles for transport to their final destinations, either inside or outside the cell.
8. If a cell's ribosomes were suddenly destroyed, what would happen?
The most immediate and critical consequence would be a complete halt in protein synthesis. Because proteins are vital for nearly every cellular task—from acting as enzymes to providing structure—the cell would be unable to repair itself, carry out metabolic functions, or grow, ultimately leading to its death.
9. What are the key organelles in a typical animal cell and their roles?
A typical animal cell contains several key organelles, each with a specific job:
- Nucleus: Controls cell activities and holds DNA.
- Mitochondria: Generate energy (ATP).
- Ribosomes: Build proteins.
- Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER): Synthesises proteins (rough ER) and lipids (smooth ER).
- Golgi Apparatus: Processes and packages proteins and lipids.
- Lysosomes: Break down waste and cellular debris.
- Cytoskeleton: Provides shape and facilitates movement.
10. Do viruses have organelles?
No, viruses do not have organelles. They are not considered true cells because they lack the complex internal machinery like mitochondria or ribosomes. A virus is much simpler, typically just genetic material (DNA or RNA) inside a protein coat. It must infect a living host cell to use its organelles to replicate.










