How Are Animals Classified Based on Their Food Habits?
Animals and Their Food is a fascinating topic that explains how different animals survive and thrive by consuming various types of food. Understanding this helps us learn about food chains, animal adaptations, and the importance of balanced diets in nature. This knowledge is vital for students, as it builds a strong foundation for understanding ecosystems, habitats, and biodiversity.
What are Animals and Their Food?
Animals and their food refers to the study of what different animals eat, how they obtain their food, and the roles they play in ecosystems. Animals depend on plants, other animals, or a combination of both to meet their nutritional needs. By examining animals and their eating habits, we can better understand the relationships they share with their environment and other living organisms.
Types of Animal Diets
Animals are classified based on their food choices and how they obtain nutrients. These classifications help us understand animal food habits and their positions in the food chain.
| Diet Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Herbivores | Eat only plants | Cows, deer, elephants, goats |
| Carnivores | Eat only other animals | Lions, tigers, sharks, hawks |
| Omnivores | Eat both plants and animals | Bears, humans, crows, pigs |
| Scavengers | Consume dead animals | Vultures, hyenas, jackals |
| Filter Feeders | Strain tiny organisms from water | Baleen whales, flamingos |
This classification, called animals food classification, is essential for understanding animals and their habitats and food, as it affects their behavior and ecosystems.
What Do Animals Eat?
The diet of animals varies widely depending on their anatomy, habitat, and evolutionary adaptations. While some animals eat only specific foods, others have flexible diets. Recognizing animals and their food chart patterns can help students relate to science in real life.
- Herbivores consume grass, leaves, fruits, and stems (e.g., rabbits eat carrots and grass).
- Carnivores feed on meat from other animals (e.g., tigers hunt deer and wild boar).
- Omnivores eat a mix, such as grains, insects, fruits, and smaller animals (e.g., humans and bears).
- Specialized diets include nectar (hummingbirds), blood (leeches), or bones (hyenas).
These examples reinforce key concepts for animals and their food for kids, and form the basics of animals and their food worksheet activities in junior classes.
Where Do Animals Get Their Food From?
Animals get their food from their surroundings, and their habitats provide the resources they need. The link between animals and their habitats and food is essential for survival and directly influences biodiversity. For example, grazing animals in grasslands consume grass, while aquatic animals eat algae or other fish, as explained in the Terrestrial Ecosystem section.
- Land animals feed on plants, insects, or other land creatures.
- Water animals may eat plankton, fish, or aquatic plants.
- Some birds and insects collect nectar or pollen from flowers, aiding both their diet and plant pollination cycles.
The availability and diversity of food in a habitat influence animal adaptation and the development of unique food habits.
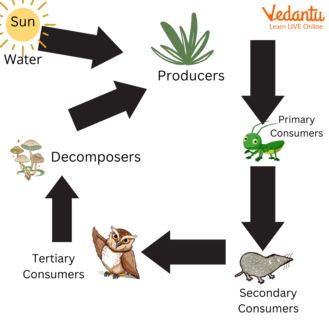
Animals and Food Chain
A food chain illustrates who eats whom in an ecosystem. It shows the transfer of energy from one organism to another through feeding relationships. Plants are known as producers as they create their own food by photosynthesis, while animals are consumers that rely directly or indirectly on plants for food. This topic connects deeply with Food Science and Nutrition in Living Organisms.
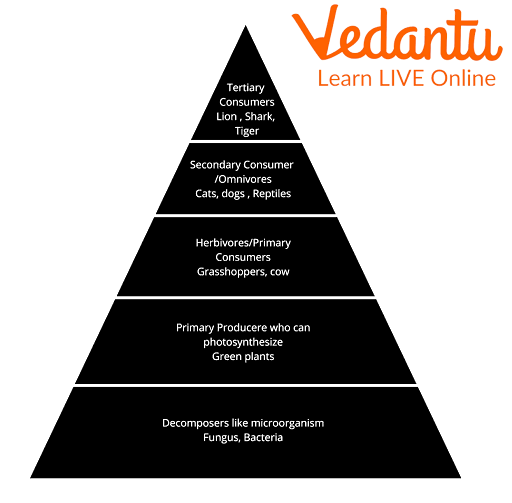
- Producers: Plants and algae that use sunlight to make food.
- Primary Consumers: Herbivores that eat plants.
- Secondary Consumers: Carnivores and omnivores that eat herbivores.
- Tertiary Consumers: Top predators that eat secondary consumers.
- Decomposers: Organisms like bacteria and fungi that break down dead material.
Food webs offer a more complex view, showing how many food chains are interlinked within an ecosystem. This highlights the concept of animals and food habits class 3 and food sources in nature.
Key Features of Animal Eating Habits
Animals show a variety of eating habits or adaptations tailored to their diet and lifestyle. These features ensure proper nutrition, energy, and health in animal populations.
- Herbivores often have flat teeth or special digestive systems for breaking down plant matter.
- Carnivores possess sharp teeth or claws for catching and eating prey.
- Omnivores have mixed features, such as varied teeth for both plants and meat.
- Birds have beaks shaped according to their diet, as discussed on Beaks and Claws of Birds.
- Some aquatic animals use filter feeding to catch tiny organisms in water.
These adaptations can be further explored in Animal Adaptations and animals and their food class 2 resources.
Interesting Facts About Animals and Their Food
Animals and their food is a diverse subject with many fascinating facts. Here are some examples that help students relate to real-world situations and spark curiosity.
- Cows, like other ruminants, chew their food twice for better digestion.
- Owls can rotate their heads up to 270 degrees, helping them spot prey easily.
- Baleen whales eat thousands of tiny krill daily by filtering seawater.
- Some birds, like the vulture, clean the environment by eating carrion (dead animals).
- Carnivores obtain certain nutrients by eating the organs of their prey.
Such facts make animals and their food for kids and animals and their food worksheet exercises more engaging. You can discover more curious facts in Facts About Animals.
Why Is It Important to Study Animals and Their Food?
Learning about animals and their food habits is not only important for exams, but it also increases our appreciation for nature. It has relevance in biology, medicine, agriculture, and environmental science. Understanding animal nutrition helps in wildlife conservation, pet care, farming, and maintaining ecological balance. For example, knowledge about What Do Various Nutrients Do For Our Body can be vital for students aspiring to work in medicine or research.
Summary of Animals and Their Food
Animals and their food explores how animals obtain, eat, and utilize food depending on their dietary habits and needs. It covers the concepts of the food chain, food webs, animal adaptations, and the relationships between food, habitat, and survival. This topic builds a deeper understanding of nature, supporting studies in science, health, and the environment.


FAQs on Animals And Their Food: Meaning, Types, and Examples
1. What are the main types of animals based on their food habits?
Animals can be categorised based on their food into three main groups:
- Herbivores – eat only plants (e.g., cow, deer, goat)
- Carnivores – feed on other animals (e.g., lion, tiger, leopard)
- Omnivores – eat both plants and animals (e.g., human, bear, crow)
2. What do herbivores eat? Give examples.
Herbivores are animals that feed only on plant materials. Examples of herbivore diets include:
- Grass (e.g., cow, horse)
- Leaves (e.g., goat, giraffe)
- Fruits and seeds (e.g., parrot, rabbit)
3. How do carnivores obtain their food?
Carnivores are animals that eat the flesh of other animals to get food and energy. They typically:
- Hunt or prey on other animals
- Have sharp teeth and claws for catching and eating meat
- Examples: tiger, lion, eagle, snake
4. What are omnivores? Name two examples.
Omnivores are animals that eat both plant and animal food sources. They have the ability to digest a variety of foods and get nutrients from both categories. Examples include:
- Humans
- Bears
- Crows
5. What is scavenging in animals?
Scavenging is when animals get their food by eating dead animals or leftover remains. Important points about scavengers:
- Help keep the environment clean by eating decaying matter
- Examples: vulture, hyena, jackal
- They are nature’s ‘cleaners’
6. Why are food habits important for animals?
Food habits help animals get the necessary energy and nutrients for survival and growth. Key reasons:
- Different animals require different types of food
- Food habits determine an animal’s habitat and role in the food chain
- Adaptation of teeth, digestive systems, and behavior depends on food habits
7. What is a food chain? Give an example involving animals and their food.
A food chain shows how energy is transferred from one organism to another in an environment. Example:
- Grass → Goat (herbivore) → Lion (carnivore)
8. Why do different animals eat different kinds of food?
Different animals eat different foods because of differences in their body structure, digestive system, and habitat. Reasons include:
- Variation in teeth shapes for eating plants or meat
- Certain animals can digest only specific foods
- Food availability in their natural habitat
9. Name two animals that eat both plants and animals.
Animals that eat both plants and animals are called omnivores. Common examples include:
- Bear
- Crow
- Human
10. How do animals get their food in the wild?
Animals obtain their food in the wild through hunting, grazing, browsing, or scavenging. Methods include:
- Herbivores graze on plants and grass
- Carnivores hunt or prey on other animals
- Scavengers eat dead or decaying matter
- Omnivores eat a wide variety of food items
11. What is the difference between a herbivore and a carnivore?
The main difference is that herbivores eat only plants while carnivores eat only animal flesh. Comparison:
- Herbivores: Blunt teeth, flat molars, eat grass, leaves, and fruits
- Carnivores: Sharp teeth, pointed canines, hunt animals for food
12. What is the role of scavengers in nature?
Scavengers help keep ecosystems clean by eating dead and decaying animals. Their important roles are:
- Prevent the spread of diseases by removing remains
- Recycle nutrients back into the soil
- Examples: vultures, jackals, hyenas










