
Why is the zener diode heavily doped?
Answer
507.9k+ views
Hint:A zener diode is a type of diode that can operate in the reverse direction. The diode behaves like a typical diode when it is forward biassed. The Zener diode, on the other hand, is strongly doped, resulting in a thin depletion region. When the applied voltage is more than the reverse voltage, the zener diode conducts like a regular diode, and when the applied voltage is greater than the reverse voltage, it also conducts in the reverse bias situation.
Complete answer:
Zener diodes are diodes that are engineered to work in the breakdown zone. The Zener diode will not be damaged if the reverse voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage as long as the current does not exceed the maximum value and the device is not overloaded.
The depletion layer becomes very thin as a result of the strong doping, and the electric field across the junction becomes quite high, even for a small reverse bias voltage. When a sufficiently enough electric field is applied to the junction, the bond can be directly ruptured. If a strong electric field acts on a bound electron, the electron can be ripped from the covalent link, resulting in a multiplicity of electron-hole pair pairings.
High field emission, also known as Zener breakdown, is the mechanism that causes this. The degree of doping in the diode determines the value of reverse voltage at which this occurs. The Zener breakdown voltage of a substantially doped diode is low, whereas the Zener breakdown voltage of a lightly doped diode is high.
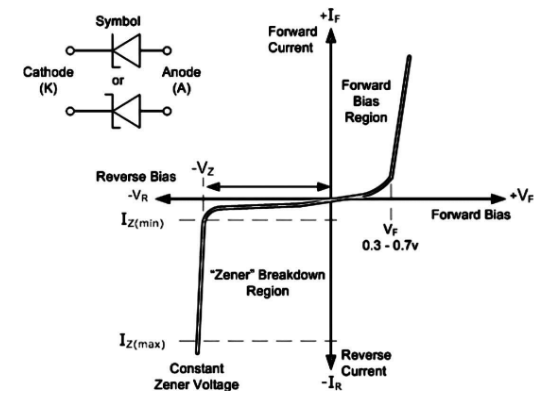
Note: Zener diodes are one of the main building blocks of electronic circuits and are widely utilised in electronic equipment of all kinds. They're used to create low-power stabilised supply rails from a larger voltage and give reference voltages for circuits, particularly stabilised power supplies. They're also employed to guard against overvoltage, particularly electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Complete answer:
Zener diodes are diodes that are engineered to work in the breakdown zone. The Zener diode will not be damaged if the reverse voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage as long as the current does not exceed the maximum value and the device is not overloaded.
The depletion layer becomes very thin as a result of the strong doping, and the electric field across the junction becomes quite high, even for a small reverse bias voltage. When a sufficiently enough electric field is applied to the junction, the bond can be directly ruptured. If a strong electric field acts on a bound electron, the electron can be ripped from the covalent link, resulting in a multiplicity of electron-hole pair pairings.
High field emission, also known as Zener breakdown, is the mechanism that causes this. The degree of doping in the diode determines the value of reverse voltage at which this occurs. The Zener breakdown voltage of a substantially doped diode is low, whereas the Zener breakdown voltage of a lightly doped diode is high.

Note: Zener diodes are one of the main building blocks of electronic circuits and are widely utilised in electronic equipment of all kinds. They're used to create low-power stabilised supply rails from a larger voltage and give reference voltages for circuits, particularly stabilised power supplies. They're also employed to guard against overvoltage, particularly electrostatic discharge (ESD).
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




