
Which of the following will accept ${{\text{H}}^{\text{ + }}}$ from ${\text{NH}}_4^ + $ ion:
A.
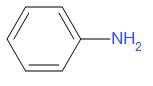
B.
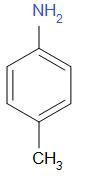
C.
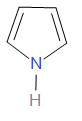
D.
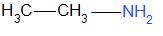



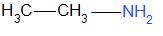
Answer
578.1k+ views
Hint: The compound that accepts a proton from an acid is said to be acting as a base. Nitrogen containing organic compounds having up to a shared electron pair on nitrogen atoms acts as an organic base.
Complete step by step answer:
The strength of organic nitrogenous bases depends upon the availability of unshared electron pairs on the nitrogen atom. The availability of unshared electron pairs on basic sites increases due to presence of electron releasing group and decreases in presence of electron withdrawing group. Availability of unshared electron pairs decreases due to delocalization of unshared electron pairs through resonance.
Generally aromatic bases are weaker than aliphatic bases. This is due to the delocalization of the unshared lone pair of electrons on nitrogen through resonance. Hence there is less availability of electron pairs for protonation. As the compounds in option A, B and C are aromatic, they are weaker bases than option D.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note:
In aliphatic amines, the availability of electron pairs increases due to the increase in inductive effect of alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. The introduction of an alkyl group into ammonia increases the basic strength significantly. The introduction of a second alkyl group further increases the basic strength of the amine, but the net effect of introducing the alkyl group is very less marked than with the first. This is due to crowding around nitrogen atoms because crowding decreases the readiness with which a basic site takes up protons. The introduction of a third alkyl group decreases the basic strength.
The basic strength is determined by the extent to which the conjugate acid can undergo solvation. More the hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen in the cation, the greater the possibilities of powerful solvation via hydrogen bonding.
Complete step by step answer:
The strength of organic nitrogenous bases depends upon the availability of unshared electron pairs on the nitrogen atom. The availability of unshared electron pairs on basic sites increases due to presence of electron releasing group and decreases in presence of electron withdrawing group. Availability of unshared electron pairs decreases due to delocalization of unshared electron pairs through resonance.
Generally aromatic bases are weaker than aliphatic bases. This is due to the delocalization of the unshared lone pair of electrons on nitrogen through resonance. Hence there is less availability of electron pairs for protonation. As the compounds in option A, B and C are aromatic, they are weaker bases than option D.
Thus, the correct option is D.
Note:
In aliphatic amines, the availability of electron pairs increases due to the increase in inductive effect of alkyl groups attached to the nitrogen atom. The introduction of an alkyl group into ammonia increases the basic strength significantly. The introduction of a second alkyl group further increases the basic strength of the amine, but the net effect of introducing the alkyl group is very less marked than with the first. This is due to crowding around nitrogen atoms because crowding decreases the readiness with which a basic site takes up protons. The introduction of a third alkyl group decreases the basic strength.
The basic strength is determined by the extent to which the conjugate acid can undergo solvation. More the hydrogen atoms attached to the nitrogen in the cation, the greater the possibilities of powerful solvation via hydrogen bonding.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




