
What is the wave front of the light waves?
Answer
595.2k+ views
Hint: The propagation of a wave can be depicted by a specific pattern so a wave propagation can have amplitude fluctuations and phase differences but however if this wave tends to have a constant phase all throughout the radiating pattern then this front is what we are interested in. This concept will help approaching the problem.
Complete step-by-step answer:
A wave front is a surface over which an optical wave has a constant phase (i.e. there is no phase difference).
Or such a surface which envelopes the particles that are in the same state of vibration is known as a wave front.
The wave front at any instant is defined as the locus of all the particles of the medium which are in the same state of vibration.
The sum of rays passing through a surface produces/creates/develops a wave front.
As we all know that the wave front always travels perpendicular to each other, this will indicate that the ray of lights falling on the wave front makes a right angle with the wave front.
This will indicate that the ray of light which is always parallel to each other makes the wave front which is perpendicular to each other.
A wave front is a surface or line in the path of wave motion on which the disturbances at every point have the same phase.
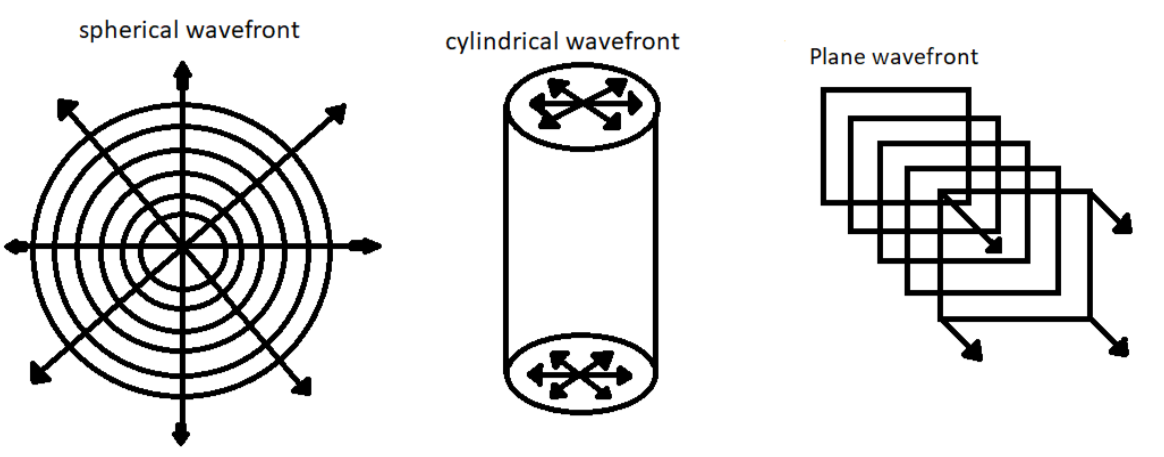
Wave front is totally depends on the source of light, which makes the wave front of three types:
$\left( i \right)$ Spherical wave front.
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Cylindrical wave front
$\left( {iii} \right)$ Plane wave front.
So this is the required answer.
Note: The type of wave front that is spherical, cylindrical or plane wave front is actually dependent upon the source through which the light is produced. A point source of light generally gives rise to spherical wave front, planar wave front is caused when the propagating waves are parallel to each other, a cylindrical wave front is caused when the source is disturbed by a slit.
Complete step-by-step answer:

A wave front is a surface over which an optical wave has a constant phase (i.e. there is no phase difference).
Or such a surface which envelopes the particles that are in the same state of vibration is known as a wave front.
The wave front at any instant is defined as the locus of all the particles of the medium which are in the same state of vibration.
The sum of rays passing through a surface produces/creates/develops a wave front.
As we all know that the wave front always travels perpendicular to each other, this will indicate that the ray of lights falling on the wave front makes a right angle with the wave front.
This will indicate that the ray of light which is always parallel to each other makes the wave front which is perpendicular to each other.
A wave front is a surface or line in the path of wave motion on which the disturbances at every point have the same phase.
Wave front is totally depends on the source of light, which makes the wave front of three types:
$\left( i \right)$ Spherical wave front.
$\left( {ii} \right)$ Cylindrical wave front
$\left( {iii} \right)$ Plane wave front.
So this is the required answer.
Note: The type of wave front that is spherical, cylindrical or plane wave front is actually dependent upon the source through which the light is produced. A point source of light generally gives rise to spherical wave front, planar wave front is caused when the propagating waves are parallel to each other, a cylindrical wave front is caused when the source is disturbed by a slit.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




