
Using the mirror formula, explain why a convex mirror always produces a virtual image.
Answer
479.1k+ views
Hint: First we will make a rough diagram of a convex mirror. Here we will use the concept of convex mirror property and nature to solve the problem. Then we will use the mirror formula. After some arrangement using sign convection we can find the image produced in a convex mirror is always virtual.
Complete answer:
As per the problem using the mirror formula we have to explain the reason behind the formation of virtual images in case of a convex mirror.
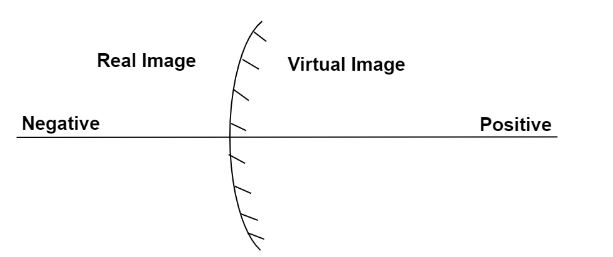
From the figure and using mirror formula we can say,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
After rearranging the equation we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where, $u$ is the distance of the object from the mirror and it is the real image of the object. Hence according to sign convention the distance is taken as negative as given in the diagram.
Now the mirror equation will be,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Hence the addition of two positive numbers will always be positive hence the image will line in the positive side of the convex mirror. This implies that the image distance will always be positive as in the case of the convex mirror and the image is always positive on the other side of the object, or we can say the image will form behind the mirror.
Therefore it is proved that the image formed in the case of a convex mirror is a virtual image.
Note: Remember that the convex mirror is also known as a diverging mirror as it diverges the light rays that strike on the reflecting surface of the convex mirror. Also keep in mind that the image formed in this case is virtual, erect and diminished in nature irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror.
Complete answer:
As per the problem using the mirror formula we have to explain the reason behind the formation of virtual images in case of a convex mirror.

From the figure and using mirror formula we can say,
$\dfrac{1}{v} + \dfrac{1}{u} = \dfrac{1}{f}$
After rearranging the equation we will get,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} - \dfrac{1}{u}$
Where, $u$ is the distance of the object from the mirror and it is the real image of the object. Hence according to sign convention the distance is taken as negative as given in the diagram.
Now the mirror equation will be,
$\dfrac{1}{v} = \dfrac{1}{f} + \dfrac{1}{u}$
Hence the addition of two positive numbers will always be positive hence the image will line in the positive side of the convex mirror. This implies that the image distance will always be positive as in the case of the convex mirror and the image is always positive on the other side of the object, or we can say the image will form behind the mirror.
Therefore it is proved that the image formed in the case of a convex mirror is a virtual image.
Note: Remember that the convex mirror is also known as a diverging mirror as it diverges the light rays that strike on the reflecting surface of the convex mirror. Also keep in mind that the image formed in this case is virtual, erect and diminished in nature irrespective of the distance between the object and the mirror.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 10 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 General Knowledge: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 10 Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
What is the median of the first 10 natural numbers class 10 maths CBSE

Which women's tennis player has 24 Grand Slam singles titles?

Who is the Brand Ambassador of Incredible India?

Why is there a time difference of about 5 hours between class 10 social science CBSE

Write a letter to the principal requesting him to grant class 10 english CBSE

A moving boat is observed from the top of a 150 m high class 10 maths CBSE




