
What do you understand by friction? Draw a graph between applied force & frictional force and mark on it static friction, limiting friction and kinetic friction.
Answer
504.3k+ views
Hint:Let us first know about the friction. Friction is the force exerted by two surfaces sliding (or attempting to slide) across each other. Friction always acts in the opposite direction from where the thing is going or attempting to move. A moving object is always slowed by friction.
Complete answer:
The friction between two surfaces turns kinetic energy into thermal energy when they move relative to each other (that is, it converts work to heat). The utilisation of friction caused by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire is an example of how this attribute can have severe repercussions.
Kinetic energy is transformed to thermal energy whenever motion with friction occurs, for example when a viscous fluid is agitated. Wear is another key consequence of various types of friction, which can result in performance degradation or component damage. The science of tribology includes friction as a component.
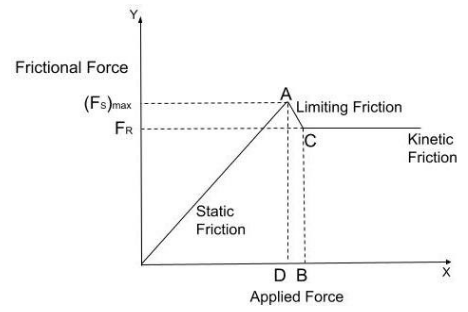
Because it occurs when one body is laying over the surface of another without moving, static friction is a self-adjusting force.When no force is applied to a body in order to move it, the frictional force is also zero. When we apply force, the frictional force increases in lockstep with the supplied force.
Until the applied force is less than the limiting frictional force, this happens. The maximum value of static friction is obtained when that body surpasses the force of static friction, which is known as limiting friction.The frictional force will not rise any more after the limiting friction. At this point, the item travels past the frictional force, which remains constant.
Note: Let us know some more things about frictions. Friction is a non-conservative force – work done against friction is path dependent. In the presence of friction, some kinetic energy is always transformed to thermal energy, so mechanical energy is not conserved.
Complete answer:
The friction between two surfaces turns kinetic energy into thermal energy when they move relative to each other (that is, it converts work to heat). The utilisation of friction caused by rubbing pieces of wood together to start a fire is an example of how this attribute can have severe repercussions.
Kinetic energy is transformed to thermal energy whenever motion with friction occurs, for example when a viscous fluid is agitated. Wear is another key consequence of various types of friction, which can result in performance degradation or component damage. The science of tribology includes friction as a component.

Because it occurs when one body is laying over the surface of another without moving, static friction is a self-adjusting force.When no force is applied to a body in order to move it, the frictional force is also zero. When we apply force, the frictional force increases in lockstep with the supplied force.
Until the applied force is less than the limiting frictional force, this happens. The maximum value of static friction is obtained when that body surpasses the force of static friction, which is known as limiting friction.The frictional force will not rise any more after the limiting friction. At this point, the item travels past the frictional force, which remains constant.
Note: Let us know some more things about frictions. Friction is a non-conservative force – work done against friction is path dependent. In the presence of friction, some kinetic energy is always transformed to thermal energy, so mechanical energy is not conserved.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




