
Two cells of each 2V and internal resistance $1\Omega $are connected in series to a resistor $R\,=\,2\Omega $. What is the maximum possible power consumed by the resistor R?
A. $\dfrac{8}{9}\,W$
B. $3.2\,W$
C. $\dfrac{16}{9}\,W$
D. $2\,W$
Answer
584.7k+ views
Hint: Draw the circuit diagram as per the details given in the question. When resistances are connected in series, the current is the same through each resistance and total resistance is the sum of all the resistances connected in series.
To determine power consumed by the resistor, first find current through the resistor and then use formula for power.
Formula used:
Net resistance connected in series, $R={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+{{R}_{3}}......$, Net potential difference of cells connected in series,${{V}_{net}}=2\,V+2\,V=4\,V$ and Power, $P={{I}^{2}}R$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Both cells and resistance are connected in series as shown below
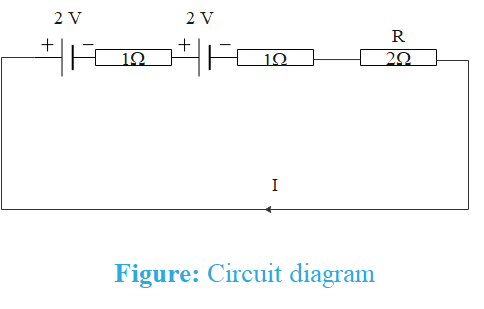
Two cells and one resistor are connected in series. In series, the value of current remains the same.
The net resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistance of each resistor.
Therefore, the net resistance of this circuit is the sum of internal resistances and resistance of R.
${{R}_{net}}=1\Omega +1\Omega +2\Omega =4\Omega $
According to Ohm’s law, the potential through a resistor R is directly proportional to current through it.
$\begin{align}
& V\propto I \\
& \Rightarrow V=IR \\
\end{align}$
Total potential difference in a series circuit is also the sum of the potential difference of each cell connected in series. Therefore,
${{V}_{net}}=2\,V+2\,V=4\,V$
Using Ohm’s law, current through the circuit is
$I=\dfrac{{{V}_{net}}}{{{R}_{net}}}$
$I=\dfrac{4\,V}{4\,\Omega }=1A$
Power in a resistance is given as
$P={{I}^{2}}R$
Therefore, the power consumed by resistance R is
$P={{1}^{2}}\times 2=2\,\,\,Watt$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The power given by each cell is 2 Watt.
When resistances are connected in series, the total resistance is the sum of each resistor’s resistance.
When two or more cells are connected in series, the net potential through the series circuit is the sum of potential difference of each cell.
To determine power consumed by the resistor, first find current through the resistor and then use formula for power.
Formula used:
Net resistance connected in series, $R={{R}_{1}}+{{R}_{2}}+{{R}_{3}}......$, Net potential difference of cells connected in series,${{V}_{net}}=2\,V+2\,V=4\,V$ and Power, $P={{I}^{2}}R$
Complete step-by-step answer:
Both cells and resistance are connected in series as shown below

Two cells and one resistor are connected in series. In series, the value of current remains the same.
The net resistance in a series circuit is the sum of the individual resistance of each resistor.
Therefore, the net resistance of this circuit is the sum of internal resistances and resistance of R.
${{R}_{net}}=1\Omega +1\Omega +2\Omega =4\Omega $
According to Ohm’s law, the potential through a resistor R is directly proportional to current through it.
$\begin{align}
& V\propto I \\
& \Rightarrow V=IR \\
\end{align}$
Total potential difference in a series circuit is also the sum of the potential difference of each cell connected in series. Therefore,
${{V}_{net}}=2\,V+2\,V=4\,V$
Using Ohm’s law, current through the circuit is
$I=\dfrac{{{V}_{net}}}{{{R}_{net}}}$
$I=\dfrac{4\,V}{4\,\Omega }=1A$
Power in a resistance is given as
$P={{I}^{2}}R$
Therefore, the power consumed by resistance R is
$P={{1}^{2}}\times 2=2\,\,\,Watt$
So, the correct answer is “Option D”.
Note: The power given by each cell is 2 Watt.
When resistances are connected in series, the total resistance is the sum of each resistor’s resistance.
When two or more cells are connected in series, the net potential through the series circuit is the sum of potential difference of each cell.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

What is a transformer Explain the principle construction class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE




