
The stress versus strain graphs for wires of two materials A and B are as shown in the figure.
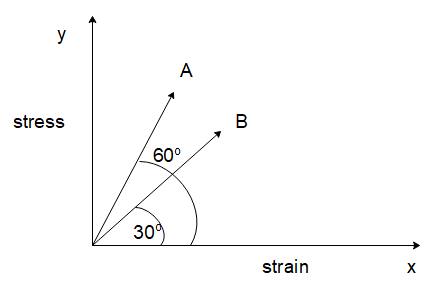
If $ {Y_A} $ and $ {Y_B} $ are the Young’s moduli of the materials, then
A) $ {Y_B} = 2{Y_A} $
B) $ {Y_A} = {Y_B} $
C) $ {Y_B} = 3{Y_A} $
D) $ {Y_A} = 3{Y_B} $

Answer
563.4k+ views
Hint : The young’s modulus of wire is the slope of the line of the wire in the graph of stress versus strain. The slope of a line can be determined using the angle the line makes with the $ x $ -axis.
Complete step by step answer
We know that the slope of the line in a stress-strain curve represents the young’s modulus for a wire. We also know that the slope of a line can be calculated as the tangent of the angle the line makes with the positive x-axis of the graph.
So, for wire A, the stress-strain line of the material is at an angle of $ 60^\circ $ from the positive $ x $ -axis. So the slope of the line $ ({m_A}) $ will be
$ {m_A} = \tan 60^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow {m_A} = \sqrt 3 $
Hence the young’s modulus of wire A will also be $ \sqrt 3 $ .
Similarly, for wire B, the stress-strain line of the material is at an angle of $ 30^\circ $ from the positive $ x $ -axis. So, the slope of the line $ ({m_B}) $ will be
$ {m_B} = \tan 30^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow {m_B} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
Hence the young’s modulus of wire B will also be $ 1/\sqrt 3 $ .
Then taking the ratio of the young’s modulus for wire A and B, we get
$ \dfrac{{{Y_A}}}{{{Y_B}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{1/\sqrt 3 }} $
$ \therefore \dfrac{{{Y_A}}}{{{Y_B}}} = 3 $
Hence, we can write
$ {Y_A} = 3{Y_B} $ which corresponds to option (D) which is the correct choice.
Note
We can only calculate the slope of the line in such a way if the stress-strain curve for a wire is a straight line. For practical wires, the stress-strain curve is linear only for a range of values of stress applied on the wire. While calculating the slope of the wire, we must calculate the tangent of the line made with the $ x $ -axis and not the $ y $ -axis if the strain is represented on the $ x $ -axis of the graph.
Complete step by step answer
We know that the slope of the line in a stress-strain curve represents the young’s modulus for a wire. We also know that the slope of a line can be calculated as the tangent of the angle the line makes with the positive x-axis of the graph.
So, for wire A, the stress-strain line of the material is at an angle of $ 60^\circ $ from the positive $ x $ -axis. So the slope of the line $ ({m_A}) $ will be
$ {m_A} = \tan 60^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow {m_A} = \sqrt 3 $
Hence the young’s modulus of wire A will also be $ \sqrt 3 $ .
Similarly, for wire B, the stress-strain line of the material is at an angle of $ 30^\circ $ from the positive $ x $ -axis. So, the slope of the line $ ({m_B}) $ will be
$ {m_B} = \tan 30^\circ $
$ \Rightarrow {m_B} = \dfrac{1}{{\sqrt 3 }} $
Hence the young’s modulus of wire B will also be $ 1/\sqrt 3 $ .
Then taking the ratio of the young’s modulus for wire A and B, we get
$ \dfrac{{{Y_A}}}{{{Y_B}}} = \dfrac{{\sqrt 3 }}{{1/\sqrt 3 }} $
$ \therefore \dfrac{{{Y_A}}}{{{Y_B}}} = 3 $
Hence, we can write
$ {Y_A} = 3{Y_B} $ which corresponds to option (D) which is the correct choice.
Note
We can only calculate the slope of the line in such a way if the stress-strain curve for a wire is a straight line. For practical wires, the stress-strain curve is linear only for a range of values of stress applied on the wire. While calculating the slope of the wire, we must calculate the tangent of the line made with the $ x $ -axis and not the $ y $ -axis if the strain is represented on the $ x $ -axis of the graph.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 11 Computer Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 11 Biology: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
One Metric ton is equal to kg A 10000 B 1000 C 100 class 11 physics CBSE

There are 720 permutations of the digits 1 2 3 4 5 class 11 maths CBSE

Discuss the various forms of bacteria class 11 biology CBSE

Draw a diagram of a plant cell and label at least eight class 11 biology CBSE

State the laws of reflection of light

Explain zero factorial class 11 maths CBSE




