
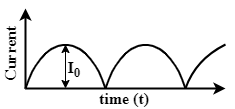
The output sinusoidal current versus time graph of a rectifier is shown in the figure. The average value of output current:
a) 0
b) \[\dfrac{{{I_0}}}{2}\]
c) $\dfrac{{{I_0}}}{4}$
d) None of these

Answer
581.1k+ views
Hint:A rectifier is an electrical device that converts any AC sinusoidal signal into a one directional DC signal. The sinusoidal signal still remains sinusoidal but the negative portion reverses its direction and current only flows in one direction as shown in the graph.
Formula used:
Time average of any sinusoidal function is given by:
\[{f_{av}} = \dfrac{{\int_0^T {f(t)\,dt} }}{{\int_0^T {dt} }}\]...................(1)
Where,
\[{f_{av}}\]is the time average of the sinusoidal function,
T is the time period of the function,
\[f(t)\]is the sinusoidal function.
Step by step answer:
Given:
From the given graph we get the given current function as:
$
I(t) = {I_0}\sin \omega t\,\,\,\,\,\,\,0 \leqslant t \leqslant \dfrac{T}{2} \\
= - {I_0}\sin \omega t\,\,\,\,\dfrac{T}{2} < t \leqslant T \\
$......................(2)
Where, time period T is given by $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$.
To find: Average value of output current.
Step 1
First, use the current function from eq.(2)and value of T to get the numerator of eq.(1) as:
$ \int_0^T {I(t)\,dt = \int_0^{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }} {{I_0}\sin \omega t\,dt} } + \int_{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }}^{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }} { - {I_0}\sin \omega t\,dt} $
$\,\,\,\, = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ { - \cos \omega t} \right]_0^{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }} - \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ { - \cos \omega t} \right]_{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }}^{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }} $
$ \,\,\,\, = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ { - ( - 1) - ( - 1)} \right] - \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ {( - 1) - 1} \right] $
$ \,\,\,\, = \dfrac{{4{I_0}}}{\omega } $
Step 2
Now, use the value of T to calculate the denominator of eq.(1) as:
\[
\int_0^T {dt} = \left[ t \right]_0^{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }} \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, = \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega } - 0} \right) = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega } \\
\]
Step 3
From the obtained value of the numerator and denominator get the average current as:
$
{I_{av}} = \dfrac{{\int_0^T {I(t)\,dt} }}{{\int_0^T {dt} }} \\
\therefore {I_{av}} = \dfrac{{\tfrac{{4{I_0}}}{\omega }}}{{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }}} = \dfrac{{2{I_0}}}{\pi } \\
$
Correct answer:
The average value of output current is given by (d) none of these.
Note: This problem can be solved in a tricky way. Notice, the sinusoidal function of eq.(2). From the given current function you’ll get the numerator a real value times ${I_0}$ from the integration of the sine function. Since, the time period is given by \[\dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }\] so after integration the denominator will consist of the term \[\pi \]. In the first three given options there is no term involving \[\pi \] in its denominator. Hence, the option must be option (d) and you can get that without a single calculation.
Formula used:
Time average of any sinusoidal function is given by:
\[{f_{av}} = \dfrac{{\int_0^T {f(t)\,dt} }}{{\int_0^T {dt} }}\]...................(1)
Where,
\[{f_{av}}\]is the time average of the sinusoidal function,
T is the time period of the function,
\[f(t)\]is the sinusoidal function.
Step by step answer:
Given:
From the given graph we get the given current function as:
$
I(t) = {I_0}\sin \omega t\,\,\,\,\,\,\,0 \leqslant t \leqslant \dfrac{T}{2} \\
= - {I_0}\sin \omega t\,\,\,\,\dfrac{T}{2} < t \leqslant T \\
$......................(2)
Where, time period T is given by $T = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }$.
To find: Average value of output current.
Step 1
First, use the current function from eq.(2)and value of T to get the numerator of eq.(1) as:
$ \int_0^T {I(t)\,dt = \int_0^{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }} {{I_0}\sin \omega t\,dt} } + \int_{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }}^{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }} { - {I_0}\sin \omega t\,dt} $
$\,\,\,\, = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ { - \cos \omega t} \right]_0^{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }} - \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ { - \cos \omega t} \right]_{\tfrac{\pi }{\omega }}^{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }} $
$ \,\,\,\, = \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ { - ( - 1) - ( - 1)} \right] - \dfrac{{{I_0}}}{\omega }\left[ {( - 1) - 1} \right] $
$ \,\,\,\, = \dfrac{{4{I_0}}}{\omega } $
Step 2
Now, use the value of T to calculate the denominator of eq.(1) as:
\[
\int_0^T {dt} = \left[ t \right]_0^{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }} \\
\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\, = \left( {\dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega } - 0} \right) = \dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega } \\
\]
Step 3
From the obtained value of the numerator and denominator get the average current as:
$
{I_{av}} = \dfrac{{\int_0^T {I(t)\,dt} }}{{\int_0^T {dt} }} \\
\therefore {I_{av}} = \dfrac{{\tfrac{{4{I_0}}}{\omega }}}{{\tfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }}} = \dfrac{{2{I_0}}}{\pi } \\
$
Correct answer:
The average value of output current is given by (d) none of these.
Note: This problem can be solved in a tricky way. Notice, the sinusoidal function of eq.(2). From the given current function you’ll get the numerator a real value times ${I_0}$ from the integration of the sine function. Since, the time period is given by \[\dfrac{{2\pi }}{\omega }\] so after integration the denominator will consist of the term \[\pi \]. In the first three given options there is no term involving \[\pi \] in its denominator. Hence, the option must be option (d) and you can get that without a single calculation.
Recently Updated Pages
Master Class 12 Economics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Physics: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 English: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Social Science: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Maths: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Master Class 12 Business Studies: Engaging Questions & Answers for Success

Trending doubts
Which are the Top 10 Largest Countries of the World?

What are the major means of transport Explain each class 12 social science CBSE

Draw a labelled sketch of the human eye class 12 physics CBSE

Why cannot DNA pass through cell membranes class 12 biology CBSE

Differentiate between insitu conservation and exsitu class 12 biology CBSE

Draw a neat and well labeled diagram of TS of ovary class 12 biology CBSE




